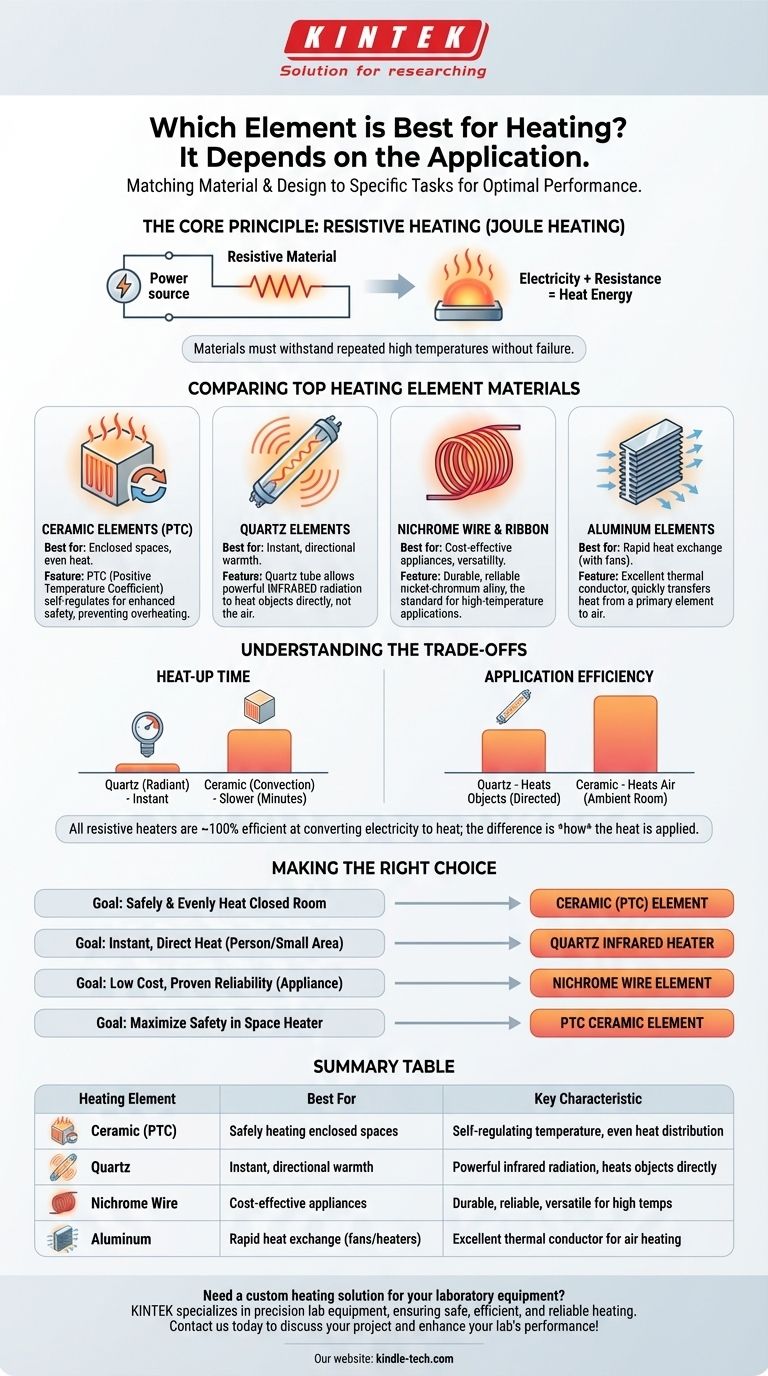
Choosing the "best" heating element is not about finding a single superior material, but about matching the right material and design to a specific task. For general-purpose space heating, ceramic is often considered the best choice due to its balance of high efficiency and safety. For instant, directional heat, quartz is superior, while Nichrome wire remains the cost-effective standard for many appliances.
The "best" heating element is a function of its intended use. The core trade-off is between the speed of heat delivery, the method of heat transfer (radiating to objects vs. heating the air), and inherent safety features. Understanding this context is the key to making the right choice.
The Core Principle: Resistive Heating
How All Electric Heaters Work
At its heart, an electric heating element is a simple device. It works by passing electricity through a material that has a moderate amount of electrical resistance.
This resistance converts electrical energy directly into heat energy, a principle known as Joule heating. The "best" materials are those that can get very hot repeatedly without melting, oxidizing, or breaking down.
Comparing the Top Heating Element Materials
The material used dictates how quickly the heater works, how it transfers heat, and its overall safety profile.
Ceramic Elements: The Safety and Efficiency Standard
Ceramic is a superb material for heating enclosed spaces. It has a high capacity to absorb and radiate heat evenly over a large surface area.
A special type, PTC (Positive Temperature Coefficient) ceramic, is a game-changer for safety. As PTC elements heat up, their electrical resistance increases automatically, causing them to self-regulate and maintain a stable temperature. This design drastically reduces the risk of overheating.
Quartz Elements: The Instant Heat Specialist
Quartz heaters don't use the quartz itself as the heating element. Instead, they use a quartz tube to encase a wire element, often made of tungsten or carbon fiber.
The element inside glows intensely, and the quartz tube allows powerful infrared radiation to pass through it. This heat works like sunlight, warming people and objects directly rather than heating the air in between. This makes it perfect for open spaces like patios or garages where heating the air would be wasteful.
Metal Wire & Ribbon (Nichrome): The Versatile Workhorse
When you think of a classic heating element glowing red-hot, you're picturing a Nichrome (nickel-chromium alloy) wire. It is durable, inexpensive to produce, and highly effective.
You will find Nichrome wire and ribbon elements in countless common appliances, including toasters, hair dryers, clothes dryers, and industrial process heaters. Its primary strength is its simplicity and reliability in high-temperature applications.
Aluminum Elements: The Rapid Heat Exchanger
Aluminum is an excellent thermal conductor. It is rarely used as the primary resistive element itself.
Instead, it's most often used in heat exchangers. A separate resistive element (like a Nichrome wire) heats up, and the aluminum fins rapidly absorb this heat and transfer it to air being blown across them by a fan.
Understanding the Trade-offs
There is no perfect heating element. Each type represents a compromise between speed, efficiency, and safety.
Heat-Up Time: Radiant vs. Convection
Quartz (radiant) heaters provide warmth almost instantly. The moment the element glows, you feel its infrared energy.
Ceramic (convection) heaters are slower. They must first heat their own mass and then gradually heat the surrounding air, which then circulates to warm the room. This process can take several minutes.
Application Efficiency: Heating the Air vs. Heating an Object
All resistive heaters are nearly 100% efficient at converting electricity into heat. The real difference lies in how effectively that heat is applied.
A quartz heater is extremely efficient for warming a person sitting in its path but is very inefficient at raising the temperature of an entire room. A ceramic convection heater is the opposite—it's highly effective for raising the ambient temperature of a closed room but poor for providing instant, targeted warmth.
Safety and Lifespan
PTC ceramic elements are the safest due to their self-regulating nature, preventing runaway temperatures.
Exposed wire elements, like those in a space heater or toaster, get extremely hot and present a higher burn and fire risk if proper guards are not in place. Quartz elements also get very hot but are almost always protected behind a metal grille.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choose your heating element based on a clear goal.
- If your primary focus is safely and evenly heating a closed room: A heater with a ceramic element is your most effective choice.
- If your primary focus is instant, direct heat for a person or a small area (like a patio or workshop): A quartz infrared heater is unmatched in performance.
- If your primary focus is low cost and proven reliability for an appliance: A Nichrome wire element is the universal standard.
- If your primary focus is maximizing safety and preventing overheating in a space heater: Look for a heater specifically advertised as using a PTC ceramic element.
By matching the element's properties to your specific need, you ensure optimal performance, safety, and efficiency.
Summary Table:
| Heating Element | Best For | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|
| Ceramic (PTC) | Safely heating enclosed spaces | Self-regulating temperature, even heat distribution |
| Quartz | Instant, directional warmth | Powerful infrared radiation, heats objects directly |
| Nichrome Wire | Cost-effective appliances | Durable, reliable, and versatile for high temperatures |
| Aluminum | Rapid heat exchange (fans/heaters) | Excellent thermal conductor for air heating |
Need a custom heating solution for your laboratory equipment? KINTEK specializes in precision lab equipment and consumables, ensuring your heating applications are safe, efficient, and reliable. Whether you require ceramic, quartz, or Nichrome elements, our experts will help you select the ideal component for your specific needs. Contact us today to discuss your project and enhance your lab's performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
- 24T 30T 60T Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- Manual Lab Heat Press
People Also Ask
- How does a heating element go bad? Understanding the 3 Main Causes of Failure
- Is tungsten a good heating element? Unlock Extreme Temperatures in Vacuum Environments
- How does a resistive heating element work? Convert Electricity to Heat Efficiently
- Is tungsten shock resistant? Uncovering the Surprising Brittleness of a Hard Metal
- Why do heating elements have high resistance? To Efficiently Convert Electricity into Heat
- What are the disadvantages of tungsten? Navigating its brittleness and high fabrication costs
- What is the most accurate temperature sensor? Why RTDs Lead in Precision and Stability
- What is the maximum temperature for silicon carbide heating element? The Real Limit for Your High-Temp Furnace















