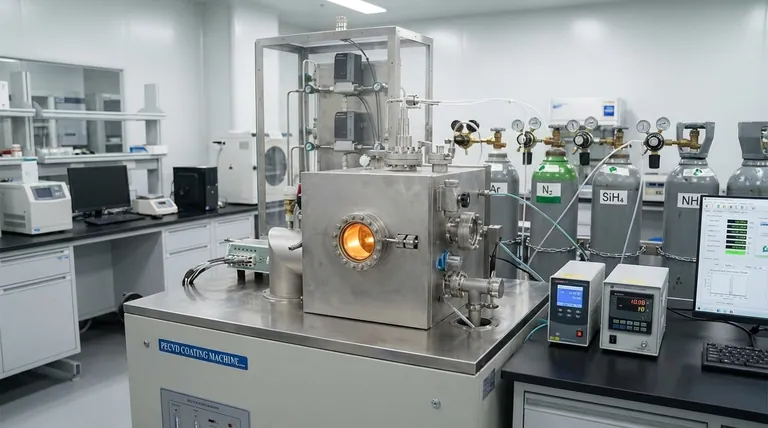
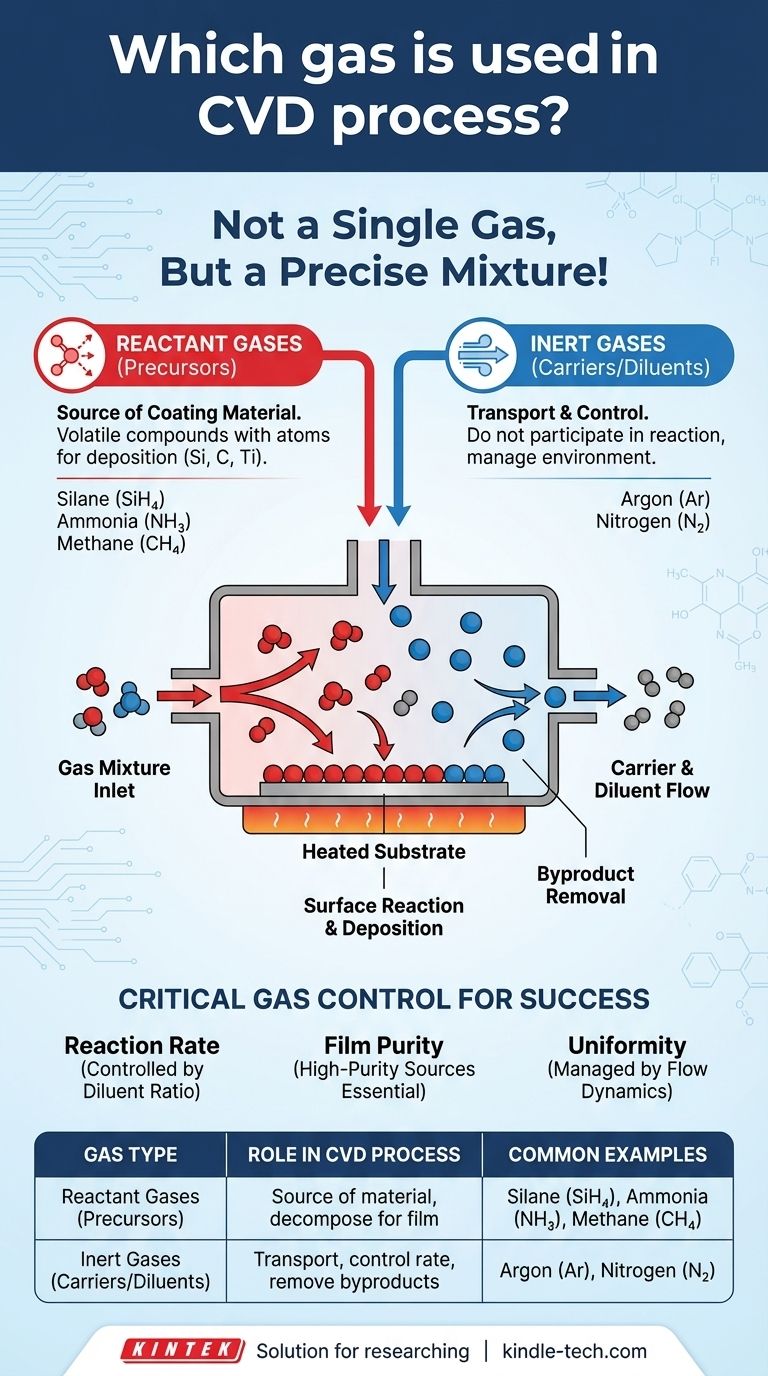
The Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) process does not use a single gas. Instead, it uses a precisely controlled mixture of two primary types: reactant gases (also called precursors) which contain the elements that will form the final coating, and inert gases, such as argon, which act as carriers or diluents to control the reaction environment. The specific reactant gases chosen depend entirely on the desired coating material.
The core principle to understand is that CVD is a gas-phase chemical process. The "gas" is a carefully engineered recipe, combining active precursors that build the film and inert carriers that manage the speed and quality of its deposition.

The Two Primary Gas Categories in CVD
To understand the process, you must first understand the distinct roles played by the different gases introduced into the reaction chamber. They are not interchangeable; each has a critical function.
Reactant Gases (The Precursors)
These are the most important gases because they are the source of the coating material. They are volatile compounds that contain the specific atoms (like silicon, carbon, or titanium) intended for deposition.
When these gases are activated inside the chamber—typically by high heat—they decompose and undergo chemical reactions. This reaction happens directly on the surface of the heated object, or substrate, forming the new, solid thin film layer by layer.
Inert Gases (The Carriers and Diluents)
These gases, most commonly argon (Ar) or nitrogen (N₂), do not participate in the chemical reaction. Their purpose is purely physical and logistical.
Their primary role is to act as a carrier, transporting the reactant gas molecules to the substrate. They also serve as a diluent, allowing engineers to precisely control the concentration of the reactant gases in the chamber, which directly influences the deposition rate and quality of the film.
How These Gases Work Together in the CVD Process
The entire CVD process is a carefully orchestrated sequence where the gas mixture is the central element.
Step 1: Introduction into the Chamber
A predefined mix of reactant and inert gases is introduced into the reaction chamber at a specified flow rate. This initial ratio is a critical parameter that dictates the outcome.
Step 2: Transport to the Substrate
The flow of the inert carrier gas moves the reactant gas species from the chamber inlet towards the target substrate. This ensures a consistent and uniform supply of precursor molecules across the entire surface.
Step 3: Activation and Surface Reaction
As the gases reach the heated substrate, the reactant precursors are activated and adsorb onto the surface. They then undergo the intended chemical reactions, depositing the desired elements and forming the solid film.
Step 4: Removal of Byproducts
The chemical reaction almost always creates unwanted gaseous byproducts. The continuous flow of the inert carrier gas is essential for sweeping these byproducts out of the chamber, preventing them from contaminating the newly formed film.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Why Gas Selection is Critical
The choice and control of the gas mixture are fundamental to the success of any CVD process. A failure to manage this aspect properly leads to poor results.
Controlling Reaction Rate
The ratio of diluent gas to reactant gas is the primary lever for controlling the deposition rate. Too high a concentration of reactants can cause gas-phase reactions (unwanted particle formation) or a deposition rate that is too fast, leading to a low-quality, porous film.
Ensuring Film Purity
The purity of the source gases is paramount. Any impurities in either the reactant or the inert gas can become incorporated into the final film, degrading its mechanical, electrical, or optical properties.
Managing Uniformity
The flow dynamics, managed by the inert gas, determine the uniformity of the coating. An inconsistent flow can lead to a film that is thicker in some areas and thinner in others, which is unacceptable for most high-performance applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The "right" gas is not a single substance but the correct combination for your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is creating a specific material (e.g., silicon nitride): Your key decision is selecting the correct reactant precursor gases that contain silicon and nitrogen (like silane and ammonia).
- If your primary focus is achieving a high-quality, uniform film: Your key decision is optimizing the flow rate and purity of your inert carrier gas (like argon) to precisely control the reaction environment.
Ultimately, mastering the CVD process is synonymous with mastering the precise control of the gas mixture that fuels it.
Summary Table:
| Gas Type | Role in CVD Process | Common Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Reactant Gases (Precursors) | Source of coating material; decompose to form the thin film | Silane (SiH₄), Ammonia (NH₃), Methane (CH₄) |
| Inert Gases (Carriers/Diluents) | Transport precursors, control reaction rate, remove byproducts | Argon (Ar), Nitrogen (N₂) |
Ready to perfect your thin film deposition process? The precise control of CVD gas mixtures is critical for achieving high-purity, uniform coatings. KINTEK specializes in providing high-purity lab gases and equipment tailored for advanced CVD applications. Our experts can help you select the optimal gas combinations and flow parameters for your specific material and quality goals.
Contact our team today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's CVD needs and enhance your research and production outcomes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Laboratory CVD Boron Doped Diamond Materials
People Also Ask
- How are thin films deposited? A Guide to PVD vs. CVD Methods for Your Application
- Why is a Matching Network Indispensable in RF-PECVD for Siloxane Films? Ensure Stable Plasma and Uniform Deposition
- Can plasma enhanced CVD deposit metals? Why PECVD is rarely used for metal deposition
- What are different types of thin films? A Guide to Function, Material, and Deposition Methods
- What is the difference between plasma CVD and thermal CVD? Choose the Right Method for Your Substrate



















