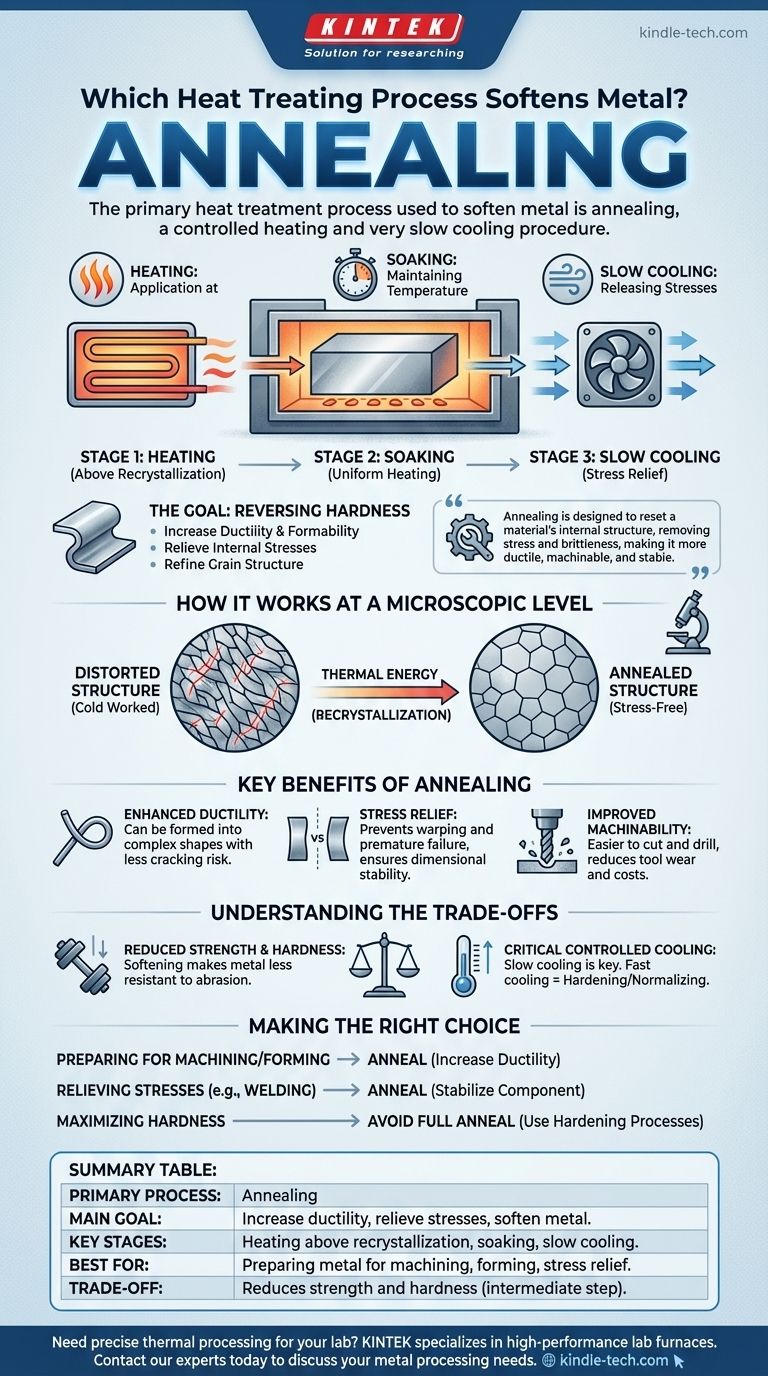
The primary heat treatment process used to soften metal is annealing. This controlled procedure involves heating a material above its recrystallization temperature, maintaining that temperature for a specific duration, and then cooling it at a very slow rate. Unlike hardening treatments that trap the material in a stressed state, annealing's purpose is to relieve internal stresses, increase ductility, and refine the metal's internal grain structure.
Annealing is not merely about making a metal softer. It is a precise thermal process designed to reset a material's internal structure, removing the stress and brittleness induced by previous work to make it more ductile, machinable, and stable.

The Goal of Annealing: Reversing Hardness
The decision to anneal a metal is driven by the need to make it more workable for subsequent manufacturing steps or to stabilize it for its final application. It is the direct opposite of hardening.
What is Annealing?
At its core, annealing is a three-stage process. First, the metal is heated to a specific temperature where its internal crystal structure can reform. Second, it is held at that temperature—a step called "soaking"—to ensure the entire part is evenly heated. Finally, and most critically, it is cooled very slowly.
The "Why" Behind Softening
Softness itself is often a means to an end. The true goals of annealing are typically to increase ductility (the ability to be deformed without fracturing) and to relieve internal stresses that may have built up from processes like welding, casting, or cold forming.
How It Works at a Microscopic Level
Processes like bending or hammering a metal (cold working) distort and strain its internal crystal lattice, or "grain structure." This makes the metal harder but also more brittle.
Annealing provides the thermal energy needed for these distorted grains to recrystallize. The atoms rearrange themselves into a more uniform, stress-free structure, which is what manifests as increased softness and ductility on a macro level.
Key Benefits of the Annealing Process
Choosing to anneal a material provides several distinct advantages that are critical for manufacturing and engineering.
Enhanced Ductility and Formability
The primary benefit is a significant increase in the metal's ability to be formed. An annealed metal can be bent, stamped, or drawn into complex shapes with a much lower risk of cracking, making it essential for producing items like wire, sheet metal, and tubing.
Stress Relief
Internal stresses are a hidden danger in metal components. They can cause a part to warp over time or lead to premature failure under load. Annealing neutralizes these stresses, creating a more dimensionally stable and reliable product.
Improved Machinability
A softer, less brittle metal is easier to cut, drill, and machine. Annealing can reduce wear and tear on cutting tools and result in a better surface finish, which often translates to lower manufacturing costs.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, annealing is a specific tool for a specific purpose, and its application comes with clear consequences that must be understood.
Reduced Strength and Hardness
The most direct trade-off of annealing is a reduction in tensile strength and hardness. By making the metal softer and more ductile, you inherently make it less resistant to abrasion and deformation. The softened state is often an intermediate step before a final hardening process.
The Importance of Controlled Cooling
The slow cooling rate is the defining characteristic of annealing. If the metal is cooled too quickly (for instance, in open air), you are performing a different heat treatment called normalizing, which produces a harder and stronger result. If cooled extremely rapidly (by quenching in water or oil), you will harden the steel. The process requires precise control to achieve the desired softness.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a heat treatment depends entirely on the intended function of the component. Annealing is a preparatory or corrective step, not typically a final one for parts requiring high strength.
- If your primary focus is preparing metal for extensive machining or forming: Annealing is the correct choice to increase ductility and reduce tool wear.
- If your primary focus is to relieve internal stresses from prior work like welding: Annealing will stabilize the component and prevent future distortion or cracking.
- If your primary focus is maximizing hardness and wear resistance: You must avoid full annealing and instead use hardening processes like quenching and tempering.
Ultimately, annealing is a foundational tool for controlling a metal's properties, enabling it to be properly shaped and stabilized for its final purpose.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Process | Annealing |
| Main Goal | Increase ductility, relieve internal stresses, and soften the metal |
| Key Stages | Heating above recrystallization temperature, soaking, and slow cooling |
| Best For | Preparing metal for machining, forming, or stress relief after welding/casting |
| Trade-off | Reduces strength and hardness (often an intermediate step) |
Need precise thermal processing for your lab or production line? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab furnaces and thermal processing equipment ideal for controlled annealing and other heat treatment applications. Our solutions help you achieve consistent material properties, improve manufacturing outcomes, and ensure reliable results. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your specific metal processing needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Pressure Sintering Furnace for High Temperature Applications
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- 1200℃ Muffle Furnace Oven for Laboratory
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace Negative Material Graphitization Furnace
- Horizontal High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is sputtering technology? A Guide to Precision Thin Film Deposition
- What is a sputtering machine? A Guide to High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is the purpose of using vacuum-sealed glass tubes for Thio-LISICON sintering? Optimize Solid Electrolyte Purity
- What is the boiling point of THC under a vacuum? A Guide to Safe Distillation
- How does a sputtering machine work? Achieve Atomic-Level Precision for Your Coatings



















