The better heating element depends entirely on how you need to transfer heat. For direct, line-of-sight heating of a specific person or object, a quartz element is superior due to its radiant heat properties. For creating a uniform, warm ambient temperature throughout an enclosed space, a ceramic element is the more effective choice because it operates through convection.
The core decision is not about which technology is "better," but which method of heat transfer—direct radiation or ambient convection—solves your specific problem. Quartz provides targeted, fast heat, while ceramic delivers stable, room-filling warmth.
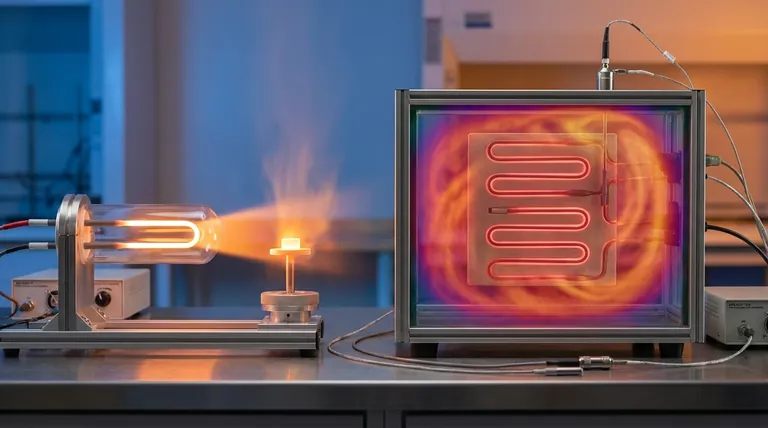

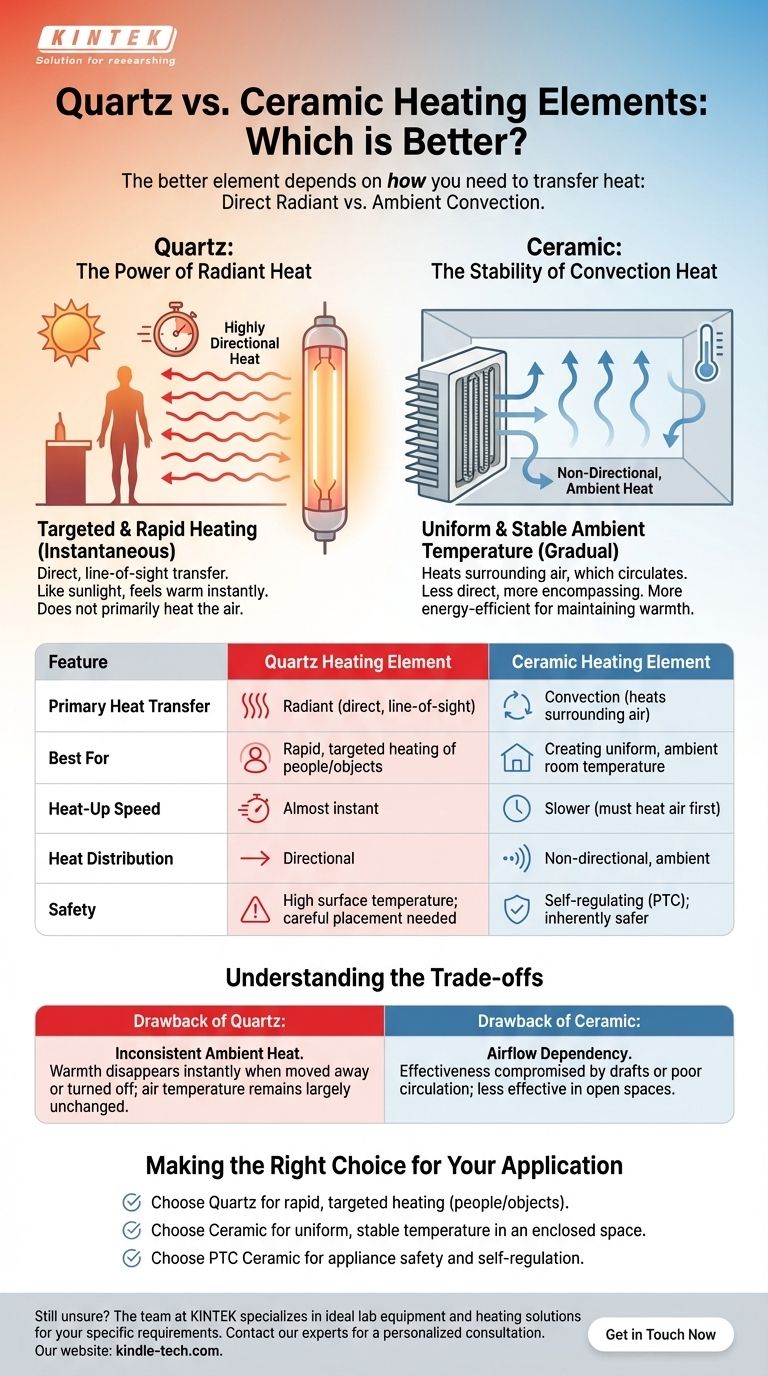
The Fundamental Difference: Radiant vs. Convection
To choose the right element, you must first understand the two different ways they heat. This single distinction is the most important factor in your decision.
Quartz Elements: The Power of Radiant Heat
Quartz elements do not primarily heat the air. Instead, they emit infrared radiation, a form of energy that travels in a straight line until it is absorbed by an object.
Think of it like the sun. When you stand in sunlight, you feel warm instantly, even if the air around you is cool. The energy is transferred directly to you. This makes quartz ideal for targeted and rapid heating.
Ceramic Elements: The Stability of Convection Heat
Ceramic elements work by heating up and transferring that thermal energy to the surrounding air, a process called convection.
This heated air then circulates throughout a space, gradually raising the overall ambient temperature. It's a less direct but more encompassing method, perfect for achieving a uniform and stable temperature in a room.
A Head-to-Head Comparison
With the core physics understood, we can compare the practical performance of each element.
Speed and Efficiency
Quartz elements provide a feeling of warmth almost instantly because the radiant energy travels at the speed of light.
Ceramic heaters take longer to feel because they must first heat the air, which then needs to circulate. However, for maintaining warmth in a well-insulated room over hours, they can be more energy-efficient.
Heat Distribution
The heat from a quartz element is highly directional. If you move out of its direct line of sight, you will no longer feel its effect.
Ceramic heaters provide non-directional, ambient heat. Once the air in the room is warm, you will feel it everywhere, regardless of your position relative to the heater.
Safety and Regulation
Modern ceramic heaters, particularly Positive Temperature Coefficient (PTC) types, are inherently safe. They are self-regulating, meaning their resistance increases as they get hotter, which naturally limits their maximum temperature and reduces the risk of overheating.
Quartz elements can reach very high surface temperatures. While safe when used as directed, they pose a higher immediate burn risk if touched and require careful placement away from flammable materials.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither technology is perfect. Acknowledging their limitations is key to avoiding frustration.
The Drawback of Quartz: Inconsistent Ambient Heat
A quartz heater will warm you, but it will not effectively warm the room. The air temperature will remain largely unchanged. This means that as soon as you turn it off or move away, the feeling of warmth disappears instantly.
The Drawback of Ceramic: Airflow Dependency
Because ceramic heaters rely on warming the air, their effectiveness can be compromised by drafts or poor air circulation. As noted in technical analyses, the heat will go "wherever the air currents in the process go," making them less effective in open or drafty spaces.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Select your heating element based on a clear understanding of your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is rapid, targeted heating of people or objects: Choose a quartz element for its unmatched speed and direct radiant energy transfer.
- If your primary focus is creating a uniform, stable temperature in an enclosed space: Choose a ceramic element for its effective and even convection heating.
- If your primary focus is safety and self-regulation for an appliance: A PTC ceramic element is the superior choice due to its inherent thermal stability and durability.
Ultimately, understanding the physics of heat transfer—radiant versus convection—is the key to selecting the right tool for your specific job.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Quartz Heating Element | Ceramic Heating Element |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Heat Transfer | Radiant (direct, line-of-sight) | Convection (heats surrounding air) |
| Best For | Rapid, targeted heating of people/objects | Creating uniform, ambient room temperature |
| Heat-Up Speed | Almost instant | Slower (must heat air first) |
| Heat Distribution | Directional | Non-directional, ambient |
| Safety | High surface temperature; careful placement needed | Self-regulating (PTC); inherently safer |
Still unsure which heating element is right for your lab or process?
The team at KINTEK specializes in providing the ideal lab equipment, including heating solutions, for your specific requirements. We can help you select the perfect heating element to ensure efficiency, safety, and performance in your application.
Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation and discover how KINTEK can support your laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Cylindrical Lab Electric Heating Press Mold for Laboratory Applications
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- Silicon Carbide (SIC) Ceramic Sheet Flat Corrugated Heat Sink for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
People Also Ask
- What are the properties of molybdenum heating element? Choose the Right Type for Your Furnace Atmosphere
- Which high temperature furnace elements to be used in oxidizing atmosphere? MoSi2 or SiC for Superior Performance
- Is molybdenum disulfide a heating element? Discover the best material for high-temperature applications.
- What is molybdenum disilicide used for? Powering High-Temperature Furnaces Up to 1800°C
- What material is used for furnace heating? Select the Right Element for Your Process



















