In the context of pure energy generation, gasification is considered a more efficient process than pyrolysis. Its primary advantage is the direct conversion of biomass or waste into a synthesis gas (syngas) specifically designed for immediate use in generating electricity and heat, maximizing the energy yield from the feedstock.
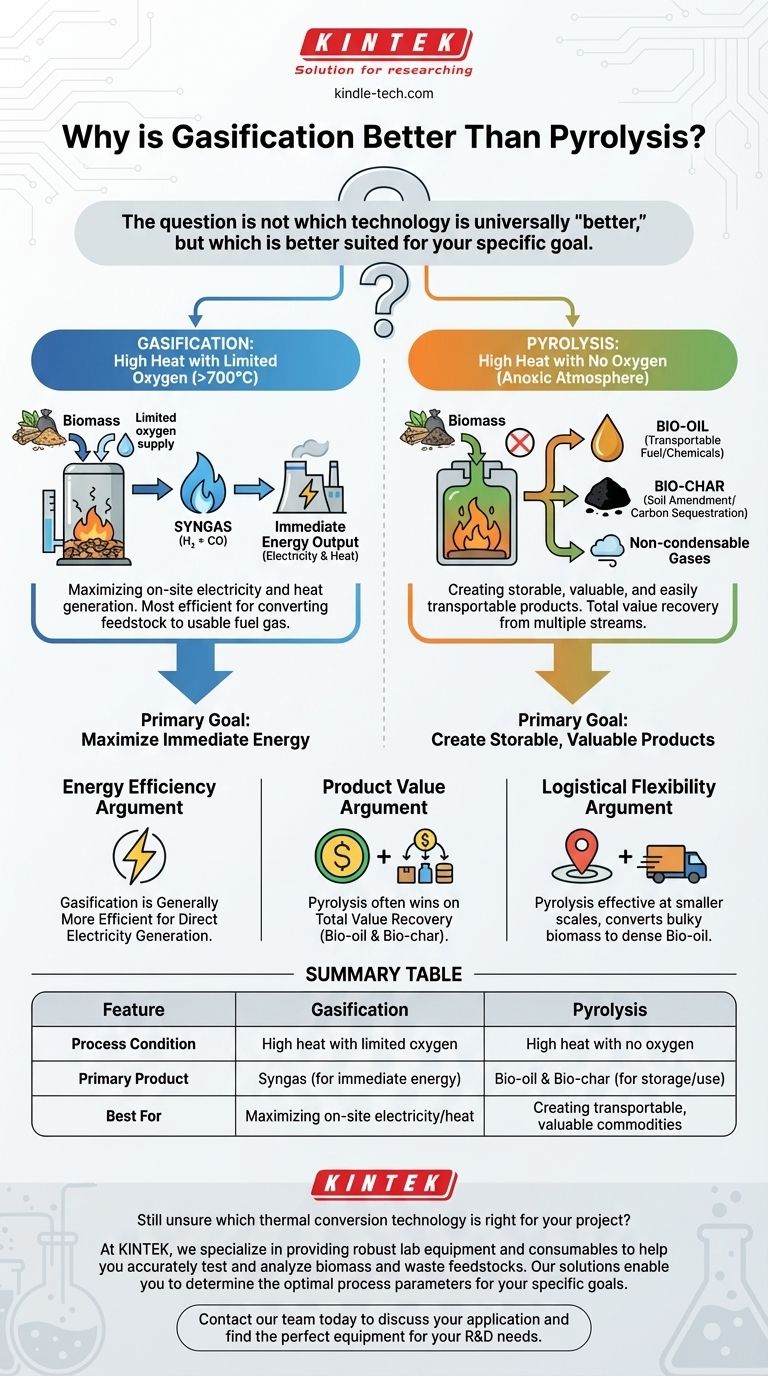
The question is not which technology is universally "better," but which is better suited for your specific goal. Gasification excels at maximizing immediate energy output, while pyrolysis excels at creating storable, valuable products like bio-oil and bio-char.

Deconstructing the Processes: Oxygen is the Key
The fundamental difference between gasification and pyrolysis lies in the presence or absence of a controlled amount of oxygen, which dictates the final output.
Gasification: High Heat with Limited Oxygen
Gasification exposes organic materials to very high temperatures (typically above 700°C) in an environment with a limited and controlled amount of oxygen.
This is not enough oxygen for full combustion. Instead, it drives chemical reactions that break down the feedstock into a mixture of hydrogen and carbon monoxide, known as syngas. This gas is a clean, combustible fuel.
Pyrolysis: High Heat with No Oxygen
Pyrolysis involves heating organic materials at high temperatures in a completely oxygen-free environment (an anoxic atmosphere).
The absence of oxygen prevents combustion. Instead, the material thermally decomposes into three distinct outputs: a liquid bio-oil, a solid bio-char, and a smaller amount of non-condensable gases.
Aligning the Process with the Desired Outcome
Choosing between these technologies depends entirely on whether your primary goal is immediate energy production or the creation of valuable, storable commodities.
When to Choose Gasification: Maximizing Energy Output
Gasification is the preferred route when the main objective is on-site power and heat generation.
The syngas it produces can be directly fed into gas engines or turbines to generate electricity with high efficiency. It is a direct and streamlined path from solid biomass to usable energy.
When to Choose Pyrolysis: Creating Storable, Valuable Products
Pyrolysis is superior when the goal is to convert biomass or waste into easily transportable and valuable materials.
The liquid bio-oil it creates is essentially a form of crude oil that can be stored, transported, and later refined into transportation fuels or chemicals. The solid bio-char is a valuable soil amendment that improves agricultural productivity and sequesters carbon. This flexibility makes pyrolysis ideal for distributed or remote operations.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither technology is a silver bullet. The "better" choice is a function of your specific economic and logistical constraints.
The Energy Efficiency Argument
For the single purpose of converting the chemical energy in feedstock into electricity, gasification is generally more efficient. It converts a higher percentage of the material's energy directly into a usable fuel gas in a single step.
The Product Value Argument
Pyrolysis often wins on total value recovery. While less efficient for immediate electricity generation, its outputs (bio-oil and bio-char) are often more valuable commodities than the raw electricity produced by gasification. It turns a single waste stream into multiple potential revenue streams.
The Logistical Flexibility Argument
Pyrolysis systems can be effective at smaller scales. This allows for the processing of biomass in remote locations, converting bulky, low-density feedstock into a dense, energy-rich liquid (bio-oil) that is far cheaper to transport than the original material.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the correct technology, you must first define your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is maximizing on-site electricity and heat generation: Gasification is the most direct and efficient pathway.
- If your primary focus is producing a storable liquid fuel or diverse chemical products: Pyrolysis offers unmatched flexibility and product creation capabilities.
- If your primary focus is waste valorization and carbon sequestration: Pyrolysis is superior, as it produces bio-char, a stable form of carbon that can be returned to the soil.
Ultimately, the best technology is the one that most effectively transforms your available feedstock into the end product you value most.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Gasification | Pyrolysis |
|---|---|---|
| Process Condition | High heat with limited oxygen | High heat with no oxygen |
| Primary Product | Syngas (for immediate energy) | Bio-oil & Bio-char (for storage/use) |
| Best For | Maximizing on-site electricity/heat | Creating transportable, valuable commodities |
Still unsure which thermal conversion technology is right for your project?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing robust lab equipment and consumables to help you accurately test and analyze biomass and waste feedstocks. Our solutions enable you to determine the optimal process parameters for your specific goals, whether you're focused on energy generation or product creation.
Let our experts help you make an informed decision. Contact our team today to discuss your application and find the perfect equipment for your research and development needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the industrial applications of pyrolysis? Transform Waste into Energy and Valuable Products
- What is the principle of rotary kiln? Mastering Continuous Thermal Processing
- What biomass is used in pyrolysis? Selecting the Optimal Feedstock for Your Goals
- What are the different types of reactors in plastic pyrolysis? Choose the Right System for Your Waste
- What equipment is used in pyrolysis? Choosing the Right Reactor for Your Feedstock and Products



















