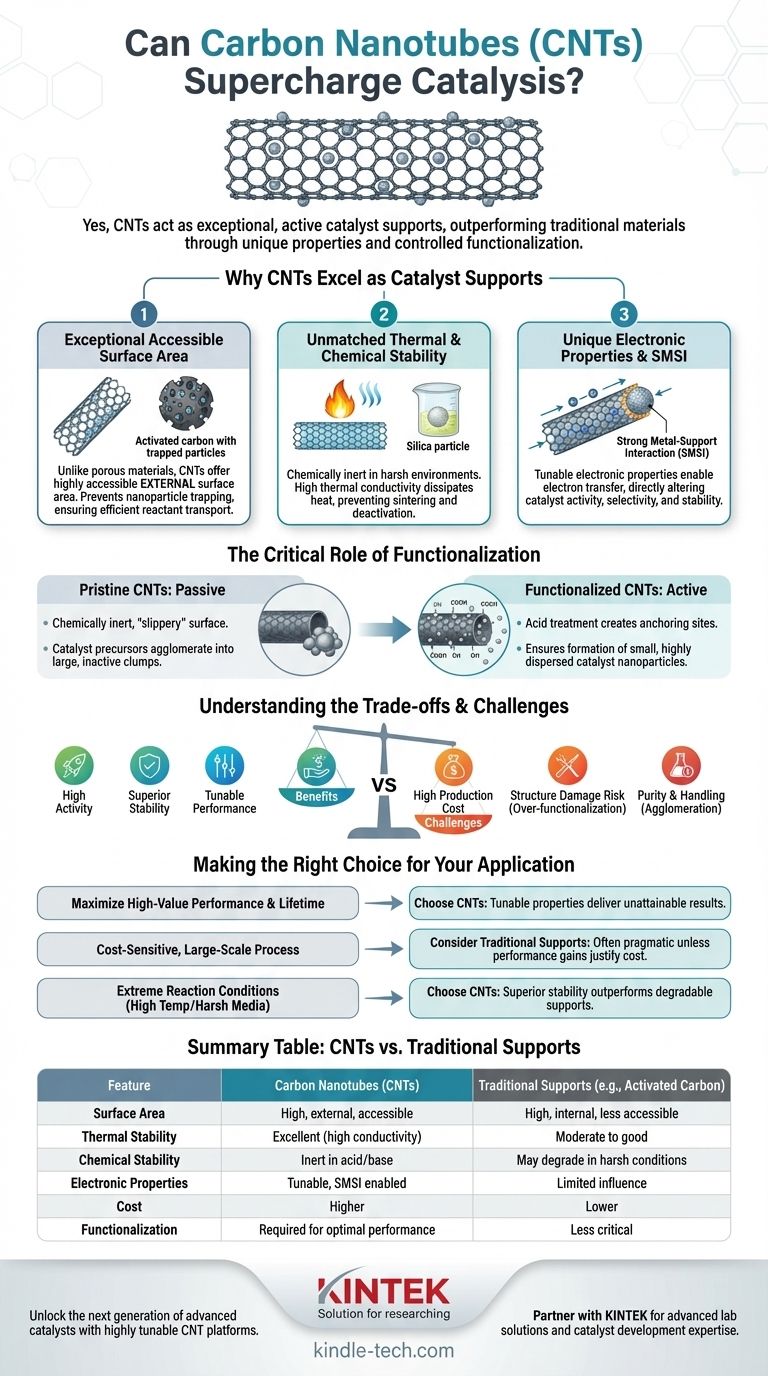
Yes, carbon nanotubes (CNTs) are not only viable but are often exceptional catalyst supports. Their unique combination of high surface area, excellent thermal and chemical stability, and tunable electronic properties allows them to significantly enhance catalytic performance compared to many conventional materials like activated carbon, alumina, or silica.
While traditional supports are passive platforms, carbon nanotubes can be an active component in catalysis. Their true potential is unlocked through controlled surface modification, which creates a highly stable and electronically favorable environment for catalyst nanoparticles, though this adds a layer of complexity to their implementation.

Why CNTs Excel as Catalyst Supports
The effectiveness of CNTs stems from a unique convergence of physical and electronic characteristics that directly influence the catalytic process. These properties allow for a level of design and control that is difficult to achieve with amorphous or ceramic supports.
Exceptional Surface Area and Porosity
Unlike porous materials like activated carbon, which have high internal surface areas, most of the surface area of CNTs is external and highly accessible. This prevents catalyst nanoparticles from being trapped within deep pores, ensuring reactants can easily reach the active sites. This open structure promotes efficient mass transport, which is critical for high reaction rates.
Unmatched Thermal and Chemical Stability
CNTs possess a highly stable graphitic structure. They are chemically inert in a wide range of acidic and basic environments where traditional supports like silica or alumina might dissolve or react. Furthermore, their high thermal conductivity is a major advantage in exothermic reactions, as it efficiently dissipates heat from the catalyst's active sites, preventing sintering and deactivation.
Unique Electronic Properties
The interaction between the support and the catalyst nanoparticle—known as the strong metal-support interaction (SMSI)—is a key factor in catalysis. The electronic nature of CNTs (which can be either metallic or semiconducting depending on their structure) allows them to donate or accept electrons from the catalyst nanoparticles. This electronic modulation can alter the catalyst's activity, selectivity, and stability in profound ways.
Controllable Surface Chemistry
In their pristine, as-grown state, CNTs have smooth, chemically inert surfaces. This makes it difficult to anchor catalyst nanoparticles, which can lead to aggregation and poor performance. However, their surface can be intentionally modified through a process called functionalization.
The Critical Role of Functionalization
Functionalization is the process of introducing chemical groups onto the surface of the CNTs. This step is not optional; it is essential for transforming CNTs from a passive scaffold into a high-performance support.
The Problem with Pristine CNTs
Pristine CNTs are hydrophobic and have a low density of surface defects. This "slippery" surface provides very few stable nucleation sites for metal precursors, causing them to move and agglomerate into large, inactive clumps during catalyst preparation or reaction.
Creating Anchoring Sites
The most common method of functionalization is oxidation using strong acids (e.g., a mix of nitric and sulfuric acid). This process etches the CNT surface, creating defects and introducing oxygen-containing functional groups like carboxyl (-COOH) and hydroxyl (-OH). These groups act as powerful anchoring sites that can bind strongly to metal catalyst precursors.
Impact on Nanoparticle Dispersion
By providing a high density of uniform anchoring sites, functionalization enables the formation of small, highly dispersed catalyst nanoparticles. Achieving this high dispersion is crucial because it maximizes the number of active sites available to the reactants, directly translating to higher overall catalytic activity.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
While the benefits are significant, CNTs are not a universal solution. Adopting them requires a clear understanding of their practical limitations and costs.
The High Cost of Production
High-purity, well-structured CNTs remain significantly more expensive than bulk commodity supports like activated carbon, silica, or alumina. This cost can be a major barrier for large-scale industrial applications where the catalyst is a disposable or low-margin component.
The Risk of Damaging the Structure
Functionalization is a delicate balancing act. While necessary, overly aggressive acid treatments can severely damage the graphitic structure of the CNTs. This structural damage can reduce their mechanical strength and, critically, their electrical and thermal conductivity, negating some of their key advantages.
Purity and Handling
As-produced CNTs often contain impurities like amorphous carbon or residual metal catalysts from their synthesis. These impurities must be removed through costly purification steps. Furthermore, CNTs tend to agglomerate into tight bundles due to strong van der Waals forces, which can make them difficult to disperse in solvents during catalyst preparation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The decision to use CNTs as a catalyst support hinges on a careful analysis of your specific performance requirements, reaction conditions, and economic constraints.
- If your primary focus is maximizing catalytic activity, selectivity, and lifetime for a high-value product: CNTs are an excellent choice, as their tunable properties can deliver performance unattainable with conventional supports.
- If your primary focus is a cost-sensitive, large-scale industrial process: Traditional supports often remain the more pragmatic choice unless the performance gains from CNTs can provide a clear and substantial return on the higher material investment.
- If your reaction involves extreme temperatures or harsh chemical media: The superior thermal and chemical stability of CNTs makes them a compelling candidate that can outperform supports that would otherwise degrade or deactivate.
Ultimately, carbon nanotubes represent a powerful and highly tunable platform for designing the next generation of advanced catalysts.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Carbon Nanotubes (CNTs) | Traditional Supports (e.g., Activated Carbon) |
|---|---|---|
| Surface Area | High, external, and accessible | High, but mostly internal and less accessible |
| Thermal Stability | Excellent (high thermal conductivity) | Moderate to good |
| Chemical Stability | Inert in acidic/basic environments | May degrade in harsh conditions |
| Electronic Properties | Tunable, enables strong metal-support interaction | Limited electronic influence |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Functionalization Need | Required for optimal performance | Less critical |
Ready to enhance your catalytic processes with high-performance supports? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables, including solutions for catalyst development and testing. Our expertise in materials like carbon nanotubes can help you achieve superior activity, selectivity, and stability in your reactions. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's innovation goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Lab and Diamond Growth
- Glassy Carbon Sheet RVC for Electrochemical Experiments
- Optical Window Glass Substrate Wafer CaF2 Substrate Window Lens
People Also Ask
- What are the practical uses of thin film interference? Control Light for Optics, Security & Manufacturing
- What are the mechanical applications of carbon nanotubes? Reinforce Materials for Unmatched Strength
- Is it possible during the synthesis of CNTs to determine its chirality? Master the Challenge of CNT Purity Control
- What are diamond coated tools used for? Conquer Abrasive Materials with Superior Tool Life
- What is the synthesis process of graphene? A Guide to Top-Down and Bottom-Up Methods
- How does sputtering the plasma formation happen? A Guide to Generating and Controlling Sputtering Plasma
- Can graphene be made artificially? A Guide to Synthesis Methods for Your Application
- What are the different types of sputtering targets? Choose the Right Material Source for Your Thin-Film Process



















