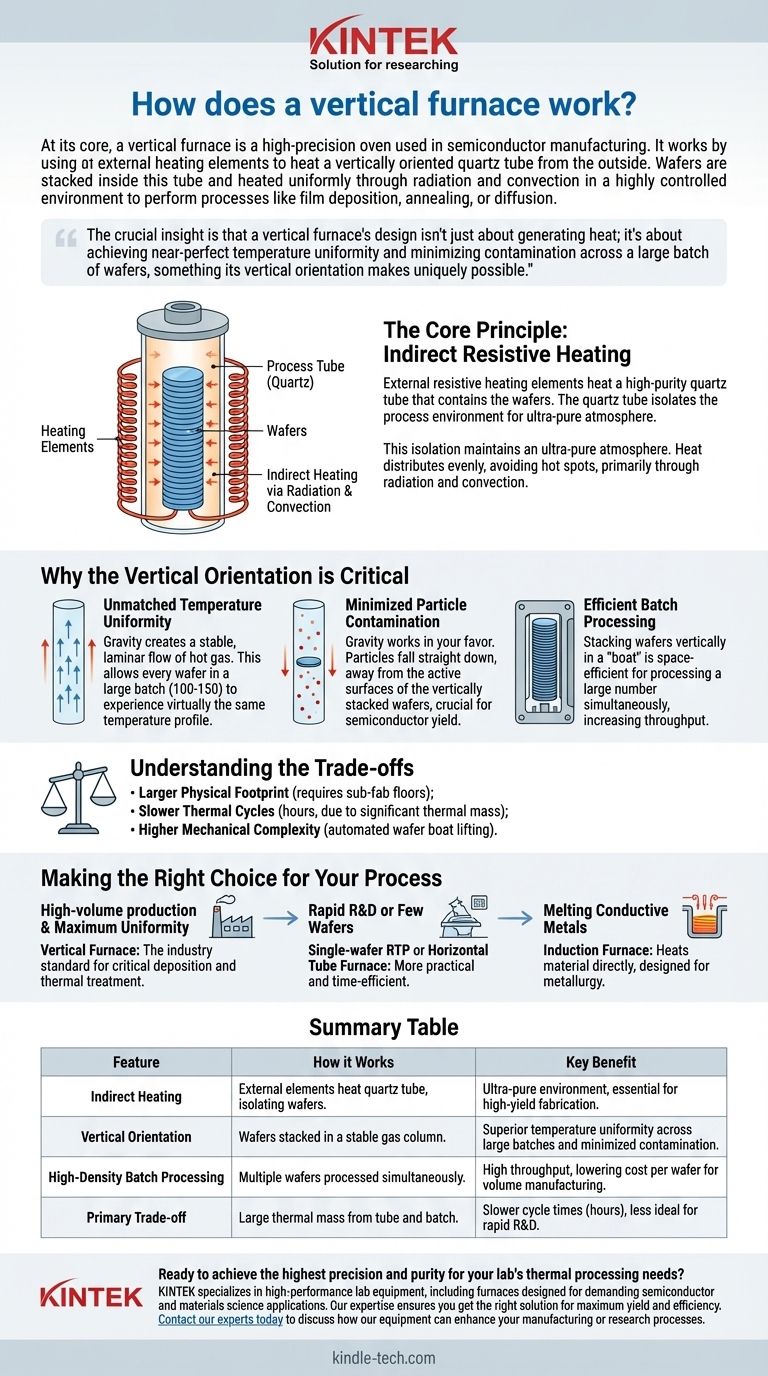
At its core, a vertical furnace is a high-precision oven used in semiconductor manufacturing. It works by using external heating elements to heat a vertically oriented quartz tube from the outside. Wafers are stacked inside this tube and heated uniformly through radiation and convection in a highly controlled environment to perform processes like film deposition, annealing, or diffusion.
The crucial insight is that a vertical furnace's design isn't just about generating heat; it's about achieving near-perfect temperature uniformity and minimizing contamination across a large batch of wafers, something its vertical orientation makes uniquely possible.

The Core Principle: Indirect Resistive Heating
Most vertical furnaces operate on a principle of indirect heating, much like a high-tech muffle furnace. The heat source does not directly touch the silicon wafers.
The Heating Elements
The workhorse of the furnace is a set of resistive heating elements that encircle the main process chamber. When a controlled electric current is passed through these elements, they heat up to extremely high temperatures.
The Process Tube
Sitting inside these hot elements is a high-purity quartz tube. This tube serves two critical functions: it contains the wafers and it acts as a "muffle," isolating the process environment from the heating elements and the outside air.
This isolation is essential for maintaining the ultra-pure atmosphere required for semiconductor fabrication.
Heat Transfer to the Wafers
The heat from the elements radiates inward, heating the walls of the quartz tube. The hot tube walls then transfer this thermal energy to the wafers stacked inside, primarily through radiation and convection.
Because the wafers are suspended in a sealed, stable column of gas, heat distributes very evenly, avoiding hot spots.
Why the Vertical Orientation is Critical
The decision to orient the furnace vertically is a deliberate engineering choice driven by the demands of modern chip manufacturing. It directly addresses the primary challenges of process control and contamination.
Unmatched Temperature Uniformity
In a vertical setup, gravity helps create a stable and symmetrical thermal environment. Hot gas naturally rises, creating a laminar flow that is far more predictable and uniform than the turbulent flows often found in horizontal furnaces.
This allows every wafer in a large batch—often 100 to 150 at a time—to experience virtually the same temperature profile.
Minimized Particle Contamination
Contamination is the enemy of semiconductor yield. In a horizontal furnace, particles can fall from the top of the tube directly onto the surface of the wafers below.
In a vertical furnace, gravity works in your favor. Any particles that do form tend to fall straight down to the bottom of the tube, away from the active surfaces of the vertically stacked wafers.
Efficient Batch Processing
Stacking wafers vertically in a "boat" or "cassette" is a highly space-efficient method for processing a large number of wafers simultaneously. This high-density batch processing increases throughput and lowers the cost per wafer.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While superior for high-volume, high-precision manufacturing, the vertical furnace design is not without its complexities and costs.
Larger Physical Footprint
Vertical furnaces are tall, often requiring multiple floors of a fabrication facility (a "sub-fab" or "cleanroom basement") to house the lower loading mechanisms and gas panels. This increases facility construction costs.
Slower Thermal Cycles
Heating and cooling a large batch of over 100 wafers and the heavy quartz tube is a slow process. The thermal mass is significant, meaning cycle times are measured in hours, not minutes. This makes them less suitable for rapid R&D or single-wafer experiments.
Higher Mechanical Complexity
Automated systems that lift the heavy and fragile wafer boats into the base of the furnace are mechanically more complex and require more maintenance than the simple "push/pull" rods used in horizontal furnaces.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
The ideal heating technology depends entirely on your specific goal, whether it's manufacturing, research, or materials processing.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production with maximum uniformity: The vertical furnace is the undisputed industry standard for critical deposition and thermal treatment steps.
- If your primary focus is rapid R&D or processing a few wafers at a time: A single-wafer rapid thermal processing (RTP) system or a smaller horizontal tube furnace is often a more practical and time-efficient choice.
- If your primary focus is melting conductive metals or creating alloys: An induction furnace is the correct tool, as it heats the material directly and is designed for metallurgy, not wafer processing.
Ultimately, choosing a vertical furnace is a commitment to achieving the highest possible precision and purity at scale.
Summary Table:
| Feature | How it Works | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Indirect Heating | External elements heat a quartz tube, isolating wafers from the heat source. | Ultra-pure process environment, essential for high-yield semiconductor fabrication. |
| Vertical Orientation | Wafers are stacked vertically in a stable column of gas. | Superior temperature uniformity across large batches (100-150 wafers) and minimized particle contamination. |
| High-Density Batch Processing | Multiple wafers are processed simultaneously in a single run. | High throughput, lowering the cost per wafer for volume manufacturing. |
| Primary Trade-off | Large thermal mass from the quartz tube and wafer batch. | Slower cycle times (hours), making it less ideal for rapid R&D. |
Ready to achieve the highest precision and purity for your lab's thermal processing needs?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including furnaces designed for demanding semiconductor and materials science applications. Our expertise ensures you get the right solution for maximum yield and efficiency.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our equipment can enhance your manufacturing or research processes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- How do you clean a tube furnace tube? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe and Effective Cleaning
- What temperature is alumina activated? Unlock Optimal Porosity for Adsorption
- Why is an Alumina Ceramic Tube Support Necessary for 1100°C Experiments? Ensure Data Accuracy and Chemical Inertness
- What is the pressure on a tube furnace? Essential Safety Limits for Your Lab
- What tube is used for tubular furnace? Choose the Right Material for Temperature & Atmosphere



















