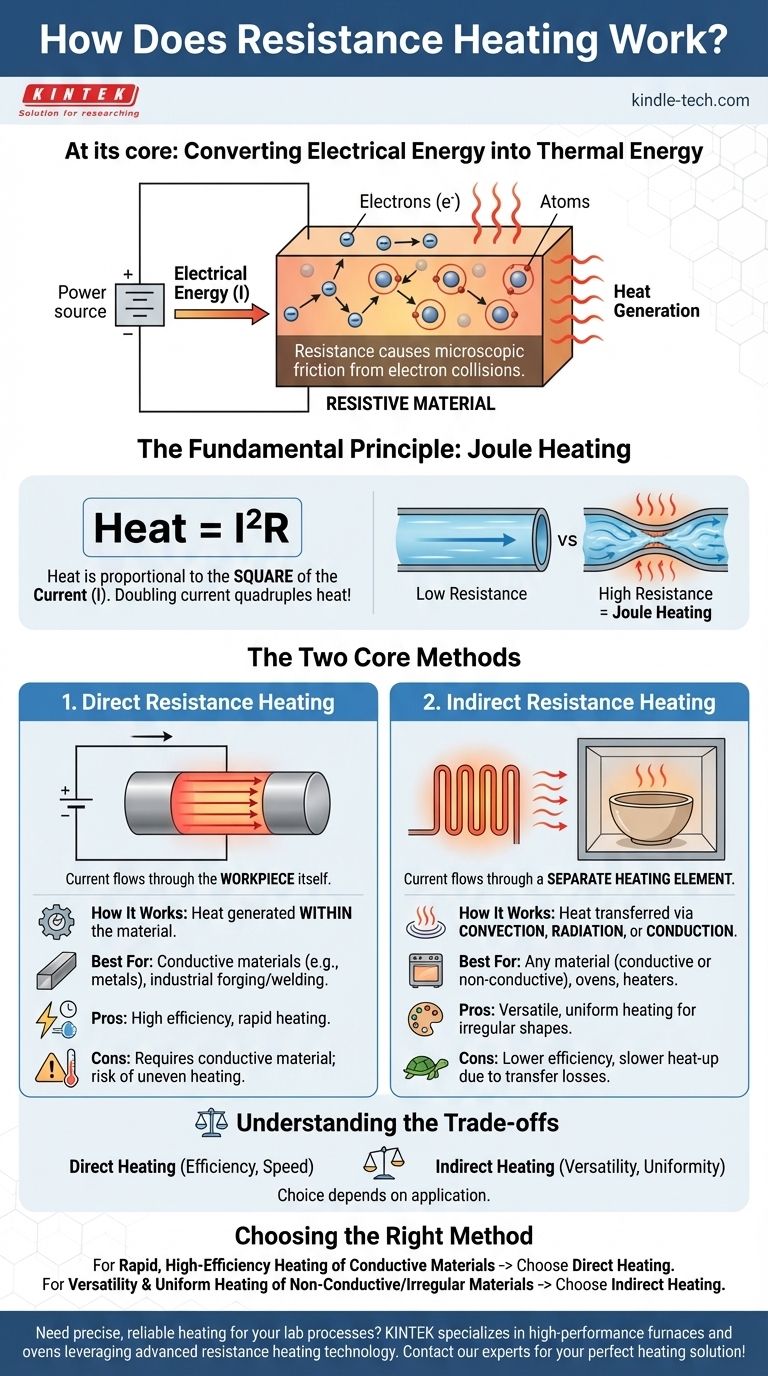
At its core, resistance heating is the process of converting electrical energy into thermal energy. It works by passing an electric current through a material that resists the flow of electricity. This resistance causes friction at a microscopic level, as flowing electrons collide with the atoms of the material, transferring their energy and generating heat.
Resistance heating is not a single technology, but a fundamental principle with two distinct applications. The key is understanding whether the object you want to heat is the resistor (Direct Heating) or if it's being heated by a separate resistor (Indirect Heating).
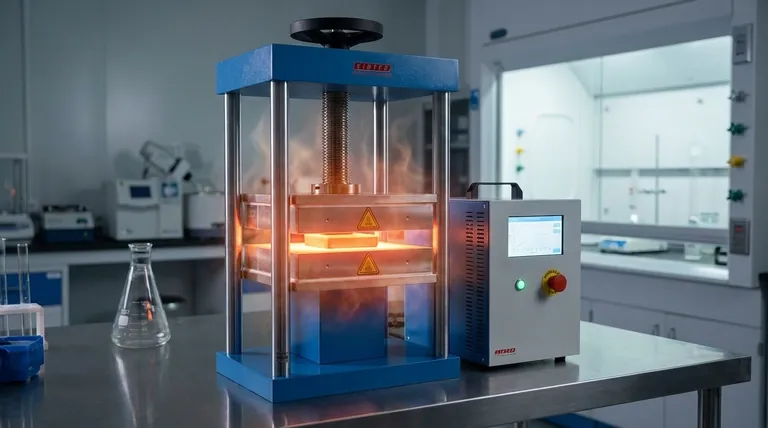

The Fundamental Principle: Joule Heating
The "Friction" of Electricity
Think of electrical current as water flowing through a pipe. If the pipe is wide and smooth, the water flows easily. If the pipe is narrow and filled with obstacles, the water has to work harder to get through, creating turbulence and friction.
In an electrical circuit, a material with high electrical resistance acts like that narrow, obstructed pipe. As electrons are forced through it, they constantly collide with the material's atoms, generating heat in a process known as Joule heating.
The I²R Effect Explained
This process is quantified by a simple formula: Heat = I²R. This is Joule's Law.
- I stands for current, the amount of electricity flowing.
- R stands for resistance, the material's opposition to that flow.
The most important insight here is that the heat generated is proportional to the square of the current. This means doubling the current doesn't just double the heat—it quadruples it, making resistance heating a powerful and responsive method.
The Two Core Methods of Resistance Heating
The principle of Joule heating is applied in two primary ways, defined by the relationship between the heating element and the object being heated (the "charge" or "workpiece").
Method 1: Direct Resistance Heating
In direct resistance heating, the object you intend to heat serves as its own heating element. A large electric current is passed directly through the workpiece.
The heat is generated within the material itself. This is common in industrial applications, like heating a metal billet before forging or welding. The current flows through the billet, causing its internal temperature to rise rapidly.
Method 2: Indirect Resistance Heating
In indirect resistance heating, the electric current flows through a separate, dedicated heating element. This element—often a coil, rod, or ceramic component—gets extremely hot.
This heat is then transferred to the target object through convection (air movement), radiation (infrared energy), or conduction (direct contact). Common examples include electric furnaces, space heaters, and kitchen toasters, where glowing coils heat the air or your bread.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between direct and indirect heating involves clear engineering trade-offs. There is no universally "better" method; the choice depends entirely on the application.
The Challenge of Direct Heating: Uniformity and Control
Direct heating is incredibly energy-efficient because there is no intermediate transfer step. However, it requires the workpiece to be electrically conductive.
Furthermore, achieving uniform heat can be difficult if the object has an irregular shape or non-uniform internal resistance, which can lead to undesirable hot spots.
The Limitation of Indirect Heating: Efficiency and Speed
Indirect heating is far more versatile because it can heat any material, regardless of its conductivity. You can place insulators, plastics, or food inside an electric oven.
The primary downside is lower efficiency. Heat must first be generated in the element and then transferred to the workpiece, a process that always involves some energy loss to the surrounding environment. This transfer step also means it can take longer to reach the desired temperature.
Choosing the Right Method for the Application
Your goal determines the correct approach. The decision hinges on the properties of the material you need to heat and your requirements for speed and efficiency.
- If your primary focus is rapid, high-efficiency heating of a conductive material: Direct resistance heating is the superior choice because it generates heat precisely where it is needed with minimal loss.
- If your primary focus is versatility for heating non-conductive or irregularly shaped materials: Indirect resistance heating provides the flexibility needed, as it decouples the heating mechanism from the object itself.
By understanding the distinction between these two methods, you can recognize how this simple principle powers everything from massive industrial furnaces to your kitchen appliances.
Summary Table:
| Method | How It Works | Best For | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Direct Heating | Current flows through the workpiece itself, generating internal heat. | Electrically conductive materials (e.g., metals). | High efficiency, rapid heating. | Requires conductive material; risk of uneven heating. |
| Indirect Heating | Current flows through a separate heating element; heat transfers to the workpiece. | Any material (conductive or non-conductive). | Versatile, uniform heating for irregular shapes. | Lower efficiency, slower heat-up due to transfer losses. |
Need precise, reliable heating for your lab processes? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including furnaces and ovens that leverage advanced resistance heating technology. Whether you require the rapid efficiency of direct heating or the versatile control of indirect heating, our solutions are engineered for accuracy and durability. Contact our experts today to find the perfect heating system for your laboratory needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
- Manual Lab Heat Press
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Integrated Manual Heated Plates for Lab Use
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates Split Manual Laboratory Hot Press
People Also Ask
- Are hydraulic presses powered by water? Discover the critical role of hydraulic oil.
- What is the use of KBr? Master Sample Prep for Accurate IR Spectroscopy
- How does a laboratory hydraulic press improve XRF accuracy for catalyst samples? Enhance Precision & Signal Stability
- What role does a laboratory hydraulic press play in the preparation of solid electrolyte pellets? Ensure Data Accuracy
- What is the pellet technique in IR? Master Solid Sample Preparation for Clear Spectroscopy



















