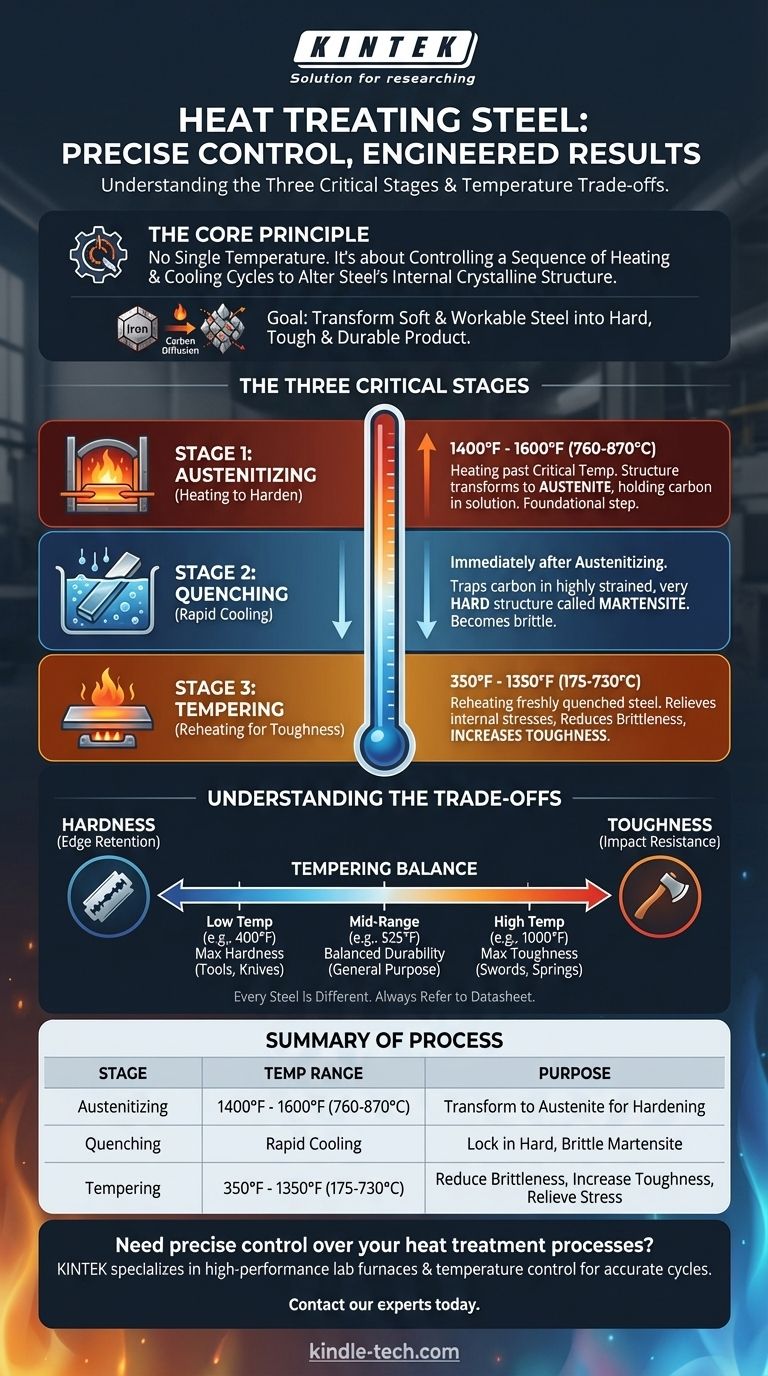
There is no single temperature for heat treating steel; rather, it is a precise, multi-stage process involving different temperatures to achieve specific results. The full cycle involves heating steel anywhere from 350°F (175°C) for a low-temperature temper up to well over 1500°F (815°C) for initial hardening. The exact temperature at each stage depends entirely on the type of steel and the desired final properties.
The core principle of heat treating is not about reaching one specific temperature, but about carefully controlling a sequence of heating and cooling cycles. This manipulation of temperature alters the steel's internal crystalline structure to achieve a target balance between hardness and toughness.

The Goal of Heat Treatment: Engineering Steel's Structure
Heat treatment is the process of using controlled heating and cooling to change the physical properties of steel. It allows you to take a piece of steel that is relatively soft and workable and transform it into a final product that is hard, tough, and durable.
The Role of Temperature and Carbon
Steel is an alloy of iron and carbon. At room temperature, the carbon is locked within the iron's crystal structure. When you heat the steel, these crystals change form, allowing the carbon atoms to dissolve and spread out more evenly, much like dissolving sugar in hot water.
The Critical Transformation to Austenite
As you heat steel past its critical temperature—typically between 1400°F and 1600°F (760-870°C)—it undergoes a phase transformation. Its crystal structure shifts into a state known as austenite, which can hold a significant amount of carbon in solution. This is the foundational step for hardening steel.
The Three Critical Stages of Heat Treatment
True heat treatment for hardening is a three-part process. Skipping or improperly executing any stage will result in a failed part.
Stage 1: Austenitizing (Heating to Harden)
This is the initial heating phase. The goal is to heat the steel hot enough and hold it long enough for its entire structure to transform into austenite. The exact temperature is critical and depends on the steel's specific carbon content and other alloys.
Stage 2: Quenching (Rapid Cooling)
Immediately after the steel becomes austenite, it must be cooled very rapidly, or "quenched." This rapid cooling does not give the crystal structure time to revert to its soft state. Instead, it traps the carbon atoms in a new, highly strained, and very hard structure called martensite. This state, however, is also extremely brittle.
Stage 3: Tempering (Reheating for Toughness)
A freshly quenched piece of steel is too brittle for most practical uses. The final step is tempering, which involves reheating the steel to a much lower temperature, typically between 350°F and 1350°F (175-730°C). This process relieves internal stresses and reduces brittleness, increasing toughness.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The art of heat treatment lies in managing the inherent compromises between different material properties. You are always balancing one attribute against another.
The Hardness vs. Toughness Spectrum
Tempering is a direct trade-off between hardness and toughness.
- A low tempering temperature (e.g., 400°F / 205°C) reduces brittleness only slightly, retaining maximum hardness. This is ideal for tools that need a keen edge, like a knife or razor.
- A high tempering temperature (e.g., 1000°F / 540°C) sacrifices significant hardness to gain a large amount of toughness. This is necessary for tools that must withstand impact, like an axe or a pry bar.
Why "Every Steel is Different"
The specific carbon content and alloying elements (like chromium, molybdenum, or vanadium) in a steel change its behavior dramatically. These alloys alter the critical austenitizing temperature and how the steel responds to a given tempering temperature. Always refer to the datasheet for your specific type of steel.
The Risk of Improper Heating
Heating the steel too high during the austenitizing phase can cause the grain structure to grow, making the final product weak and brittle even after tempering. Furthermore, an uncontrolled atmosphere during heating can strip carbon from the surface of the steel, a flaw known as decarburization, which prevents it from hardening properly.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your choice of tempering temperature is dictated entirely by the intended use of the steel part.
- If your primary focus is maximum hardness and edge retention (e.g., a file or razor): Temper at a lower temperature, typically between 350°F and 500°F (175-260°C).
- If your primary focus is a balance of hardness and durability (e.g., a general-purpose knife blade): Temper in the mid-range, often between 450°F and 600°F (230-315°C).
- If your primary focus is maximum toughness and shock resistance (e.g., a sword, axe, or spring): Temper at a higher temperature, from 600°F up to 1100°F (315-600°C) or more.
By understanding this process, you gain direct control over the final performance of your steel.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Temperature Range | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Austenitizing | 1400°F - 1600°F (760-870°C) | Transform steel structure to austenite for hardening |
| Quenching | Rapid cooling from austenitizing temp | Lock in hard, brittle martensite structure |
| Tempering | 350°F - 1350°F (175-730°C) | Reduce brittleness, increase toughness, relieve stress |
Need precise control over your heat treatment processes? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab furnaces and temperature control equipment designed for accurate and repeatable heat treatment cycles. Whether you're working with tool steels, alloys, or developing new materials, our solutions ensure you hit the exact temperatures required for perfect results. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can enhance your laboratory's capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the different types of laboratory furnaces? Find the Perfect Fit for Your Application
- How do you control a muffle furnace? Master Precise Temperature Control for Your Lab
- What is done by ashing in muffle furnace? A Guide to Precise Inorganic Content Analysis
- What is the difference between muffle furnace and air oven? Choose the Right Tool for Your Thermal Process
- What is the difference between a box furnace and a muffle furnace? Choose the Right Lab Furnace for Your Application



















