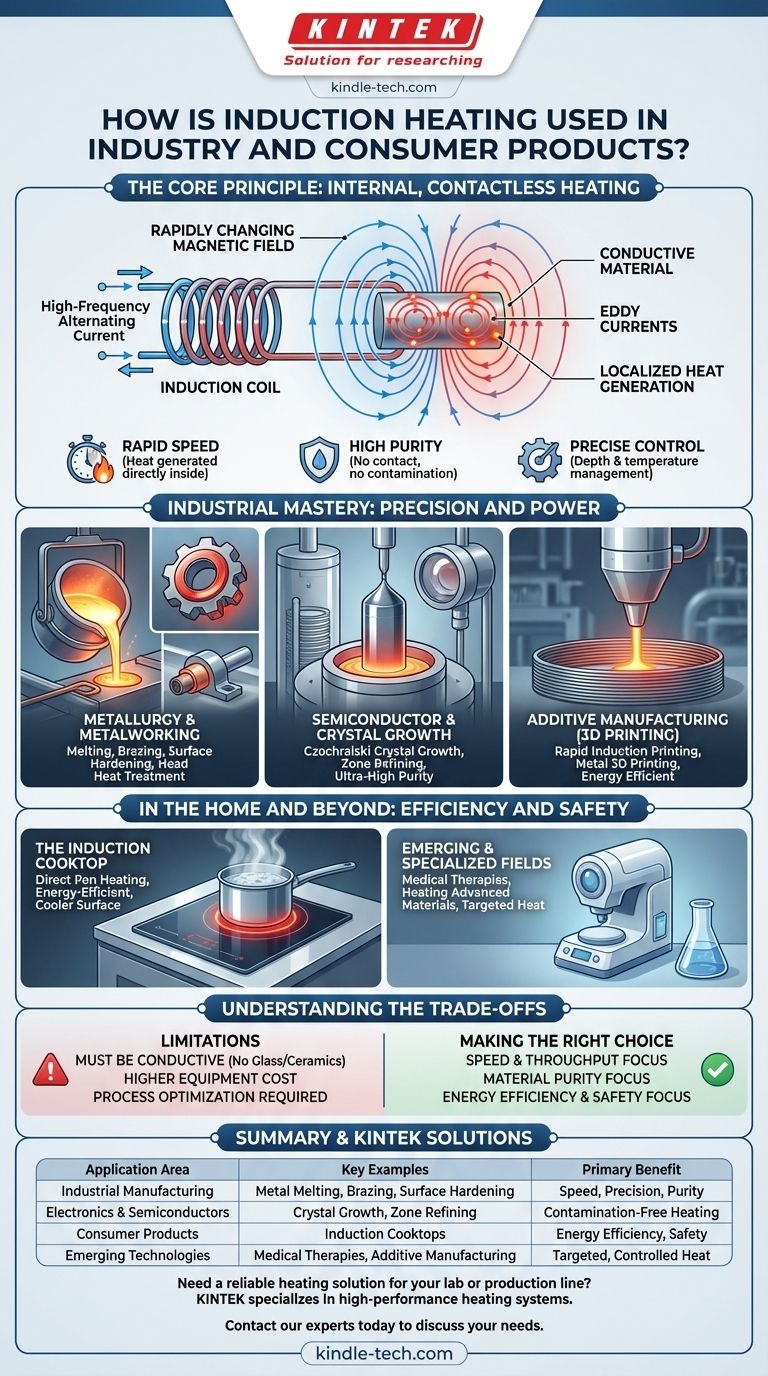
In short, induction heating is used wherever precise, rapid, and clean heating of a conductive material is required. Its applications range from large-scale industrial processes like metal melting, surface hardening, and semiconductor crystal growth to common consumer products, most notably the induction cooktop. The core principle allows for targeted heat generation directly within the material itself without any physical contact.
The versatility of induction heating stems from a single, powerful principle: it generates heat inside an object using an electromagnetic field. This fundamental difference from conventional heating is what makes it faster, cleaner, more precise, and often more energy-efficient for a vast array of applications.

The Core Principle: Internal, Contactless Heating
To understand why induction is chosen for so many different tasks, we must first look at how it works. Unlike a furnace or a flame, it does not rely on external heat transferring into a material.
How It Works: An Electromagnetic Field
An induction system uses a coil through which a high-frequency alternating current is passed. This creates a powerful and rapidly changing magnetic field. When a conductive material (like a metal pan or a steel part) is placed within this field, the field induces electrical currents—known as eddy currents—inside the material itself. The material's natural resistance to the flow of these currents generates intense, localized heat.
The Benefit of Speed
Because the heat is generated directly inside the part, the heating process is exceptionally fast. There is no delay waiting for thermal energy to conduct from an external source to the object's core. This allows for rapid temperature increases that are critical in high-throughput manufacturing lines.
The Benefit of Purity
Induction heating is a non-contact process. The part being heated never touches a flame or a heating element. This is a crucial advantage in applications where even the slightest contamination is unacceptable, such as in the production of medical-grade alloys or high-purity silicon crystals for the semiconductor industry.
Industrial Mastery: Precision and Power
In industrial settings, the control and power of induction heating are leveraged for demanding processes that define modern manufacturing.
Metallurgy and Metalworking
Induction is a cornerstone of metallurgy. It is used for melting metals in foundries, brazing or soldering components together, and surface hardening gears and shafts. By controlling the frequency of the magnetic field, engineers can precisely dictate the depth of heat penetration, allowing them to harden just the outer surface of a part while leaving the core ductile and tough.
Semiconductor and Crystal Growth
The production of modern electronics relies on flawless silicon crystals. Processes like Czochralski crystal growth and zone refining use induction to melt and purify materials in a highly controlled, contamination-free vacuum. The contactless nature of the heating is non-negotiable here.
Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing)
A cutting-edge application is in metal 3D printing, such as Rapid Induction Printing. In this process, a metal wire is fed through a nozzle and instantly melted by induction before being deposited. This method is often more energy-efficient and safer than laser-based printing, as it doesn't involve high-power lasers or fine metal powders.
In the Home and Beyond: Efficiency and Safety
The same principles that benefit heavy industry also make induction technology ideal for consumer and emerging applications.
The Induction Cooktop
This is the most familiar application of induction heating. The cooktop's surface generates a magnetic field that directly heats the conductive metal of the pot or pan. This is highly energy-efficient because very little heat is wasted warming the surrounding air or the glass surface. It is also safer, as there is no open flame and the cooktop itself remains much cooler to the touch.
Emerging and Specialized Fields
Research is expanding induction's reach. It is being explored for specialized medical uses, such as precisely heating biological tissues for therapeutic purposes. Engineers are also developing methods to efficiently heat new, highly engineered materials that have low electrical resistivity, opening the door to future innovations.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, induction heating is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Material Limitation: It Must Be Conductive
The primary requirement for induction heating is that the target material must be electrically conductive. This is why it works on metals like iron, steel, and copper, but not directly on materials like glass, ceramics, or most plastics. Special induction cookware, for example, has a ferrous metal base to enable heating.
Equipment Complexity and Cost
The initial investment in induction heating equipment—the high-frequency power supply and custom-designed coils—can be more significant than for a simple resistive heater or gas furnace. The technology is more complex, requiring a higher level of technical expertise to design and maintain.
The Need for Process Optimization
Achieving the desired heating profile is not always a "plug-and-play" operation. It requires careful engineering to match the coil geometry, power, and frequency to the specific part and material. This optimization is critical for success but requires upfront development effort.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Deciding to use induction heating depends entirely on your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is process speed and throughput: Induction heating's rapid, internal heating is unparalleled for high-volume manufacturing where seconds count.
- If your primary focus is material purity and quality: The contactless nature prevents contamination, making it the superior choice for semiconductors, medical devices, and high-purity alloys.
- If your primary focus is energy efficiency and safety: For applications like cooking or some forms of additive manufacturing, induction offers a more efficient and safer alternative to traditional flame or laser-based methods.
Ultimately, induction heating provides a powerful toolkit for any application demanding fast, precise, and clean thermal energy.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Examples | Primary Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Industrial Manufacturing | Metal Melting, Brazing, Surface Hardening | Speed, Precision, Purity |
| Electronics & Semiconductors | Crystal Growth, Zone Refining | Contamination-Free Heating |
| Consumer Products | Induction Cooktops | Energy Efficiency, Safety |
| Emerging Technologies | Medical Therapies, Additive Manufacturing | Targeted, Controlled Heat |
Need a reliable heating solution for your lab or production line? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including advanced heating systems. Whether you require precise temperature control for material testing or efficient heating for manufacturing processes, our expertise can help you achieve superior results. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your specific laboratory and industrial heating needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Platinum Sheet Electrode for Laboratory and Industrial Applications
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
People Also Ask
- What are the primary functions of a vacuum hot press furnace? Optimize WC/Cu-Zr-Ti Composite Consolidation
- How does the mechanical pressure from a vacuum hot-pressing furnace facilitate the densification of B4C/Al composites?
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing furnace over HIP? Optimize Fiber-Foil Composite Production
- What role does a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace play in the fabrication of CuCrFeMnNi alloys? Achieve High Purity
- What are the advantages of a vacuum hot pressing furnace? Achieve Superior Lithium Niobate Piezoelectric Density



















