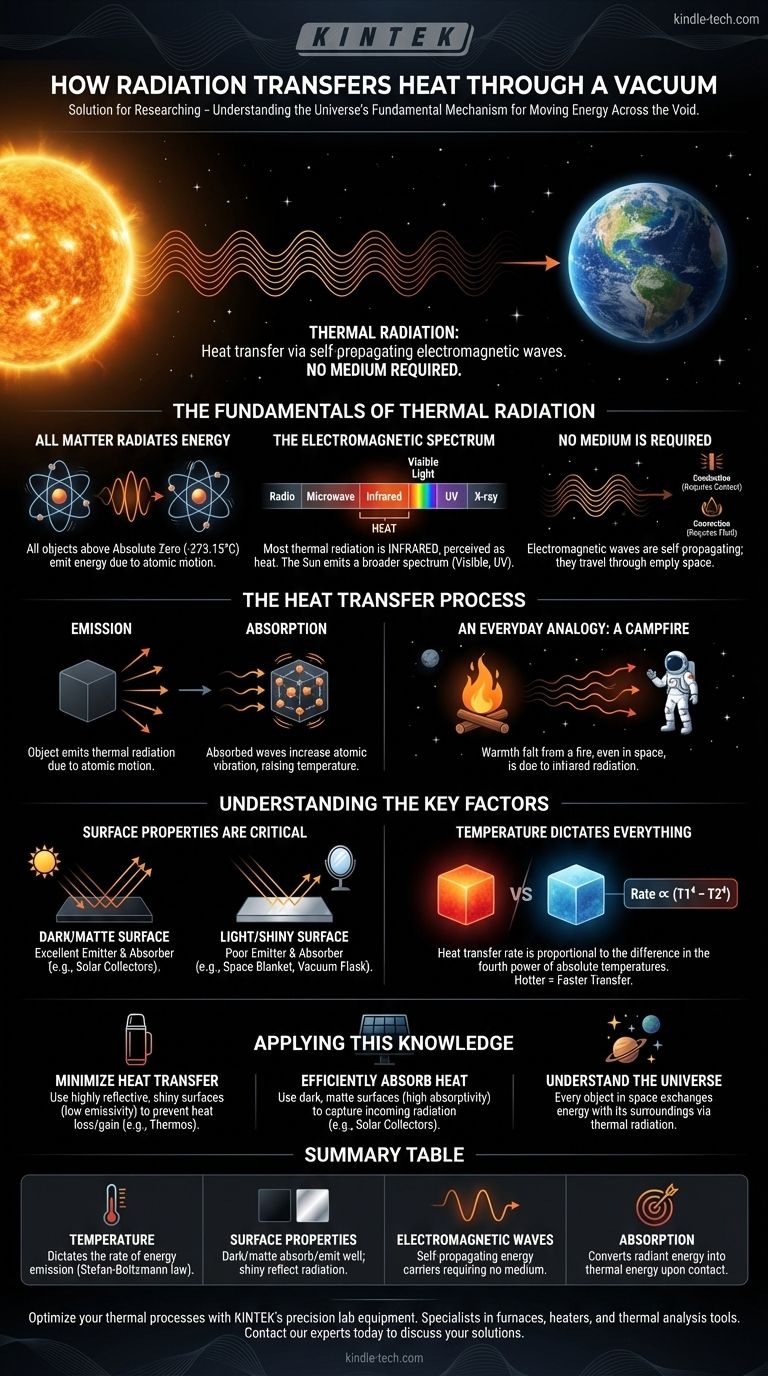
In short, heat is transferred through a vacuum via thermal radiation. This process does not require a physical medium because the energy travels in the form of self-propagating electromagnetic waves, much like how light from the sun reaches Earth.
The core principle is that all matter with a temperature above absolute zero emits energy. This energy, in the form of electromagnetic waves, can travel through a vacuum, and when it is absorbed by another object, it transfers its thermal energy.
The Fundamentals of Thermal Radiation
To understand how this works, we need to look at the behavior of matter at the atomic level.
All Matter Radiates Energy
Every object with a temperature above absolute zero (-273.15°C or 0 Kelvin) is composed of atoms and molecules that are in constant motion. This vibration and movement of charged particles generates electromagnetic radiation.
This emission of energy is a fundamental property of matter. Hotter objects have more vigorous atomic motion, so they radiate more energy at higher frequencies.
The Electromagnetic Spectrum
This "thermal radiation" is a part of the electromagnetic spectrum, which also includes radio waves, microwaves, visible light, and X-rays. For most everyday objects, this energy is primarily emitted as infrared radiation, which we perceive as heat.
The sun, being extremely hot, radiates energy across a broader spectrum, including the visible light we see and the ultraviolet (UV) light that can cause sunburn.
No Medium is Required
Unlike conduction (which requires direct contact) or convection (which requires the movement of a fluid like air or water), electromagnetic waves are disturbances in electric and magnetic fields. They are self-propagating and do not need a medium to travel.
This is the critical property that allows radiation to be the sole method of heat transfer in a perfect vacuum.
How This Process Transfers Heat
The transfer of heat via radiation is a two-step process involving emission and absorption.
From Emission to Absorption
First, an object emits thermal radiation due to the motion of its atoms. These electromagnetic waves then travel outwards from the source.
When these waves strike another object, they can be absorbed. The energy from the absorbed waves increases the vibration of the atoms in the second object, which we measure as an increase in its temperature.
An Everyday Analogy: A Campfire
Imagine standing near a campfire. You feel its warmth on your face even though you are not touching the flames (conduction) and the hot air isn't necessarily blowing on you (convection). That warmth you feel is infrared radiation traveling from the fire to you.
Now, imagine that campfire in the vacuum of space. The principle remains identical. The heat would still radiate outwards and warm any object in its path.
Understanding the Key Factors
While radiation is the only method of heat transfer in a vacuum, its effectiveness depends on several factors.
Surface Properties Are Critical
An object's surface has a huge impact on how well it radiates and absorbs energy.
A dark, matte surface is an excellent emitter and absorber of radiation. This is why solar water heaters are painted black.
A light-colored, shiny surface is a poor emitter and a poor absorber because it reflects most of the radiation that hits it. This is the principle behind an emergency space blanket—its shiny surface reflects your own body heat back to you, keeping you warm.
Temperature Dictates Everything
The rate of heat transfer is profoundly affected by temperature. Specifically, it is proportional to the difference of the fourth powers of the absolute temperatures of the two objects (Stefan-Boltzmann law).
In simple terms, the hotter an object is, the more energy it radiates, and the greater the temperature difference between two objects, the faster the net heat transfer will be.
Applying This Knowledge
Understanding thermal radiation is key to solving engineering challenges in environments from deep space to your kitchen.
- If your goal is to minimize heat transfer in a vacuum: Use highly reflective, shiny surfaces (low emissivity) to prevent both the loss and gain of heat via radiation. This is the core principle behind a vacuum flask or thermos.
- If your goal is to efficiently absorb heat from a distant source: Use dark, matte surfaces (high absorptivity) to capture as much incoming radiation as possible, like the collectors on a solar panel.
- If you are simply trying to understand the universe: Remember that every star, planet, and object in space is constantly exchanging energy with its surroundings through this silent, invisible process.
Ultimately, thermal radiation is the universe's fundamental mechanism for moving energy across the void.

Summary Table:
| Key Factor | Role in Thermal Radiation |
|---|---|
| Temperature | Dictates the rate of energy emission (Stefan-Boltzmann law) |
| Surface Properties | Dark/matte surfaces absorb/emit well; shiny surfaces reflect radiation |
| Electromagnetic Waves | Self-propagating energy carriers requiring no medium |
| Absorption | Converts radiant energy into thermal energy upon contact |
Optimize your thermal processes with KINTEK's precision lab equipment. Whether you're designing high-temperature applications or need reliable thermal analysis tools, KINTEK specializes in furnaces, heaters, and consumables tailored for laboratory environments. Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your research and operational efficiency.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Heated Vacuum Press Machine Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is vacuum sintering equipment essential for hot pressing sub-micron metal powders? Ensure Purity and Conductivity
- What are the core advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing furnace for Cr50Cu50 alloys? Achieve 96.09% Density
- How does the 25MPa pressure in a vacuum hot pressing furnace affect C-SiC-B4C sintering? Enhance Composite Density
- What are the steps in the hot pressing process? Achieve Maximum Density for Complex Parts
- How does the vacuum environment within a hot-pressing furnace improve the performance of B4C/Al composites? Boost Density



















