The primary function of hot press forming is to use a combination of high temperature and significant pressure to shape, bond, or cure materials. This controlled process is essential for manufacturing high-quality, dimensionally stable, and structurally robust products from materials like wood composites, laminates, and advanced metals.
The core purpose of hot press forming isn't just to shape a material, but to fundamentally alter its internal structure—increasing density, ensuring adhesion, and eliminating defects to achieve a level of quality and performance that other methods cannot match.
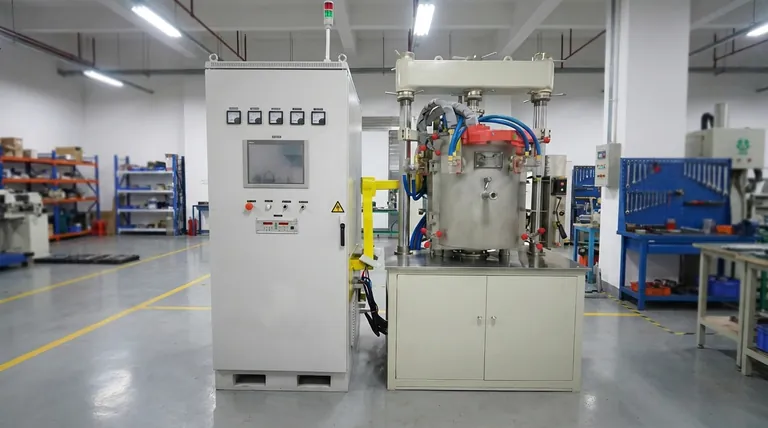

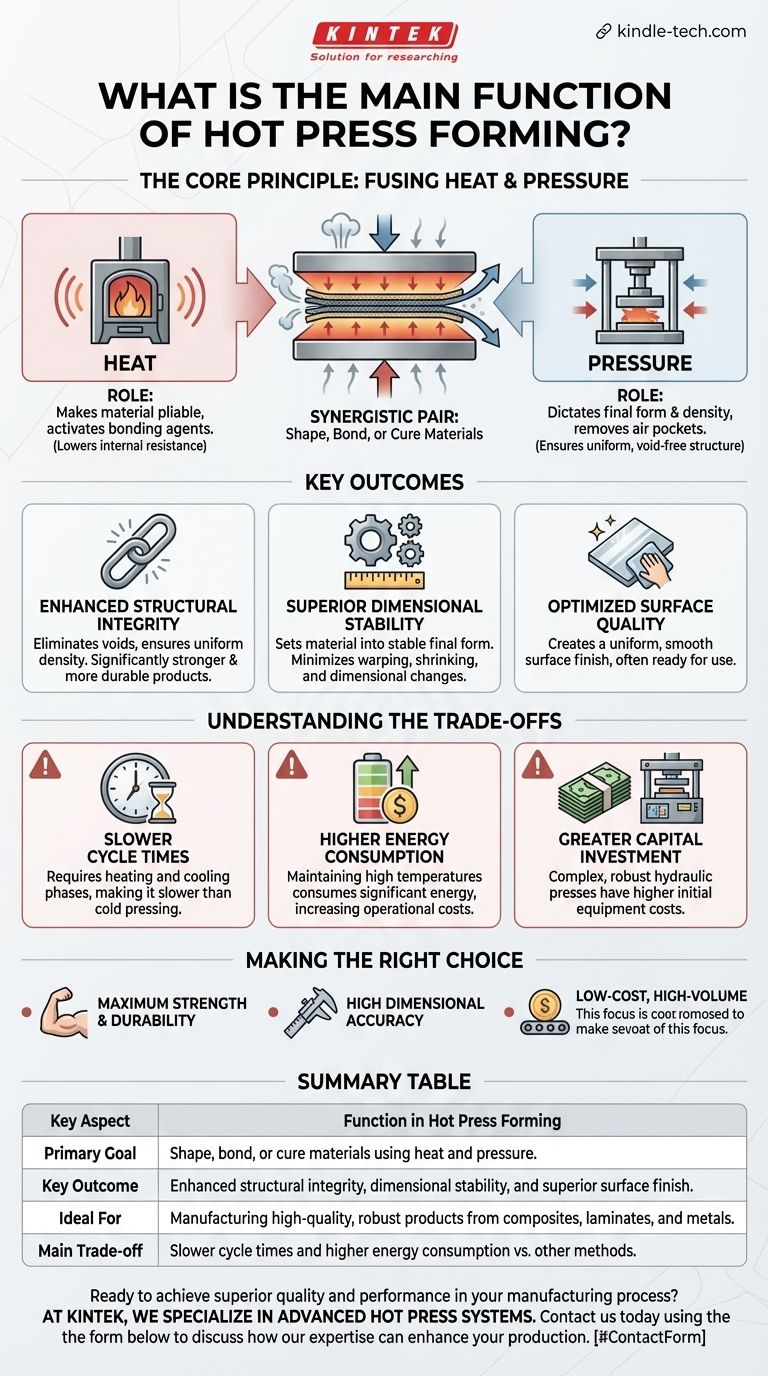
The Core Principle: Fusing Heat and Pressure
Hot press forming is a sophisticated process where temperature and pressure are not independent variables but a synergistic pair. The "technical control" mentioned in manufacturing is all about the precise manipulation of these two forces to achieve a desired outcome.
The Role of Temperature
Heat is the catalyst for change in the material. Its primary function is to make the material pliable or to activate bonding agents.
By raising the temperature, the material's internal resistance to deformation is significantly lowered. For metals, this means reaching a point where they can be shaped with less force, while for wood composites, it activates resins and adhesives that will bond the particles or veneers together.
The Role of Pressure
Pressure is the force that dictates the final form and density. A hydraulic system applies immense, uniform pressure across the material's surface.
This forces the heated material to conform perfectly to the mold or platen, squeezing out air pockets and ensuring a dense, void-free structure. In composite materials, this pressure guarantees intimate contact between layers, resulting in a superior, permanent bond.
Key Outcomes of the Hot Press Process
The precise control over heat and pressure directly translates into superior product characteristics. This is how the process ensures the quality of processed products.
Enhanced Structural Integrity
By eliminating internal voids and ensuring uniform density, hot pressing creates products that are significantly stronger and more durable than those made with pressure alone. This is critical for structural components in aerospace, automotive, and construction.
Superior Dimensional Stability
The combination of heat and pressure sets the material into a stable final form. This process minimizes the risk of warping, shrinking, or other dimensional changes over time, which is essential for products requiring tight tolerances, like high-end cabinetry or laminated flooring.
Optimized Surface Quality
The process results in a smooth, consistent surface finish. The pressure applied by the heated platens or molds creates a uniform surface that is often ready for use with minimal secondary finishing.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, hot press forming is not the universal solution for every application. Understanding its limitations is key to making an informed decision.
Slower Cycle Times
The process requires time to heat the material to the target temperature and often a cooling phase under pressure to set the final shape. This makes it inherently slower than cold pressing or other forming methods.
Higher Energy Consumption
Maintaining the high temperatures required for the press platens consumes a significant amount of energy. This can lead to higher operational costs compared to ambient temperature processes.
Greater Capital Investment
Hydraulic hot presses are complex, robust machines built to withstand extreme temperatures and pressures. This makes the initial equipment cost substantially higher than that for less demanding forming technologies.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting hot press forming depends entirely on the required quality and performance characteristics of the final product.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength and durability: Hot pressing is the ideal choice for creating dense, structurally sound components with superior material properties.
- If your primary focus is high dimensional accuracy and a premium finish: The controlled nature of the process delivers the precision necessary for high-value products where quality cannot be compromised.
- If your primary focus is low-cost, high-volume production for non-structural parts: The slower cycle times and higher energy costs may make simpler methods like cold pressing a more economical alternative.
Ultimately, choosing hot press forming is a strategic investment in achieving the highest possible product quality and long-term performance.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Function in Hot Press Forming |
|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Shape, bond, or cure materials using heat and pressure. |
| Key Outcome | Enhanced structural integrity, dimensional stability, and superior surface finish. |
| Ideal For | Manufacturing high-quality, robust products from composites, laminates, and metals. |
| Main Trade-off | Slower cycle times and higher energy consumption vs. other methods. |
Ready to achieve superior quality and performance in your manufacturing process?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing advanced laboratory equipment, including high-performance hot press systems. Our solutions are designed to help you create dense, structurally sound, and precision-finished products from composites and advanced materials.
Contact us today using the form below to discuss how our expertise and equipment can enhance your production capabilities and deliver the robust results your projects demand.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Heated Vacuum Press Machine Tube Furnace
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Electric Heated Hydraulic Vacuum Heat Press for Lab
People Also Ask
- What is the significance of precise temperature control in melt infiltration? Achieve High-Performance Li-Alloy Electrodes
- What are the primary advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace? Maximize Density in B4C-CeB6 Ceramics
- Why is a vacuum essential for sintering metal-ceramic composites? Achieve Pure, High-Density Results
- How does the uniaxial pressing function of a vacuum hot press furnace influence the microstructure of ZrC-SiC ceramics?
- What role does a high-temperature hot press play in the sintering of NITE-SiC? Optimize Your Densification Process



















