Vacuum brazing is a high-purity joining process that uses a specialized filler metal to fuse two or more base metals together inside a controlled vacuum furnace. By heating the assembly in a near-vacuum, the filler metal melts at a temperature lower than the base metals, flowing into the tight gaps between them to form an exceptionally clean, strong, and permanent bond upon cooling.
The core advantage of vacuum brazing is its ability to create superior metallurgical bonds without corrosive chemical fluxes. The vacuum environment itself prevents oxidation and actively cleans the component surfaces, resulting in a joint that is often stronger and more reliable than the base metals it joins.
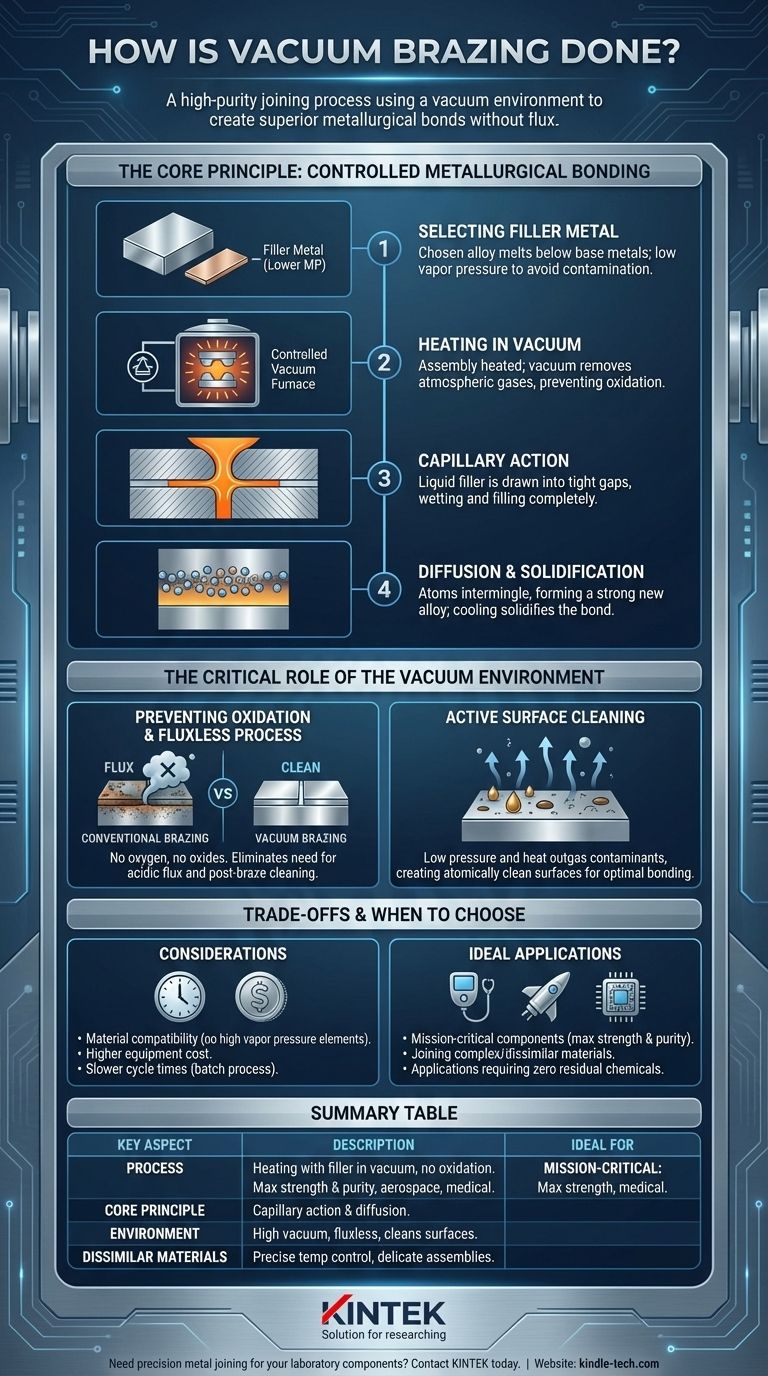
The Core Principle: Controlled Metallurgical Bonding
Vacuum brazing is a precise thermal and chemical process. Success depends on the interaction between the filler metal, the base metals, and the vacuum environment.
Selecting the Filler Metal
The process hinges on a filler metal (or brazing alloy) with a melting point significantly lower than the components being joined. This allows the filler to become liquid while the base metals remain solid.
These alloys are carefully chosen to ensure they do not contain elements with high vapor pressure, which could evaporate in the vacuum and contaminate the furnace and the final joint.
Capillary Action in the Joint
Once the filler metal melts, a natural phenomenon called capillary action takes over. The liquid alloy is drawn into the narrow, uniform gap between the closely-fitted base metal parts.
This action ensures the entire joint is wetted and filled completely, which is critical for achieving a void-free, high-strength bond.
Diffusion and Solidification
At the brazing temperature, atoms from the liquid filler metal begin to diffuse into the solid base metal surfaces, and vice versa. This intermingling creates a new, strong alloy at the joint interface.
As the assembly is carefully cooled, the filler metal solidifies, creating a continuous, solid metallurgical connection between the components.
The Critical Role of the Vacuum Environment
The use of a vacuum furnace is what fundamentally distinguishes this process from other brazing methods. The vacuum is not just an empty space; it is an active part of the process.
Preventing Oxidation
The primary function of the vacuum is to remove atmospheric gases, especially oxygen. Without oxygen present during the high-temperature heating cycle, no oxides can form on the metal surfaces.
This is why the process is fluxless. In conventional brazing, acidic flux is required to dissolve oxides, but the vacuum makes this step unnecessary, eliminating the risk of flux entrapment and post-braze corrosion.
Deoxidizing and Cleaning the Surface
A high vacuum does more than just prevent oxidation; it can actively clean the components. The combination of low pressure and high heat causes contaminants like trace oils and even some surface oxides to turn into a gas and be pumped away.
This "outgassing" effect results in atomically clean surfaces, which is the ideal condition for creating the strongest possible metallurgical bond.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While powerful, vacuum brazing is a specialized process with specific requirements and limitations that must be understood for successful application.
Filler Metal and Base Metal Compatibility
The selection of a filler alloy is critical. Using an alloy with elements like zinc, lead, or cadmium will cause them to evaporate in the vacuum, leading to poor joint quality and severe contamination of the expensive furnace equipment.
Similarly, some base materials are not suitable for vacuum brazing because they have high vapor pressures and may degrade under vacuum at elevated temperatures.
High Equipment and Process Costs
Vacuum furnaces represent a significant capital investment. The process itself is also more time-consuming than open-air methods due to the need to pump down the chamber, run precise heating and cooling profiles, and maintain the equipment.
Slower Cycle Times
The entire process—from loading and pumping down the vacuum to heating, soaking at temperature, and cooling—is inherently slower than most welding or torch brazing operations. This makes it better suited for batch production rather than single-piece flow.
When to Choose Vacuum Brazing
The decision to use vacuum brazing should be driven by the technical requirements of the final product.
- If your primary focus is maximum joint strength and purity: Vacuum brazing is the superior choice for mission-critical components in aerospace, medical, and high-performance electronics where joint integrity is non-negotiable.
- If your primary focus is joining complex or dissimilar materials: The process offers exceptionally precise and uniform temperature control, making it ideal for bonding delicate assemblies or materials with different thermal expansion rates.
- If your primary focus is eliminating post-braze cleaning: The fluxless nature of vacuum brazing produces finished parts that are bright and clean directly from the furnace, saving significant labor and preventing issues with residual chemicals.
By controlling the joining environment at a molecular level, vacuum brazing delivers a level of quality and reliability that conventional methods cannot easily match.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Process | Heating metal assembly with filler metal in a vacuum furnace to create a metallurgical bond without oxidation. |
| Core Principle | Controlled capillary action and diffusion of filler metal into base metals under vacuum. |
| Environment | High vacuum prevents oxidation, eliminates need for flux, and actively cleans surfaces. |
| Ideal For | Joining complex or dissimilar materials, mission-critical components requiring maximum strength and purity. |
| Considerations | Higher equipment cost, slower cycle times, requires compatible filler/base metals. |
Need precision metal joining for your laboratory components? KINTEK specializes in advanced thermal processing solutions, including vacuum brazing systems designed for superior metallurgical bonds. Our lab equipment ensures clean, strong, and reliable joints for aerospace, medical, and high-performance electronics applications. Contact us today to discuss how our vacuum brazing expertise can enhance your lab's capabilities and product quality!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the process of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Purity and Precision in High-Temp Processing
- Can you braze two different metals? Yes, and here’s how to do it successfully.
- What is the difference between welding and vacuum brazing? Choose the Right Joining Method for Your Project
- What metals can be joined by brazing? Discover the Versatility of Modern Brazing Techniques
- What are the factors that affect the strength of a brazed joint? Master the 4 Keys to a Perfect Bond



















