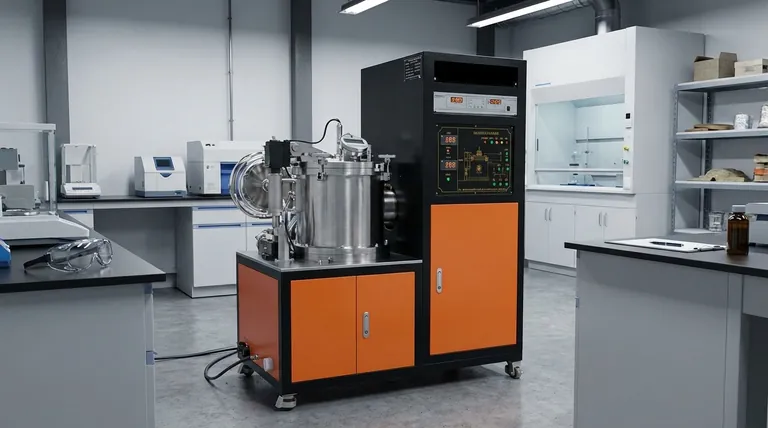
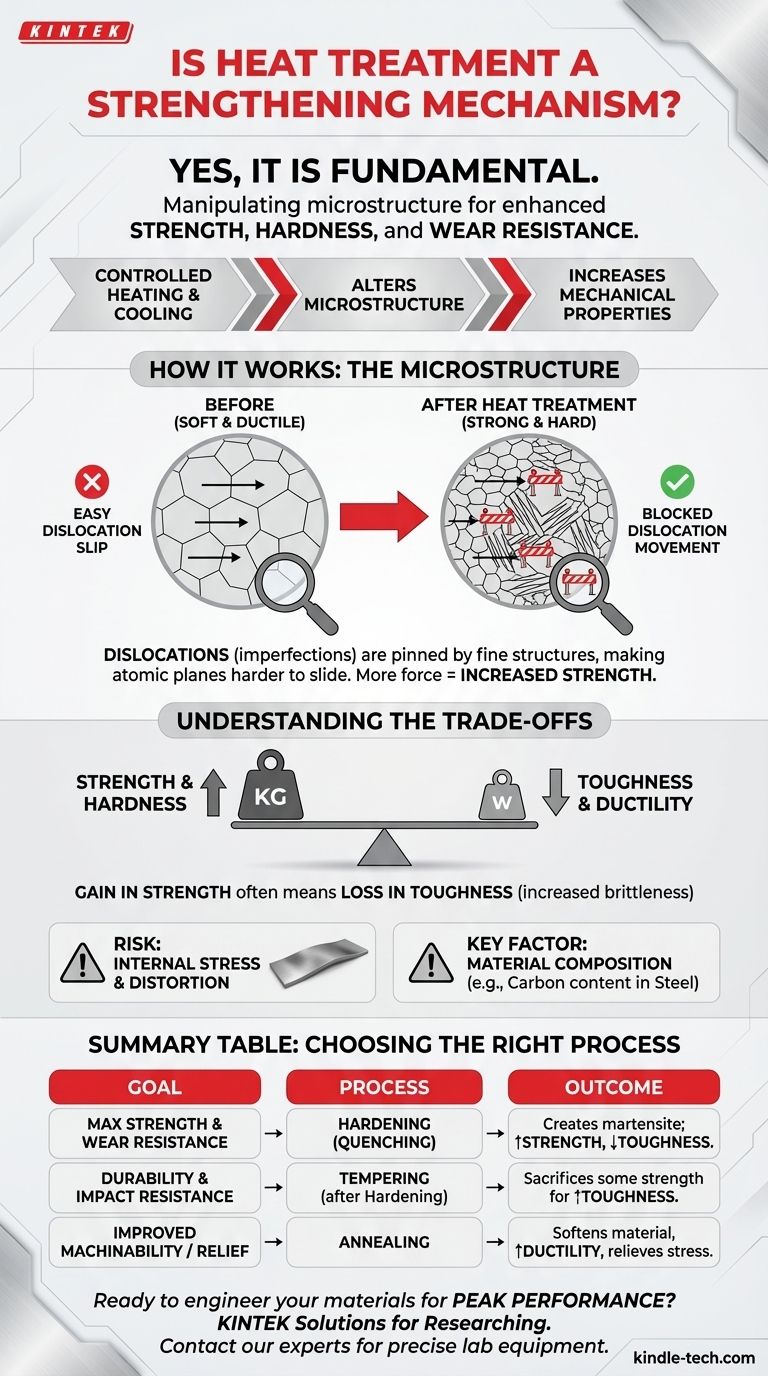
Yes, heat treatment is a fundamental strengthening mechanism for many materials, particularly for metals like steel. By precisely controlling cycles of heating and cooling, you can deliberately alter a material's internal crystal structure, or microstructure. This manipulation allows you to significantly increase key mechanical properties like strength, hardness, and wear resistance to meet specific engineering demands.
Heat treatment is not a single action but a set of controlled processes designed to manipulate a material's internal microstructure. While it is a powerful method for increasing strength and hardness, this gain is almost always achieved by trading off other properties, most notably ductility.

How Heat Treatment Fundamentally Increases Strength
The strength of a material is not an inherent, fixed value. It is a direct result of its internal structure at a microscopic level. Heat treatment is the tool used to engineer that structure.
The Role of Microstructure
Metals are composed of crystalline grains. The size, shape, and arrangement of these grains—the microstructure—dictate the material's mechanical properties. A coarse, uniform grain structure is typically softer and more ductile, while a fine, distorted structure is harder and stronger.
Creating Obstacles to Dislocation Movement
At the atomic level, a material deforms when planes of atoms slide over one another. These imperfections in the crystal lattice are called dislocations. Strength is essentially the material's resistance to this dislocation movement.
Heat treatment processes like hardening create new, very fine and hard microstructures (such as martensite in steel). These structures act as microscopic roadblocks, pinning dislocations and making it much more difficult for atomic planes to slide. More force is then required to deform the material, which we perceive as increased strength.
The Example of Transformation Hardening
Transformation-hardened steels, which rely on carbon and manganese, are a perfect example. Heating the steel allows carbon atoms to dissolve uniformly into the iron crystal lattice.
When the steel is cooled rapidly (a process called quenching), the carbon atoms are trapped. This creates a highly strained and distorted crystal structure—martensite—that is exceptionally hard and strong.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Heat treatment is not a "free lunch." The significant gains in one property often come at the expense of another. Understanding these compromises is critical for successful engineering.
The Strength vs. Toughness Balance
The most common trade-off is between strength and toughness. Hardening a material to increase its strength almost always reduces its ductility and toughness, making it more brittle.
A highly hardened part may resist scratching and wear, but it might shatter like glass under a sudden impact instead of bending. This is why hardened parts are often subsequently tempered—a secondary heat treatment that sacrifices some strength to regain essential toughness.
Risk of Internal Stress and Distortion
The rapid cooling involved in quenching is a thermally violent process. It can introduce significant internal stresses within the material as different sections of the part cool and contract at different rates.
These stresses can cause the part to warp, distort, or even crack during or after treatment. This risk must be carefully managed through process control and proper part design.
Material Composition is Key
Heat treatment is not a universal solution. A material's ability to be strengthened is highly dependent on its chemical composition. For steels, the carbon content is the single most important factor determining its "hardenability." Low-carbon steels cannot be significantly strengthened by heat treatment alone.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The right heat treatment process is determined entirely by the final application's requirements.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength and wear resistance: A hardening process like quenching is the correct path, but you must be prepared to manage the resulting brittleness.
- If your primary focus is durability and preventing sudden failure: Tempering after hardening is non-negotiable, as it sacrifices some peak strength for a crucial increase in toughness.
- If your primary focus is machinability or relieving stress after welding: An annealing process is used to soften the material and improve its ductility, even though this reduces its strength.
Ultimately, heat treatment empowers you to engineer a material's properties, turning a standard metal into a high-performance component tailored for a specific task.
Summary Table:
| Goal | Recommended Heat Treatment Process | Key Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum Strength & Wear Resistance | Hardening (Quenching) | Creates hard martensite; increases strength but reduces toughness. |
| Durability & Impact Resistance | Tempering (after Hardening) | Sacrifices some strength to regain crucial toughness. |
| Improved Machinability / Stress Relief | Annealing | Softens material, improves ductility, and relieves internal stresses. |
Ready to engineer your materials for peak performance?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables needed for effective heat treatment processes. Whether you are developing high-strength components or require durable materials for demanding applications, our expertise and products support your goals for superior material properties.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can help you achieve the perfect balance of strength, hardness, and toughness for your specific laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What are the three main heat treatments? Mastering Annealing, Hardening & Tempering
- How does heat treatment process work? Tailor Material Properties for Your Application
- What are the four types of heat treating processes? Master Annealing, Normalizing, Hardening, and Tempering
- What are the different types of heat treatment process for steel? Tailor Strength, Hardness & Toughness
- What is a vacuum heat treatment furnace? The Ultimate Guide to Controlled Atmosphere Processing



















