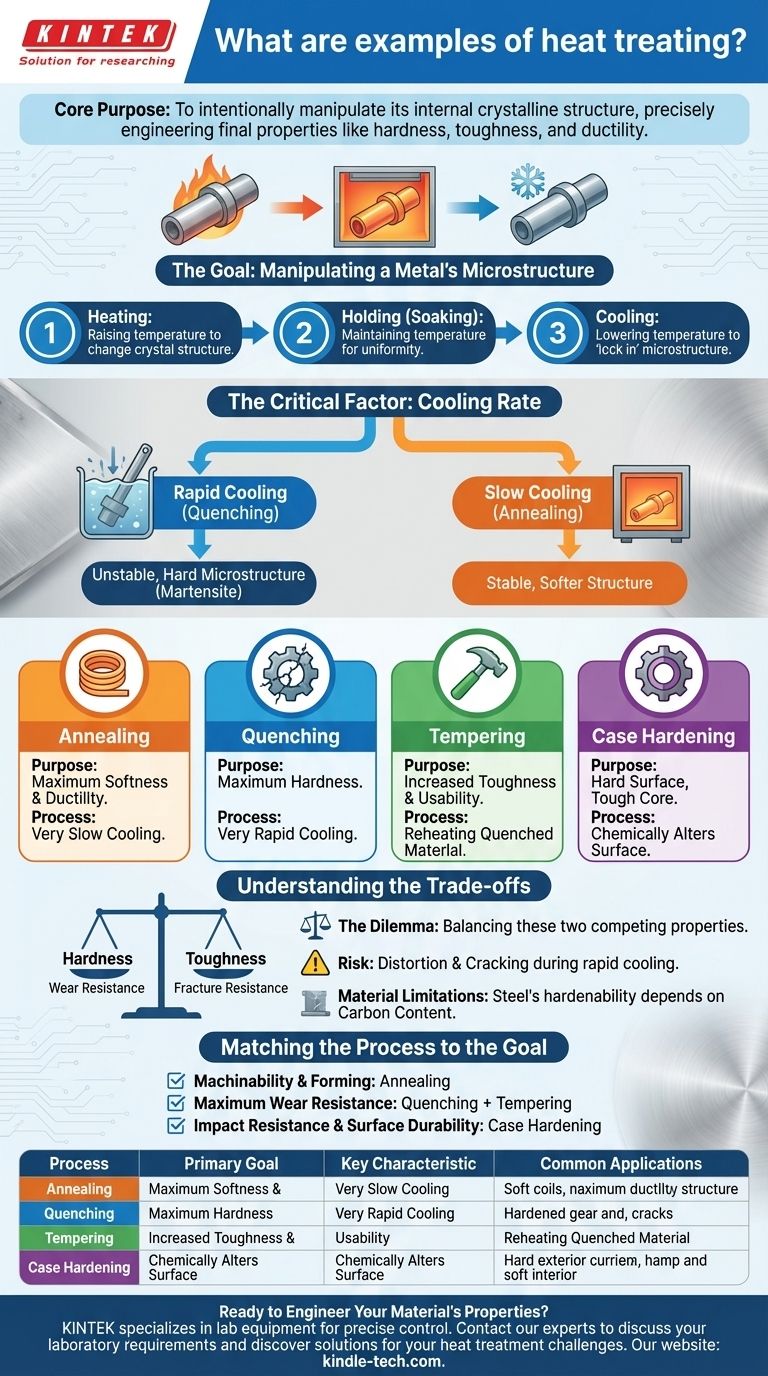
The most common examples of heat treating are annealing, quenching, tempering, and case hardening. Each process involves a precise cycle of heating, holding, and cooling a metal, but they use different temperatures, times, and cooling rates to achieve fundamentally different results—from making a metal extremely soft to making it incredibly hard and durable.
The core purpose of heat treatment is not simply to heat metal, but to intentionally manipulate its internal crystalline structure. By carefully controlling the thermal cycle, you can precisely engineer a material's final properties, such as its hardness, toughness, and ductility, to match the demands of a specific application.

The Goal: Manipulating a Metal's Microstructure
Every heat treatment process is designed to change the physical properties of a material. This is accomplished by altering its microscopic crystal structure, or "microstructure." The three stages of the process are the levers used to control this transformation.
The Three Levers of Control
Based on the foundational principle of heat treatment, every process is a function of three variables:
- Heating: Raising the material to a specific temperature to initiate a change in its crystal structure.
- Holding (Soaking): Keeping the material at that temperature for a set duration to ensure the change is uniform throughout the part.
- Cooling: Lowering the temperature at a specific rate to "lock in" the desired microstructure and its corresponding physical properties.
Why Cooling Rate is the Critical Factor
While all three steps are important, the speed of cooling is often the most critical variable that distinguishes one process from another. A rapid cooling cycle traps unstable, hard microstructures, while a slow cooling cycle allows for the formation of stable, softer structures.
Key Heat Treatment Processes and Their Purpose
Understanding the goal of each process is key to selecting the right one. Each example below uses the same levers—heat, hold, cool—to produce a unique outcome.
Annealing: For Maximum Softness and Ductility
Annealing is a process that makes a metal as soft and workable as possible. It involves heating the material and then cooling it very slowly, often by leaving it in the furnace to cool down over many hours.
This slow cool relieves internal stresses and allows the microstructure to form in its most stable, ordered, and softest state. It's often used to prepare a metal for machining or extensive forming.
Quenching: For Maximum Hardness
Quenching is the exact opposite of annealing. The goal is to make steel extremely hard. After heating, the part is cooled as rapidly as possible by plunging it into a liquid like water, brine, or oil.
This sudden cooling traps the crystal structure in a very hard but brittle state known as martensite. A quenched part is highly resistant to wear and abrasion but is too brittle for most practical uses without a follow-up process.
Tempering: For Toughness and Usability
Tempering is almost always performed after quenching. The process involves reheating the hardened part to a much lower temperature and holding it for a specific time.
This gentle reheating relieves the internal stresses from quenching and allows some of the brittle martensite to transform into a tougher structure. Tempering reduces some of the hardness gained during quenching but adds a significant amount of toughness, preventing the part from shattering under impact.
Case Hardening: For a Hard Surface and a Tough Core
Case hardening (or surface hardening) is a specialized set of processes, like carburizing, used to create a part with two different sets of properties. The surface of the material is chemically altered, typically by adding carbon, and then the part is quenched and tempered.
The result is an object with an extremely hard, wear-resistant outer "case" while maintaining a softer, more ductile, and shock-absorbent inner "core." This is ideal for components like gears and bearings that must endure surface friction while resisting impact.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a heat treatment process is always a matter of balancing competing properties. You cannot maximize every desirable trait at once.
The Hardness vs. Toughness Dilemma
The most fundamental trade-off in heat treating is between hardness (resistance to wear and scratching) and toughness (resistance to fracture or chipping). A fully quenched part is extremely hard but will shatter like glass. Tempering is the art of finding the perfect balance between these two properties for a given application.
The Risk of Distortion and Cracking
Rapid cooling from high temperatures induces immense internal stress in a material. This stress can cause parts, especially those with complex geometries, to warp, distort, or even crack during the quenching process. Proper technique and part design are essential to mitigate this risk.
Material Limitations
Not all metals are suitable for all heat treatments. For steel, the ability to be significantly hardened is directly related to its carbon content. Low-carbon steels cannot be effectively hardened through simple quenching and tempering, which is why processes like case hardening were developed for them.
Matching the Process to the Goal
Your choice of heat treatment should be driven entirely by the final performance requirements of the component.
- If your primary focus is machinability and forming: You need annealing to soften the material and relieve internal stresses before you begin work.
- If your primary focus is maximum wear resistance: You need quenching for extreme hardness, followed by a low-temperature temper to reduce brittleness without sacrificing too much hardness.
- If your primary focus is impact resistance and surface durability: You need case hardening to create a component with a tough, shock-absorbing core and a hard-wearing exterior.
Ultimately, heat treatment transforms a standard metal into a high-performance material engineered for a specific task.
Summary Table:
| Process | Primary Goal | Key Characteristic | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Annealing | Maximum Softness & Ductility | Very Slow Cooling | Preparing metal for machining/forming |
| Quenching | Maximum Hardness | Very Rapid Cooling | Creating wear-resistant surfaces |
| Tempering | Increased Toughness | Reheating Quenched Material | Reducing brittleness after quenching |
| Case Hardening | Hard Surface, Tough Core | Chemically Alters Surface | Gears, bearings, components needing surface durability |
Ready to Engineer Your Material's Properties?
Choosing the right heat treatment process is critical for achieving the perfect balance of hardness, toughness, and durability for your components. The precise control of temperature and cooling rates required for processes like annealing, quenching, and tempering demands reliable, high-performance lab equipment.
KINTEK specializes in the lab equipment and consumables you need to perfect your heat treatment workflows. Whether you are developing new alloys or ensuring quality control in production, our products provide the accuracy and consistency essential for success.
Let us help you transform your materials. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific laboratory requirements and discover the right solutions for your heat treatment challenges.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is a high-temperature furnace utilized for SAPO-34 membrane alumina supports? Achieve 950°C Precision
- What is the purpose of using a heat treatment furnace for SiCp/2024Al composites? Master Microstructural Engineering
- What is the function of a resistance furnace in the preparation of ultrafine metallic uranium powder? Guide to HDH.
- What is the purpose of a laboratory vacuum drying oven in catalyst post-processing? Preserve Activity & Pore Structure
- How does arc melting equipment facilitate the preparation of refractory multi-principal element alloys (RMPEAs)?
- Why are glove boxes or vacuum equipment indispensable for ZrO2-Li2ZrCl6 preparation? Protect Air-Sensitive Materials
- What happens if sintering temperature is too high? Avoid Irreversible Damage to Your Parts
- How do high-temperature reaction furnaces control in-situ MMCs? Master Material Precision and Structural Integrity



















