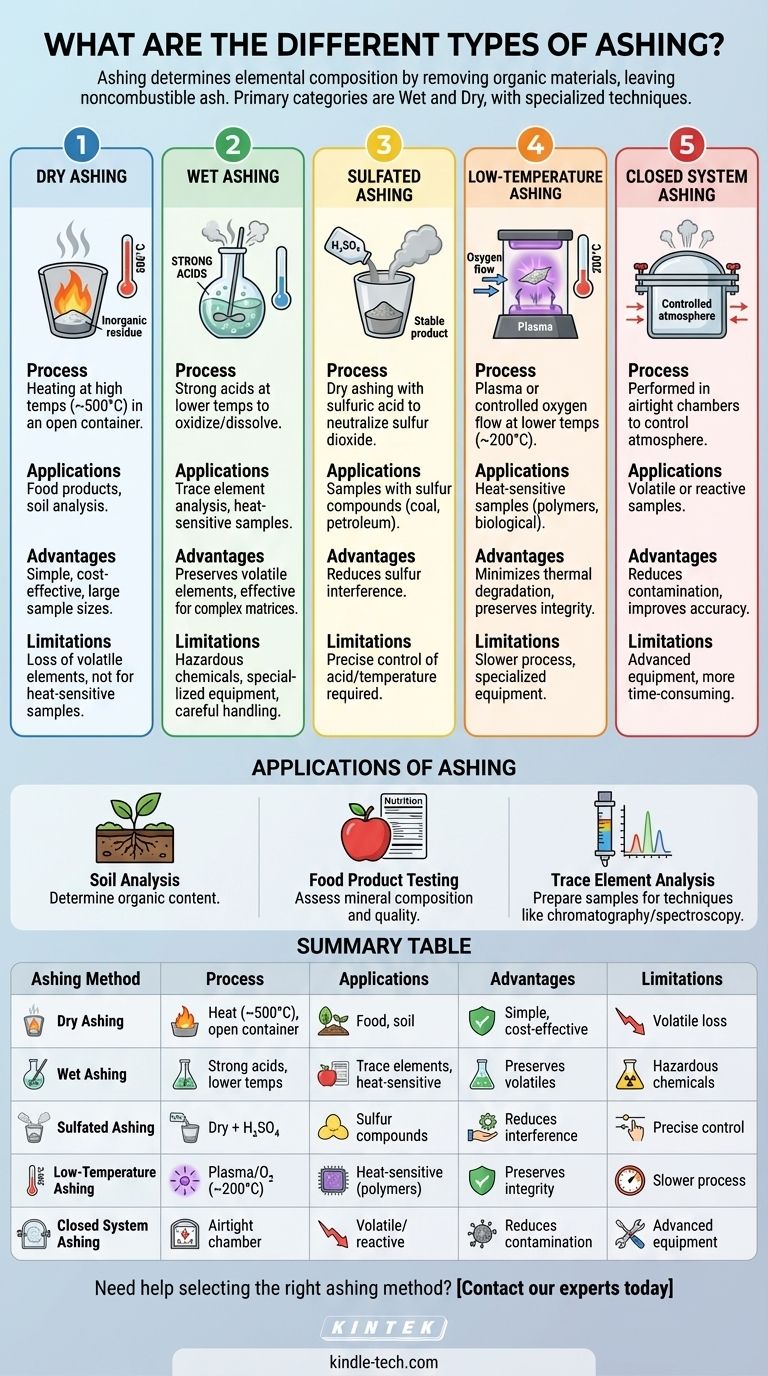
Ashing is a critical process in analytical chemistry used to determine the elemental composition of a sample by removing organic materials and leaving behind noncombustible ash. The two primary categories of ashing are wet ashing and dry ashing, but several specialized techniques also exist, such as sulfated ashing, low-temperature ashing, and closed system ashing. Each method has unique applications, advantages, and limitations, depending on the sample type, analysis requirements, and desired outcomes. This answer explores the different types of ashing, their processes, and their specific uses in various fields, such as soil analysis and food product testing.

Key Points Explained:
-
Dry Ashing
- Process: Dry ashing involves heating a sample in an open container at high temperatures (typically around 500°C) to burn off organic materials, leaving behind inorganic ash.
- Applications: Commonly used for analyzing food products, soil samples, and other materials where high-temperature decomposition is acceptable.
- Advantages: Simple, cost-effective, and suitable for large sample sizes.
- Limitations: May result in the loss of volatile elements and is not ideal for samples sensitive to high temperatures.
-
Wet Ashing
- Process: Wet ashing uses strong acids (e.g., nitric acid, sulfuric acid) at lower temperatures to oxidize and dissolve organic materials, leaving behind inorganic residues.
- Applications: Ideal for samples that cannot withstand high temperatures or for trace element analysis.
- Advantages: Preserves volatile elements and is effective for complex matrices.
- Limitations: Requires hazardous chemicals, specialized equipment, and careful handling.
-
Sulfated Ashing
- Process: A variation of dry ashing where sulfuric acid is added to the sample to neutralize and remove sulfur dioxide, converting sulfates into stable ash.
- Applications: Useful for samples containing sulfur compounds, such as coal or petroleum products.
- Advantages: Reduces sulfur interference in ash analysis.
- Limitations: Requires precise control of acid addition and temperature.
-
Low-Temperature Ashing
- Process: Conducted at lower temperatures (around 200°C) using plasma or controlled oxygen flow to oxidize organic materials gently.
- Applications: Suitable for heat-sensitive samples, such as polymers or biological materials.
- Advantages: Minimizes thermal degradation and preserves sample integrity.
- Limitations: Slower process and requires specialized equipment.
-
Closed System Ashing
- Process: Performed in airtight chambers to control the atmosphere, preventing contamination and loss of volatile elements.
- Applications: Used for precise analysis of volatile or reactive samples.
- Advantages: Reduces contamination and improves accuracy.
- Limitations: Requires advanced equipment and is more time-consuming.
-
Applications of Ashing
- Soil Analysis: Used to determine the organic content of soil by comparing mass before and after ashing.
- Food Product Testing: Measures ash content to assess mineral composition and quality.
- Trace Element Analysis: Prepares samples for techniques like chromatography or spectroscopy by removing organic interference.
Each ashing method has specific use cases and is chosen based on the sample type, analysis requirements, and desired outcomes. Understanding these differences helps in selecting the most appropriate technique for accurate and reliable results.
Summary Table:
| Ashing Method | Process | Applications | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dry Ashing | Heating at high temperatures (~500°C) in an open container. | Food products, soil analysis. | Simple, cost-effective, suitable for large samples. | Loss of volatile elements; not ideal for heat-sensitive samples. |
| Wet Ashing | Uses strong acids at lower temperatures to oxidize organic materials. | Trace element analysis, heat-sensitive samples. | Preserves volatile elements; effective for complex matrices. | Requires hazardous chemicals and specialized equipment. |
| Sulfated Ashing | Dry ashing with sulfuric acid to neutralize sulfur dioxide. | Samples with sulfur compounds (e.g., coal, petroleum). | Reduces sulfur interference. | Requires precise control of acid addition and temperature. |
| Low-Temperature Ashing | Uses plasma or controlled oxygen flow at ~200°C. | Heat-sensitive samples (e.g., polymers, biological materials). | Minimizes thermal degradation; preserves sample integrity. | Slower process; requires specialized equipment. |
| Closed System Ashing | Performed in airtight chambers to control the atmosphere. | Volatile or reactive samples. | Reduces contamination; improves accuracy. | Requires advanced equipment; more time-consuming. |
Need help selecting the right ashing method for your analysis? Contact our experts today!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between a muffle furnace and a blast furnace? Precision vs. Production
- What is the body structure of a furnace? Unlocking the Dual-Layer Design for Superior Thermal Control
- What is the inside material of a muffle furnace? Choose the Right Lining for Your Application
- Why is ceramic used in making furnace? Achieve Superior Heat Resistance and Efficiency
- What is the temperature of furnace exhaust? A Key Indicator of Efficiency and Safety



















