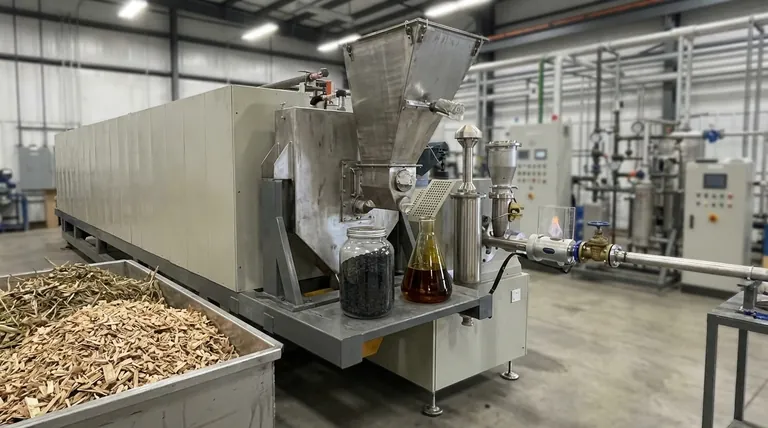
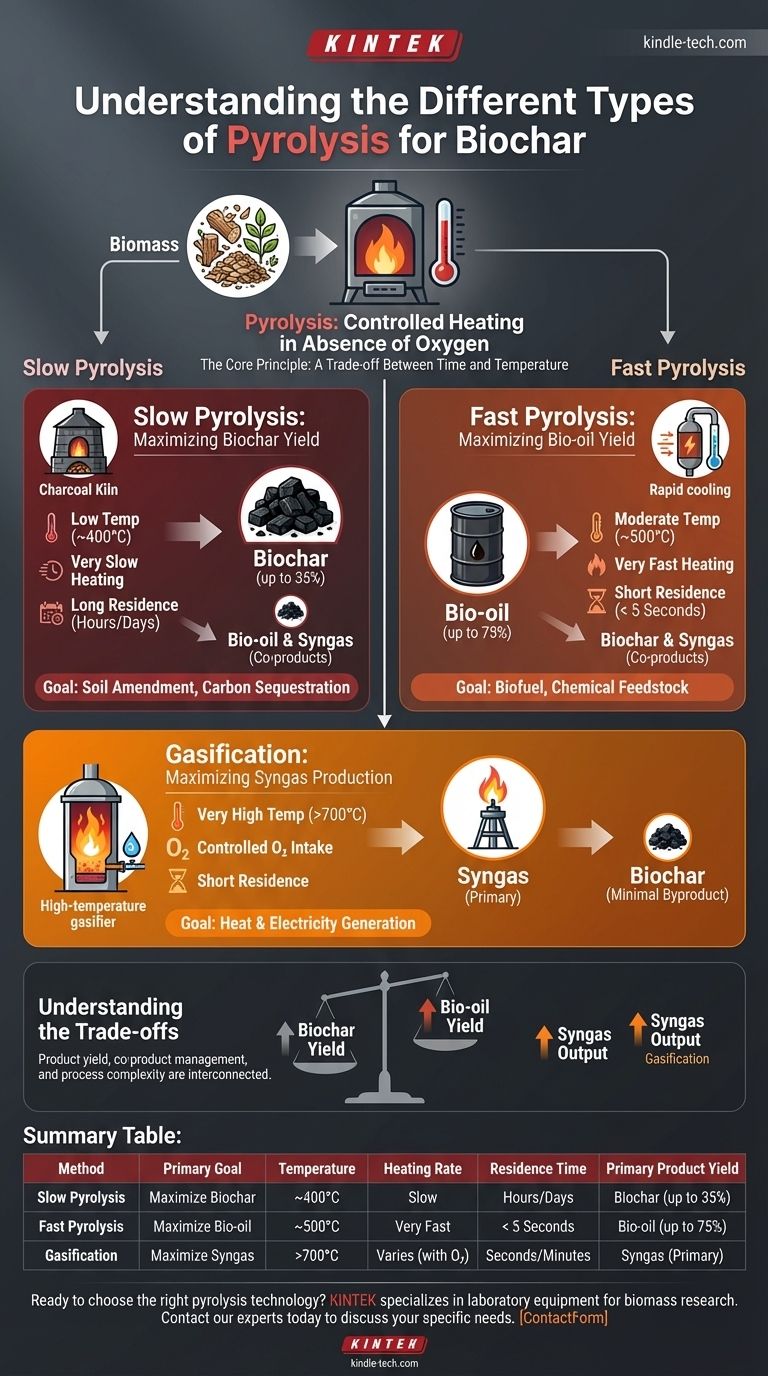
To produce biochar, the primary methods involve variations of pyrolysis, a process of heating biomass in the absence of oxygen. The main types are slow pyrolysis, which is optimized for maximum biochar yield, and fast pyrolysis, which prioritizes the production of liquid bio-oil, with biochar as a co-product. Gasification is another related thermal process, but it uses very high temperatures and a controlled amount of oxygen to primarily produce flammable gas.
The choice between pyrolysis methods is not about which is "better," but about defining your primary goal. The process conditions—specifically temperature, heating rate, and time—are deliberately manipulated to maximize the yield of one specific output: solid biochar, liquid bio-oil, or combustible gas.

The Core Principle: A Trade-off Between Time and Temperature
Think of pyrolysis as a controlled form of "cooking" for biomass. Just as different cooking methods produce different results from the same ingredients, different pyrolysis methods break down biomass into distinct products.
The key variables are heating rate (how fast the temperature rises) and residence time (how long the biomass is held at the target temperature). Manipulating these dictates whether the complex organic molecules in the biomass break down into solid carbon (biochar), condensable liquids (bio-oil), or non-condensable gases (syngas).
Decoding the Pyrolysis Methods
Each method is optimized to favor a specific chemical reaction pathway, resulting in a different primary product.
Slow Pyrolysis: Maximizing Biochar Yield
Slow pyrolysis is the traditional method for making charcoal. It uses relatively low temperatures (around 400°C) and very slow heating rates over several hours or even days.
This long residence time allows for secondary char-forming reactions to occur, maximizing the conversion of biomass into a stable, solid carbon structure. This process yields the highest amount of biochar (up to 35% by weight).
Fast Pyrolysis: Maximizing Bio-oil Yield
Fast pyrolysis is engineered for a completely different outcome. It uses moderate temperatures (around 500°C) but an extremely high heating rate and a very short residence time (typically less than 5 seconds).
These conditions rapidly break down the biomass, and the resulting vapors are cooled just as quickly. This "flash" process prevents the secondary reactions that form char, thereby maximizing the yield of liquid bio-oil, which can be up to 75% of the product volume. Biochar is still produced, but as a smaller co-product.
Gasification: Maximizing Syngas Production
Though sometimes grouped with pyrolysis, gasification is distinct because it introduces a small, controlled amount of oxygen. It operates at very high temperatures (over 700°C).
The goal here is not to create solids or liquids, but to convert nearly all the biomass into non-condensable combustible gases, collectively known as syngas (synthesis gas). Biochar is a minimal byproduct in this energy-focused process.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a method requires acknowledging the inherent compromises in process complexity and product handling.
Yield vs. Desired Output
The most fundamental trade-off is in product yield. You cannot maximize the output of biochar, bio-oil, and syngas simultaneously. Your primary goal dictates the process, which in turn determines your primary product and secondary co-products.
Co-Product Management
Each process creates a unique set of outputs that must be managed. Slow pyrolysis produces less bio-oil and gas, simplifying collection. Fast pyrolysis, however, requires a robust system to condense, collect, and store large volumes of corrosive bio-oil and wood vinegar.
Process Complexity and Cost
Slow pyrolysis systems can be relatively simple and low-cost, aligning with their historical use in charcoal production. In contrast, the ultra-high heating rates and short residence times of fast pyrolysis demand more sophisticated, precisely controlled, and therefore more expensive engineering and equipment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The optimal method is entirely dependent on your intended application.
- If your primary focus is soil amendment or carbon sequestration: Slow pyrolysis is the ideal choice as it is specifically designed to maximize the yield of stable, solid biochar.
- If your primary focus is producing liquid biofuel or chemical feedstocks: Fast pyrolysis is the correct pathway, as its entire process is engineered to maximize the output of bio-oil.
- If your primary focus is generating on-site heat or electricity: Gasification is the most direct method for converting biomass into a combustible syngas for immediate energy use.
Ultimately, aligning your chosen technology with your end-product goal is the most critical step toward a successful outcome.
Summary Table:
| Method | Primary Goal | Temperature | Heating Rate | Residence Time | Primary Product Yield |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Slow Pyrolysis | Maximize Biochar | ~400°C | Slow | Hours/Days | Biochar (up to 35%) |
| Fast Pyrolysis | Maximize Bio-oil | ~500°C | Very Fast | < 5 Seconds | Bio-oil (up to 75%) |
| Gasification | Maximize Syngas | >700°C | Varies | Seconds/Minutes | Syngas (Primary) |
Ready to choose the right pyrolysis technology for your biochar, bio-oil, or syngas project?
KINTEK specializes in laboratory equipment and consumables for biomass research and development. Whether you are optimizing slow pyrolysis for soil amendment or scaling up fast pyrolysis for biofuel production, our expertise and robust equipment can help you achieve precise, reliable results.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific needs and discover how KINTEK can support your laboratory's success in thermal conversion technology.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
People Also Ask
- How does precision temperature control impact TiAl alloy sintering? Master Microstructure Development
- What is the drying zone in a rotary kiln? Boost Efficiency with Modern Drying Solutions
- What are the equipment for pyrolysis laboratory? Choosing the Right Reactor for Your Research
- How is the operational mode of bed motion selected for a rotary kiln? Optimize Heat Transfer and Material Homogeneity
- What are the zones in rotary kiln in cement production? Master the Core Process for High-Quality Clinker



















