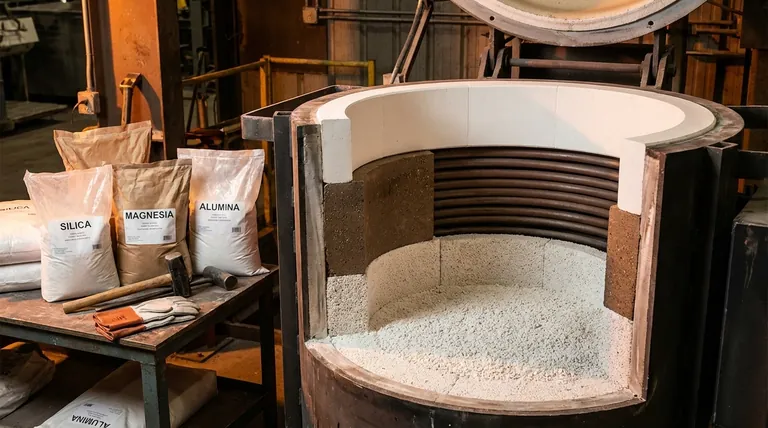
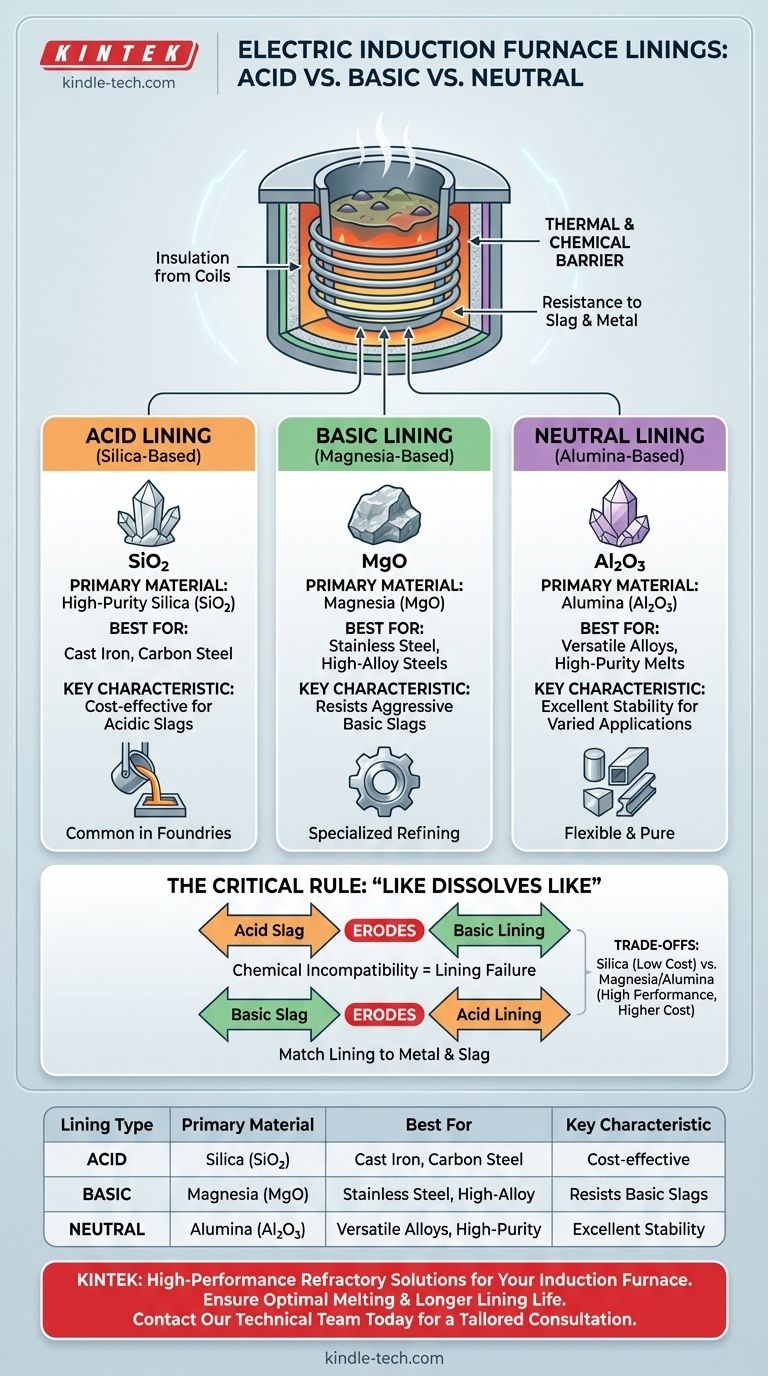
The primary material for an acid lining in an induction furnace is high-purity **silica (SiO₂) **, while the primary material for a basic lining is magnesia (MgO). Neutral linings, which offer a compromise between the two, are typically made from alumina (Al₂O₃) or chrome-magnesia compounds.
The choice of lining material is not arbitrary; it is a critical decision dictated by the fundamental chemistry of the metal being melted and the slag it produces. Selecting a lining that is chemically incompatible with the molten charge will lead to rapid erosion, contamination of the melt, and potential furnace failure.

The Critical Role of the Refractory Lining
The lining in an induction furnace is more than just a container. It serves as a crucial thermal and chemical barrier.
### A Thermal Barrier
The lining must withstand extreme temperatures, often well over 1600°C (2900°F), without melting or deforming. It insulates the water-cooled copper induction coils from the intense heat of the molten metal.
### A Chemical Barrier
This is the most important function. The lining must be chemically resistant to the specific type of molten metal and, more importantly, the slag that forms on its surface. Slag is a byproduct of the melting process that contains impurities and oxides.
A Breakdown of Lining Materials
Lining materials are categorized by their chemical properties—acid, basic, or neutral—which determines their application.
### Acid Linings (Silica-Based)
An acid lining is primarily composed of high-purity silica (SiO₂), often installed as a dry-vibrated mix using a material like quartzite.
These linings are highly effective and cost-efficient for melting metals that produce an acidic slag, which is high in silica content. This makes them the standard choice for most cast iron and carbon steel foundries.
### Basic Linings (Magnesia-Based)
A basic lining uses magnesia (MgO) as its primary component, sometimes mixed with other minerals like chrome ore.
These are required when melting metals that produce a basic slag, which is rich in oxides like calcium oxide (CaO) and magnesium oxide (MgO). This is typical for high-alloy steels, stainless steels, and special steels where specific refining processes are needed.
### Neutral Linings (Alumina-Based)
Neutral linings are predominantly made from alumina (Al₂O₃). Materials like chrome-magnesia can also fall into this category.
They offer excellent chemical stability against both acid and basic slags, making them highly versatile. They are often used for a wide variety of ferrous and non-ferrous metals, especially in applications demanding high purity or when melting different types of alloys in the same furnace.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The decision between acid, basic, and neutral linings involves balancing chemical compatibility, operational temperature, and cost.
### The Acid-Base Reaction Rule
The core principle is simple: "like dissolves like." An acidic slag will rapidly attack and erode a basic lining, and a basic slag will do the same to an acidic lining.
This chemical reaction is the primary cause of lining failure. Choosing the correct chemical type for your specific melting process is non-negotiable for ensuring a reasonable service life.
### Cost vs. Performance
Silica-based acid linings are generally the most economical option. Their combination of low cost and good performance for common ferrous metals makes them a popular choice.
Magnesia and alumina-based linings are significantly more expensive. However, their superior chemical resistance and higher service temperatures are essential for producing specialized, high-quality alloys, justifying the higher investment.
### Installation and Safety
Each lining type has specific installation procedures (e.g., dry ramming, casting) and requires a carefully controlled initial heating schedule, known as sintering, to form a solid, crack-free crucible. Improper installation is a common cause of premature failure.
Matching the Lining to Your Metal
Your choice must be driven by the specific metallurgical process you are running.
- If your primary focus is melting standard cast iron or carbon steels: A silica-based acid lining is the most common and cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is melting high-alloy, stainless, or special steels: A magnesia-based basic lining is essential to resist the chemically aggressive basic slag produced.
- If your primary focus is versatility for various alloys or high-purity melts: A neutral alumina-based lining offers the best overall performance and chemical resistance, justifying its higher cost.
Ultimately, the right refractory lining protects your equipment, ensures the purity of your product, and is fundamental to a safe and efficient melting operation.
Summary Table:
| Lining Type | Primary Material | Best For | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acid Lining | Silica (SiO₂) | Cast Iron, Carbon Steel | Cost-effective for acidic slags |
| Basic Lining | Magnesia (MgO) | Stainless Steel, High-Alloy Steels | Resists aggressive basic slags |
| Neutral Lining | Alumina (Al₂O₃) | Versatile Alloys, High-Purity Melts | Excellent stability for varied applications |
Selecting the correct furnace lining is critical for efficiency, safety, and product purity.
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including refractory solutions for electric induction furnaces. Our experts can help you choose the ideal lining material—whether silica, magnesia, or alumina—to match your specific metal chemistry, ensuring longer lining life, reduced contamination, and optimal melting performance for your laboratory or foundry.
Ensure your next melt is a success. Contact our technical team today for a consultation tailored to your laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the primary advantage of using a tube furnace? Achieve Superior Temperature and Atmosphere Control
- Why is a horizontal alumina tube furnace ideal for mixed gas corrosion at 650 °C? Ensure Pure Experimental Integrity
- What are the applications of tube furnace? Unlock Precise High-Temperature Processing
- What tube is used for tubular furnace? Choose the Right Material for Temperature & Atmosphere
- What happens when quartz is heated? A Guide to Its Critical Phase Transitions and Uses



















