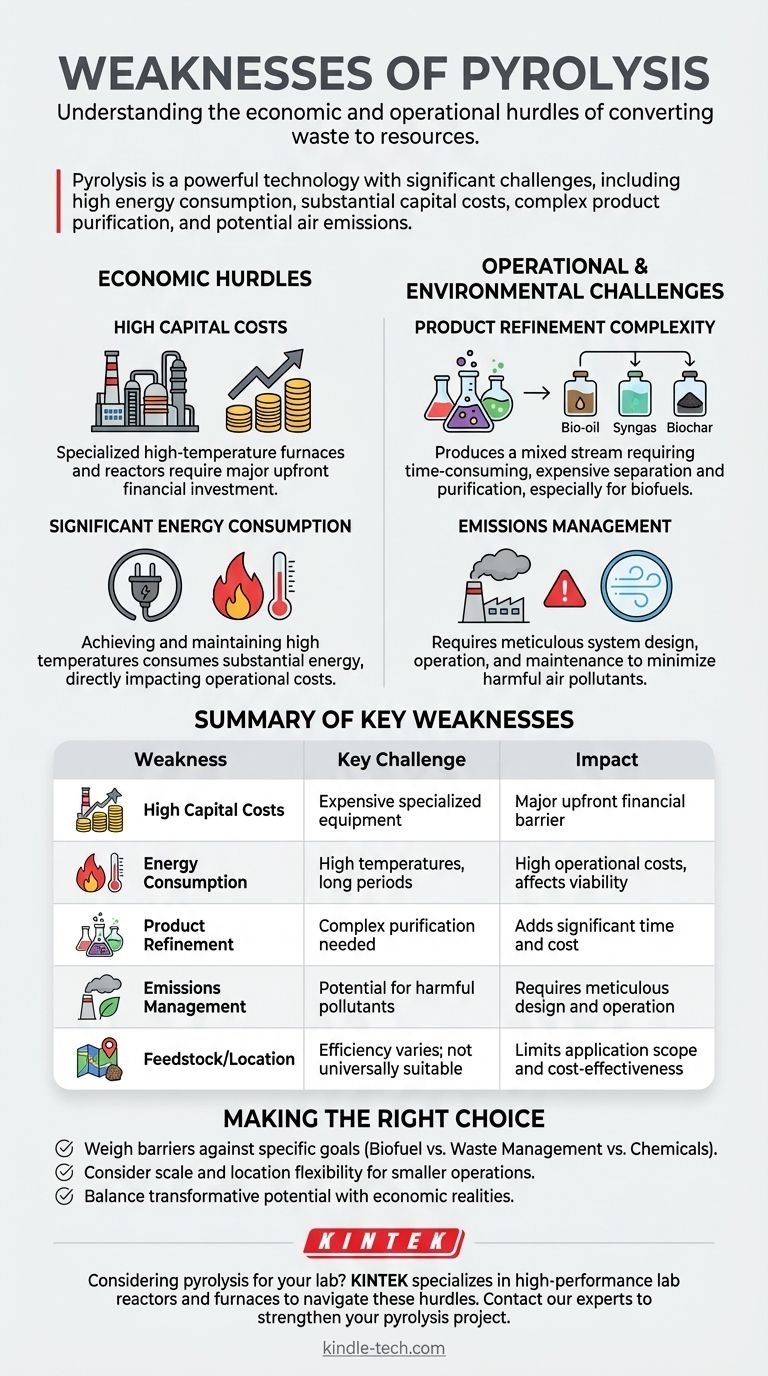
At its core, pyrolysis is a powerful technology that is fundamentally challenged by significant economic and operational hurdles. The primary weaknesses are its high energy consumption, substantial capital costs for equipment, the necessity for complex and expensive purification of its end-products, and the potential for harmful air emissions if not managed meticulously.
While pyrolysis offers a compelling method for converting waste into valuable resources, its practical implementation is often constrained by high upfront investment and the operational costs associated with energy use and product refinement.

The Economic Hurdles of Pyrolysis
The most significant barriers to the widespread adoption of pyrolysis are financial. The technology demands considerable investment in both initial setup and ongoing operations.
High Capital Costs
The specialized equipment required for pyrolysis, including high-temperature furnaces and reactors, is expensive. The initial capital outlay for constructing and installing a pyrolysis plant represents a major financial commitment.
Significant Energy Consumption
The process itself is energy-intensive. Achieving and maintaining the high temperatures necessary for pyrolysis, often over long residence times, consumes a substantial amount of energy, which directly impacts the operational cost and overall economic viability.
The Challenge of Product Refinement
Pyrolysis does not produce a single, ready-to-use product. Instead, it creates a mixed stream of bio-oil, syngas, and biochar that requires further processing.
This separation and purification can be both time-consuming and expensive. For instance, the liquid bio-oil often needs significant refining before it can be used as a transportation fuel, adding another layer of cost and complexity.
Operational and Environmental Challenges
Beyond the economics, practical and environmental factors can limit the application of pyrolysis.
Managing Harmful Emissions
The process involves high temperatures in an oxygen-starved environment, which can produce emissions that negatively impact air quality. Proper design, diligent operation, and consistent maintenance of the system are absolutely essential to minimize these emissions and ensure the process is environmentally sound.
Feedstock and Location Constraints
Pyrolysis is not a universal solution for all types of organic waste or for all locations. The efficiency and output can vary based on the feedstock, and the overall process may not be suitable or cost-effective for certain materials or geographic areas.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Despite these weaknesses, it is crucial to view them in the context of the technology's potential benefits. Pyrolysis remains a valuable tool for specific applications.
A Powerful Tool, Despite Its Flaws
The ability to convert organic waste into valuable biofuels, chemicals, and other materials is a significant advantage. It reduces landfill waste, offers alternatives to fossil fuels, and enables the recovery of resources from materials like plastics and rubber.
Scalability and Flexibility
Pyrolysis systems can be designed for relatively small-scale operations in remote locations. This flexibility allows for the conversion of biomass into an easily stored and transported liquid fuel, which can reduce handling costs and enhance local energy security.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The weaknesses of pyrolysis are not absolute barriers but are critical factors to weigh against your specific objectives.
- If your primary focus is large-scale biofuel production: The high capital costs and the expense of refining bio-oil will be the most significant hurdles to overcome for commercial viability.
- If your primary focus is localized waste management: Pyrolysis can be an excellent option, especially where waste transport costs are high, but the initial capital investment remains a key consideration.
- If your primary focus is creating high-value chemicals: Your economic model must heavily account for the complex and costly separation and purification processes required to isolate your target products.
Ultimately, successfully implementing pyrolysis requires a clear-eyed assessment that balances its transformative potential against these very real economic and operational challenges.
Summary Table:
| Weakness | Key Challenge | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| High Capital Costs | Expensive specialized equipment (reactors, furnaces) | Major upfront financial barrier |
| Energy Consumption | High temperatures required over long periods | High operational costs, affects viability |
| Product Refinement | Complex purification needed for bio-oil, syngas, char | Adds significant time and cost |
| Emissions Management | Potential for harmful air pollutants | Requires meticulous system design and operation |
| Feedstock/Location | Efficiency varies; not universally suitable | Limits application scope and cost-effectiveness |
Considering pyrolysis for your lab's waste conversion or material processing needs? The challenges of high energy use, capital costs, and product purification demand robust, reliable equipment. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab reactors and furnaces designed for efficient thermal processes. Our expertise helps you navigate these hurdles, ensuring your pyrolysis operations are both effective and economically sound. Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can strengthen your pyrolysis project and deliver value.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the full process of pyrolysis? A Step-by-Step Guide to Waste Transformation
- What is the major product of pyrolysis? Tailoring the Output for Your Specific Needs
- What is the process of pyrolysis waste management? Turn Waste into Valuable Resources
- What are the results of calcination? A Guide to Purification and Material Transformation
- What is the conversion of plastic to fuel by pyrolysis? A Complete Guide to Waste-to-Energy Technology
- What is the size of a pyrolysis plant? A Guide to Matching Capacity with Your Needs
- What is the difference between fast and flash pyrolysis? Maximize Your Bio-Oil Yield
- How does fast pyrolysis work? Quickly Convert Biomass into Liquid Biofuel



















