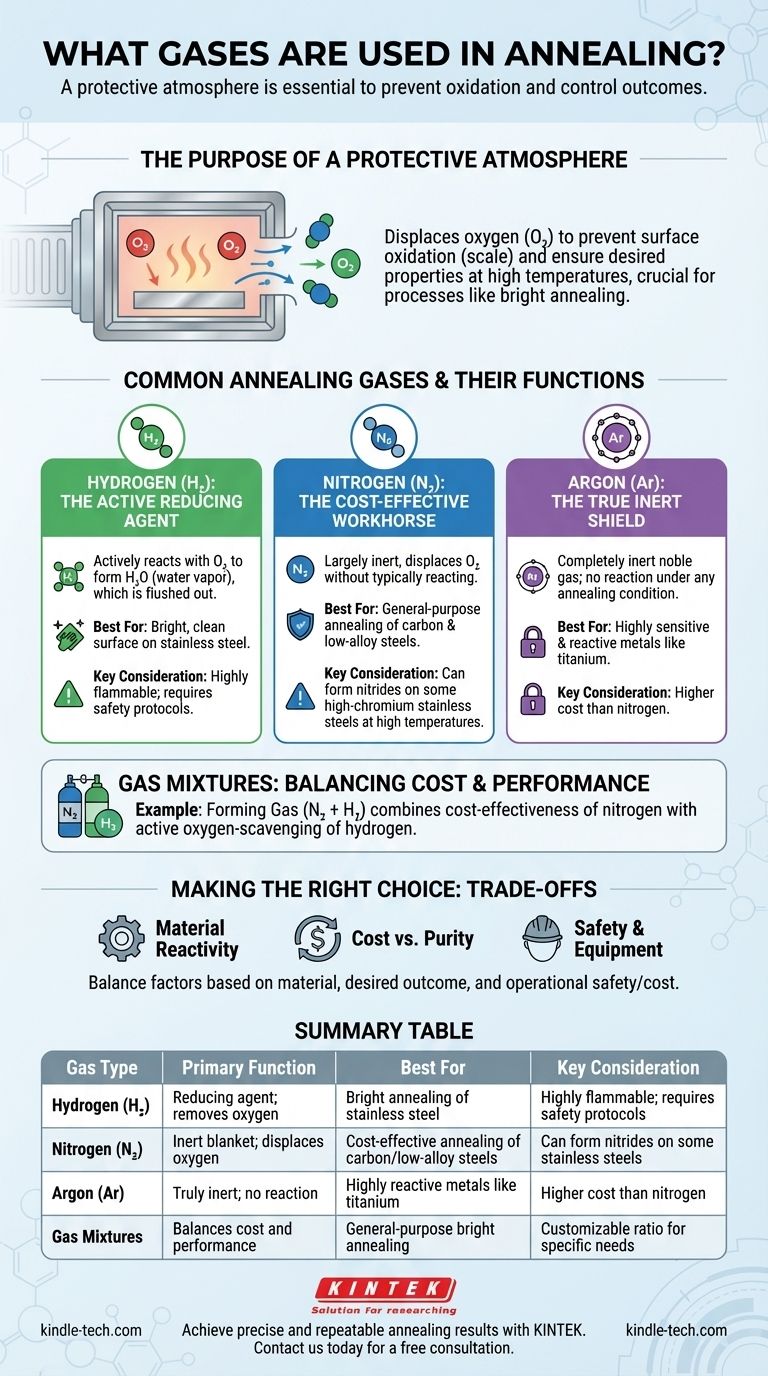
To control the outcome of the process, annealing is performed in a protective atmosphere using specific gases like hydrogen, nitrogen, argon, or a mixture of these. The primary purpose of these gases is to displace oxygen and prevent the metal surface from oxidizing at high temperatures, ensuring the material achieves the desired mechanical properties and surface finish.
The core principle is not about which gas is universally "best," but about selecting the right atmosphere—be it reducing or inert—to prevent unwanted chemical reactions like oxidation with the specific metal being treated at annealing temperatures.

The Purpose of a Protective Atmosphere
At the elevated temperatures required for annealing, most metals will readily react with oxygen in the air. This reaction, called oxidation, forms a layer of scale on the metal's surface.
This oxide layer can be detrimental, altering the material's dimensions, surface finish, and mechanical properties. A protective atmosphere is a controlled, engineered environment inside the furnace that displaces the ambient air (specifically oxygen and water vapor) to prevent these reactions from occurring.
This is the foundational concept behind processes like bright annealing, where the goal is to produce a part with a clean, mirror-like surface free of any oxides.
Common Annealing Gases and Their Functions
The choice of gas is dictated by the type of metal being annealed, the desired surface finish, and operational costs.
Hydrogen (H₂): The Active Reducing Agent
Hydrogen is a reducing gas. This means it actively reacts with any oxygen present to form water vapor (H₂O), which is then flushed from the furnace.
This active removal of oxygen makes hydrogen exceptionally effective for achieving a bright, clean surface on metals like stainless steel.
Nitrogen (N₂): The Cost-Effective Workhorse
Nitrogen is the most common and least expensive gas used for creating a protective atmosphere. It is largely inert, meaning it displaces oxygen but does not typically react with the base metal.
However, for certain materials like high-chromium stainless steels, nitrogen can react at high temperatures to form nitrides on the surface, which may be undesirable.
Argon (Ar): The True Inert Shield
Argon is a noble gas, making it completely inert under all annealing conditions. It will not react with any metal, no matter how reactive it is or how high the temperature.
This makes argon the ideal choice for annealing highly sensitive and reactive metals, such as titanium, or when even the slightest nitride formation from a nitrogen atmosphere is unacceptable.
Gas Mixtures: Balancing Cost and Performance
It is common to use mixtures to optimize for both cost and performance.
A popular blend is Forming Gas, a mixture of nitrogen and hydrogen (typically 5-10% H₂). This provides the cost-effectiveness of a nitrogen base with the active oxygen-scavenging benefits of hydrogen.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting the right atmosphere involves balancing three critical factors: material compatibility, desired outcome, and operational safety and cost.
Material Reactivity
The most important factor is how the gas interacts with the metal. Using nitrogen on a titanium alloy would be a mistake, but using expensive argon on a simple carbon steel is often unnecessary.
Cost vs. Purity
There is a direct correlation between gas purity and cost. Nitrogen is far less expensive than argon. The decision often comes down to whether the application's quality requirements justify the higher cost of a completely inert gas.
Safety and Equipment
Hydrogen is highly effective but also flammable. Using hydrogen requires furnaces with enhanced safety features and stringent operating protocols, which adds to the overall cost and complexity of the process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your choice of annealing gas directly impacts the quality, cost, and safety of your heat treatment process.
- If your primary focus is achieving a bright, oxide-free finish on stainless steel: A reducing atmosphere with a high concentration of hydrogen is the most effective approach.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose annealing of carbon or low-alloy steels: A nitrogen-based atmosphere, possibly with a small percentage of hydrogen, provides an excellent balance of cost and protection.
- If your primary focus is annealing highly reactive metals or materials sensitive to nitriding: A pure inert gas, almost always argon, is the only choice to guarantee no reaction with the atmosphere.
Ultimately, engineering the furnace atmosphere is as critical as controlling the temperature when seeking precise and repeatable results from your annealing process.
Summary Table:
| Gas Type | Primary Function | Best For | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen (H₂) | Reducing agent; removes oxygen | Bright annealing of stainless steel | Highly flammable; requires safety protocols |
| Nitrogen (N₂) | Inert blanket; displaces oxygen | Cost-effective annealing of carbon/low-alloy steels | Can form nitrides on some stainless steels |
| Argon (Ar) | Truly inert; no reaction | Highly reactive metals like titanium | Higher cost than nitrogen |
| Gas Mixtures (e.g., N₂ + H₂) | Balances cost and performance | General-purpose bright annealing | Customizable ratio for specific needs |
Achieve precise and repeatable annealing results with KINTEK.
The right protective atmosphere is critical for preventing oxidation and achieving your desired material properties. Our experts can help you select the ideal gas solution for your specific metal and application, ensuring optimal performance, surface quality, and cost-efficiency.
Contact us today to discuss your lab's annealing needs and discover how KINTEK's equipment and consumables can enhance your heat treatment processes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the functions of nitrogen (N2) in controlled furnace atmospheres? Achieve Superior Heat Treatment Results
- How does a high-temperature furnace with atmosphere control optimize spinel coatings? Achieve Redox Sintering Precision
- What are the inert gases in a heat treatment furnace? Choose the Right Shield for Your Metal
- Can nitrogen be used for brazing? Key Conditions and Applications Explained
- What is nitrogen atmosphere for annealing? Achieve Oxidation-Free Heat Treatment



















