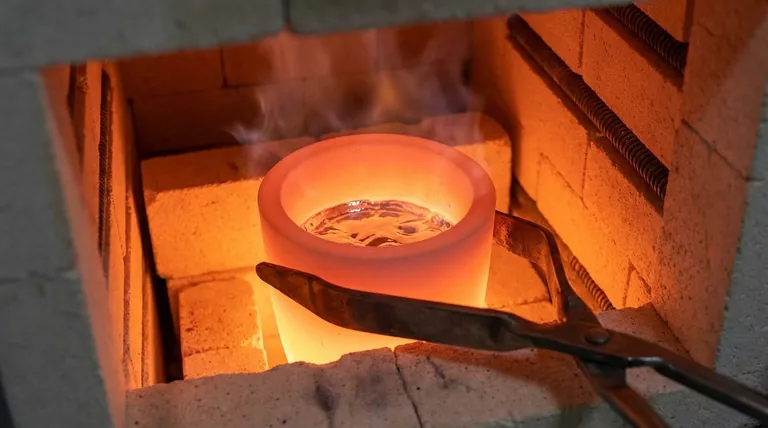
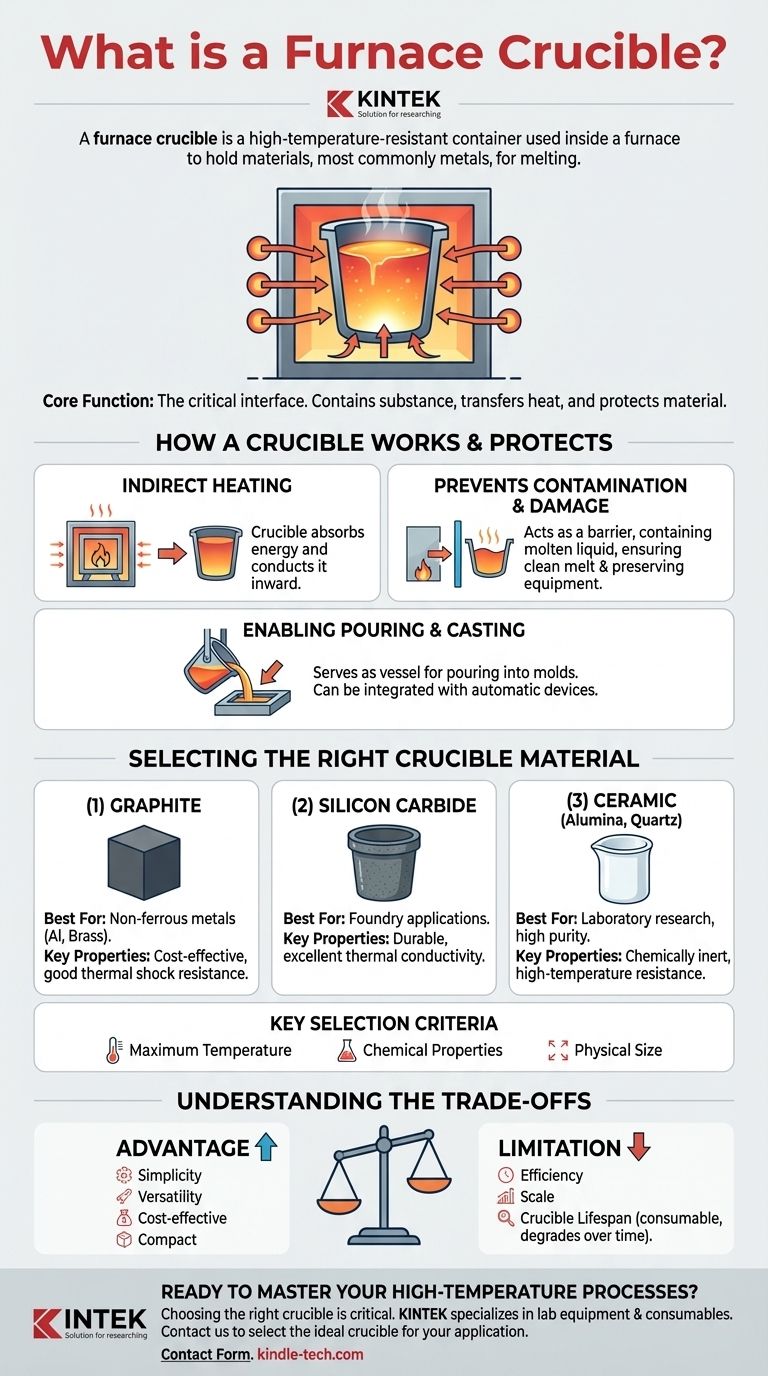
A furnace crucible is a high-temperature-resistant container used inside a furnace to hold materials, most commonly metals, for melting. Made from specialized materials like graphite, silicon carbide, or ceramic, its primary job is to contain the substance as it turns to liquid and transfer heat from the furnace to the material without contaminating it or being destroyed by the extreme temperatures.
The crucible is not merely a bucket for molten metal; it is the critical interface between the furnace's raw heat and the material being processed. It enables clean, contained, and controlled melting, which is fundamental to casting, metallurgy, and laboratory science.

The Core Function: A Protective Barrier for High-Temperature Work
The role of a crucible goes far beyond simply holding a substance. It is an active and essential component in any melting operation, designed to protect both the material and the furnace itself.
How a Crucible Works
A crucible furnace operates on the principle of indirect heating. The furnace's heating elements (in an electric furnace) or burners (in a gas-fired one) heat the crucible from the outside.
The crucible absorbs this energy and conducts it inward, efficiently and evenly transferring the heat to the material contained within until it reaches its melting point.
Preventing Contamination and Damage
You must never place materials directly into the furnace chamber without a crucible. The crucible acts as a protective barrier, containing the molten liquid.
This prevents the molten material from reacting with or destroying the furnace's internal components, ensuring a clean melt and preserving the expensive equipment.
Enabling Pouring and Casting
Once the material is fully molten, the crucible serves as the vessel for pouring. It is carefully lifted from the furnace and used to pour the liquid material into a mold.
In more advanced systems, particularly in vacuum furnaces, crucibles can be integrated with automatic pouring devices and robotic manipulators for precision and safety.
Selecting the Right Crucible Material
The choice of crucible material is dictated by the specific requirements of your process. Using the wrong type can lead to a failed melt, sample contamination, or a dangerous equipment failure.
Graphite
Graphite is a common and cost-effective choice, especially for melting non-ferrous metals like aluminum, brass, and bronze. It offers good thermal conductivity and resistance to thermal shock.
Silicon Carbide
Often mixed with graphite, silicon carbide crucibles offer superior durability, strength, and excellent thermal conductivity. They are a robust choice for many foundry applications.
Ceramic (Alumina, Quartz)
Ceramic crucibles, such as those made from alumina or quartz, are typically used in laboratory settings or for processes requiring extreme purity. They are selected for their high-temperature resistance and chemical inertness to avoid reacting with the sample.
Key Selection Criteria
Your decision should be based on three factors: the maximum temperature you need to reach, the chemical properties of the material being melted, and the physical size required for your sample and furnace.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Crucible furnaces are ancient technology, but their simplicity is both a strength and a limitation.
Advantage: Simplicity and Versatility
Crucible furnaces are relatively inexpensive, easy to operate, and compact. This makes them exceptionally versatile and ideal for small foundries, jewelry making, laboratories, and hobbyist applications.
Limitation: Efficiency and Scale
As the oldest type of melting furnace, they can be less energy-efficient than modern alternatives like induction furnaces, which heat the metal directly. For high-volume industrial production, crucible furnaces are often too slow and inefficient.
Crucible Lifespan
A crucible is a consumable item. Repeated exposure to extreme temperature cycles (thermal shock) and chemical interaction with molten materials will eventually cause it to degrade and crack. This represents an ongoing operational cost that must be factored in.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right crucible and furnace system depends entirely on your goal.
- If your primary focus is a small-scale foundry or jewelry making: A simple gas or electric furnace with a graphite or silicon carbide crucible provides the best balance of cost and performance.
- If your primary focus is laboratory research: Prioritize a high-purity ceramic crucible (like alumina or quartz) to prevent sample contamination and ensure the integrity of your results.
- If your primary focus is high-volume industrial casting: A crucible furnace may be suitable for smaller, specialized melts, but you should evaluate more efficient technologies like induction furnaces for your core production.
Ultimately, understanding the crucible is the first step toward mastering controlled, high-temperature material processing.
Summary Table:
| Crucible Material | Best For | Key Properties |
|---|---|---|
| Graphite | Non-ferrous metals (Al, Brass) | Cost-effective, good thermal shock resistance |
| Silicon Carbide | Foundry applications | Durable, excellent thermal conductivity |
| Ceramic (Alumina, Quartz) | Laboratory research, high purity | Chemically inert, high-temperature resistance |
Ready to Master Your High-Temperature Processes?
Choosing the right crucible is critical for achieving a clean, controlled melt and protecting your valuable equipment. Whether you're in a small foundry, a research lab, or a jewelry workshop, KINTEK has the expertise and products to support you.
We specialize in lab equipment and consumables, including a full range of high-performance crucibles tailored to your specific needs. Our team can help you select the ideal crucible material and size based on your application, maximum temperature, and material compatibility.
Contact us today via the form below to discuss your requirements and ensure your melting operations are efficient, safe, and contamination-free. Let KINTEK be your partner in precision heating.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Al2O3 Crucible With Lid Cylindrical Laboratory Crucible
- High Purity Pure Graphite Crucible for Evaporation
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Crucibles (Al2O3) for Thermal Analysis TGA DTA
- Arc-Shaped Alumina Ceramic Crucible High Temperature Resistant for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- High Purity Pure Graphite Crucible for Electron Beam Evaporation
People Also Ask
- Why are high-purity alumina crucibles used for LATP? Preserve Purity and Conductivity in Sintering
- Do I need different crucibles for different metals? Ensure Safety and Purity in Your Metal Melting
- What role does a corundum crucible play in TGA? Ensure High-Temperature Precision for Rock Sample Analysis
- Why is a fully closed alumina crucible required for the calcination of Wollastonite/Colemanite? Ensure Phase Purity
- What is the difference between a crucible and a furnace? Understanding the Heat Source and Container Partnership
- What are high temperature crucibles made of? Choose the Right Material for Your Lab
- What role does an Alumina Crucible play in the high-temperature solid-state synthesis of Na3OBr? Ensure Sample Purity
- Do you need to preheat a crucible? The Critical Step to Prevent Catastrophic Failure



















