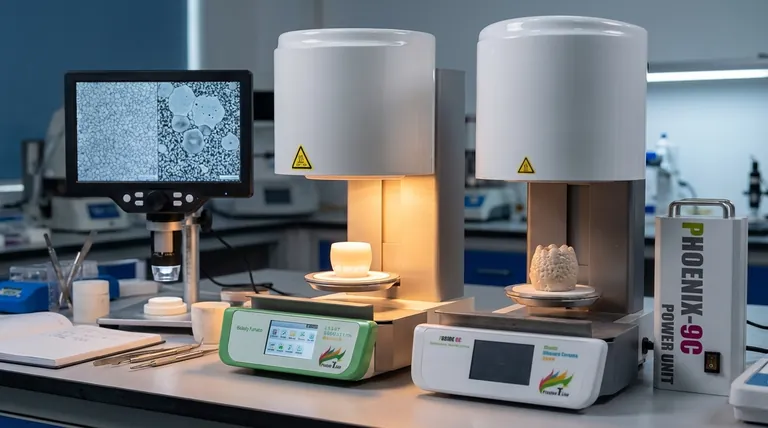
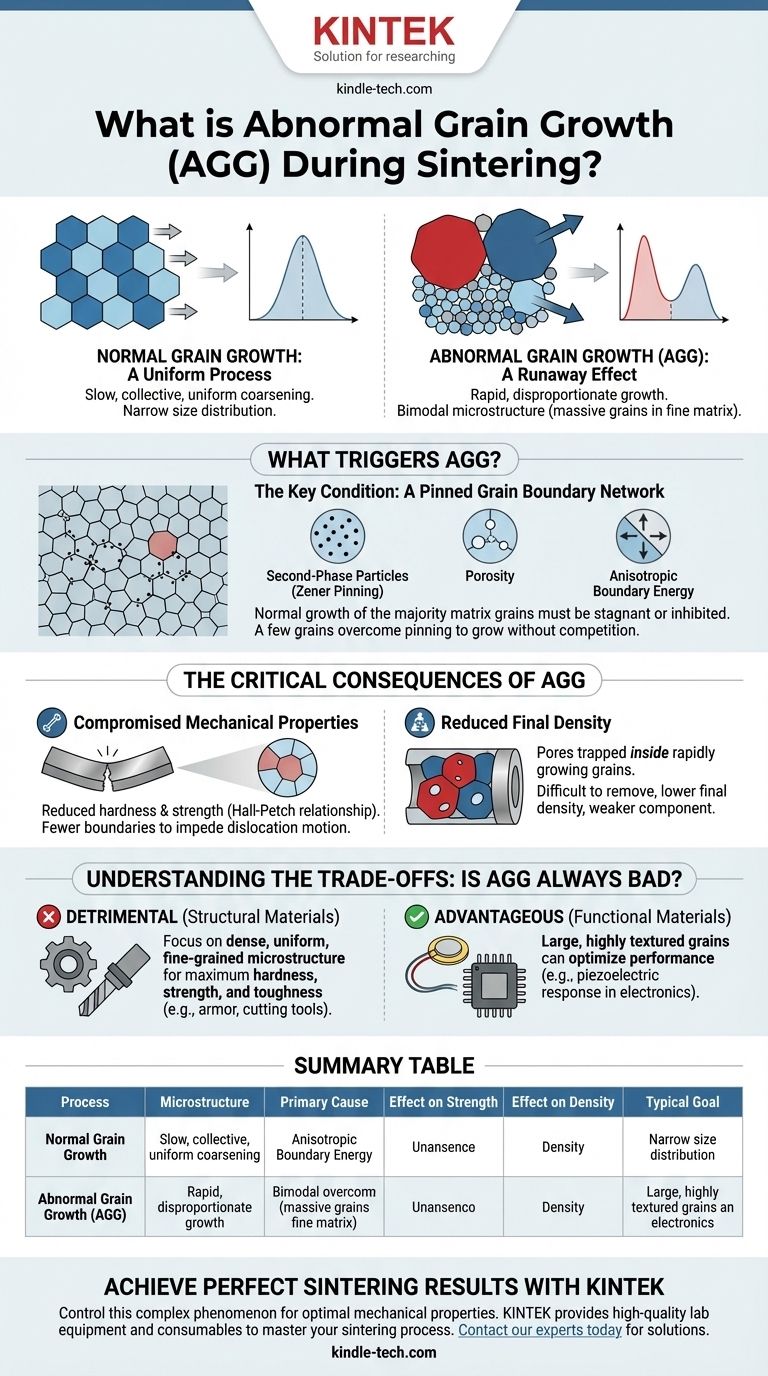
In the context of sintering, abnormal grain growth is a microstructural phenomenon where a small population of grains grows exceptionally large at the expense of the surrounding smaller grains. This process, also known as secondary recrystallization or exaggerated grain growth (EGG), results in a duplex or bimodal microstructure containing a few massive grains embedded in a matrix of much finer ones.
The core issue with abnormal grain growth is its disruption of microstructural uniformity. While normal grain growth is a slow, collective process, abnormal growth is a runaway effect where a few grains cannibalize their neighbors, often trapping defects and severely degrading the material's mechanical properties.

The Mechanics of Grain Growth: Normal vs. Abnormal
To understand what is "abnormal," we must first define what is "normal." Both processes are driven by the same fundamental force: the system's desire to reduce its total energy by minimizing the surface area of its high-energy grain boundaries.
Normal Grain Growth: A Uniform Process
During ideal sintering, all grains grow gradually and at a relatively similar rate. The average grain size of the material increases, but the size distribution remains narrow and unimodal. This process is thermally activated and proceeds as atoms move across grain boundaries, effectively allowing larger grains to slowly consume smaller ones in a uniform fashion.
Abnormal Grain Growth (AGG): A Runaway Effect
Abnormal grain growth occurs when this uniform process breaks down. It is characterized by the rapid and disproportionate growth of only a select few grains. These grains expand quickly, consuming the surrounding matrix of smaller grains that have, for some reason, stopped growing normally. The result is a non-uniform, bimodal grain size distribution.
What Triggers Abnormal Grain Growth?
AGG is not a random event; it requires a specific set of conditions. The primary condition is that the normal growth of the majority "matrix" grains must be stagnant or inhibited.
The Key Condition: A Pinned Grain Boundary Network
For a few grains to grow abnormally, the boundaries of the vast majority of other grains must be "pinned" in place. This stagnation prevents the normal, uniform coarsening process and creates an opportunity for a few grains that overcome this pinning to grow without competition.
Common Pinning Mechanisms
Several factors can inhibit normal grain boundary motion:
- Second-Phase Particles: Tiny particles or impurities can exert a drag force on grain boundaries, a phenomenon known as Zener pinning.
- Porosity: Pores, especially when located at grain boundary junctions, can anchor the boundaries and prevent their movement.
- Anisotropic Boundary Energy: If the material has a strong crystallographic texture, the energy and mobility of grain boundaries can vary significantly, stalling some while allowing others to move freely.
When the thermal energy from the sintering temperature is high enough for a few grains to break free from these pinning points, they can grow rapidly into the stagnant matrix.
The Critical Consequences of AGG
For most engineering applications, particularly those involving structural components, abnormal grain growth is considered a processing defect.
Compromised Mechanical Properties
The most significant consequence is a reduction in hardness and strength. The Hall-Petch relationship states that a material's strength increases as its grain size decreases. The numerous grain boundaries in a fine-grained material act as barriers to dislocation motion. By creating massive grains, AGG drastically reduces the density of these beneficial boundaries, softening and weakening the material.
Reduced Final Density
Ideal densification occurs when pores are attached to moving grain boundaries and are swept out of the material. When a grain grows abnormally fast, it can move past these pores, trapping them inside the grain itself. These entrapped pores are extremely difficult to remove, leading to a lower final density and a weaker component.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Is AGG Always Bad?
While AGG is often detrimental, it can be intentionally induced and exploited in the manufacturing of certain functional materials.
The Detriment in Structural Materials
For applications where mechanical performance is paramount—such as in cutting tools, armor, or load-bearing ceramic components—abnormal grain growth is highly undesirable. The focus is on achieving a dense, uniform, and fine-grained microstructure to maximize hardness, strength, and fracture toughness.
The Advantage in Functional Materials
Conversely, for some electronic or magnetic materials, large and highly textured grains are required to optimize performance. For example, in piezoelectric ceramics, large grains with a specific crystallographic orientation can enhance the piezoelectric response. In these cases, engineers carefully control the process to promote AGG and create a desired single-crystal-like structure.
Applying This to Your Sintering Process
Understanding the causes and effects of AGG allows you to control it to achieve your desired material properties.
- If your primary focus is maximizing mechanical strength: You must suppress AGG. Use high-purity powders, control particle size distribution, and consider using dopants that act as grain growth inhibitors to maintain a fine, uniform grain structure.
- If you are observing low density and high residual porosity: Investigate your sintering cycle. Abnormal grain growth may be occurring early in the process, trapping pores within grains before full densification is achieved.
- If your goal is to produce a material with specialized functional properties: You may need to intentionally trigger AGG. This can be done through techniques like seeding with large crystals or carefully controlling chemistry and temperature to create the conditions for a few grains to grow preferentially.
Ultimately, controlling grain growth is a powerful lever for tailoring a material's final microstructure and, therefore, its performance for a specific application.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Normal Grain Growth | Abnormal Grain Growth (AGG) |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Slow, uniform coarsening | Rapid, runaway growth of a few grains |
| Microstructure | Uniform, narrow size distribution | Bimodal (a few large grains in a fine matrix) |
| Primary Cause | General reduction of grain boundary energy | Pinning of most grain boundaries, allowing a few to break free |
| Effect on Strength | Gradual decrease (Hall-Petch) | Significant reduction due to very large grains |
| Effect on Density | Promotes densification (pores swept by boundaries) | Reduces final density (pores trapped inside grains) |
| Typical Goal | Often desirable for uniformity | Usually a defect in structural materials |
Achieve Perfect Sintering Results with KINTEK
Is abnormal grain growth compromising the strength and density of your sintered materials? Controlling this complex phenomenon is critical for achieving the mechanical properties your application demands.
KINTEK specializes in providing the high-quality lab equipment and consumables you need to master your sintering process. Whether you require precise temperature control furnaces, high-purity powders, or expert advice on process parameters, we have the solutions to help you suppress or exploit grain growth for optimal results.
Let us help you optimize your sintering to prevent defects and enhance performance.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific laboratory needs and discover how KINTEK's solutions can bring reliability and precision to your research and production.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature of sintering zirconia? Mastering the Protocol for Perfect Dental Restorations
- Can you change the color of zirconia crowns? Understanding the Permanent Nature of Zirconia
- What is the price of zirconia sintering furnace? Invest in Precision, Not Just a Price Tag
- What makes zirconia translucent? The Science Behind Modern Dental Aesthetics
- What are the white spots on zirconia after sintering? A Guide to Diagnosing and Preventing Defects



















