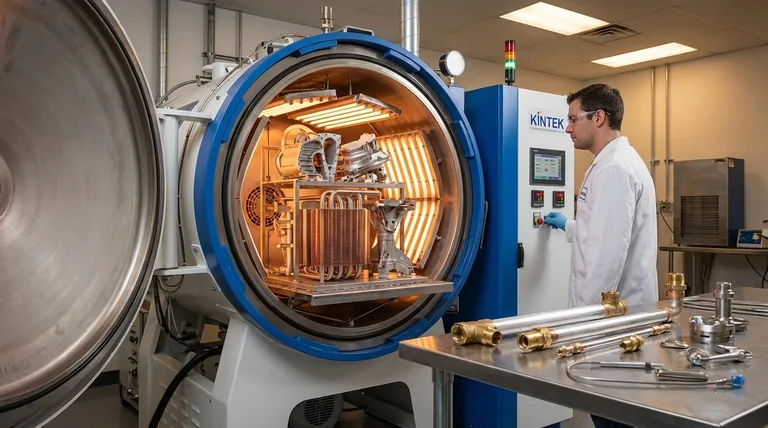
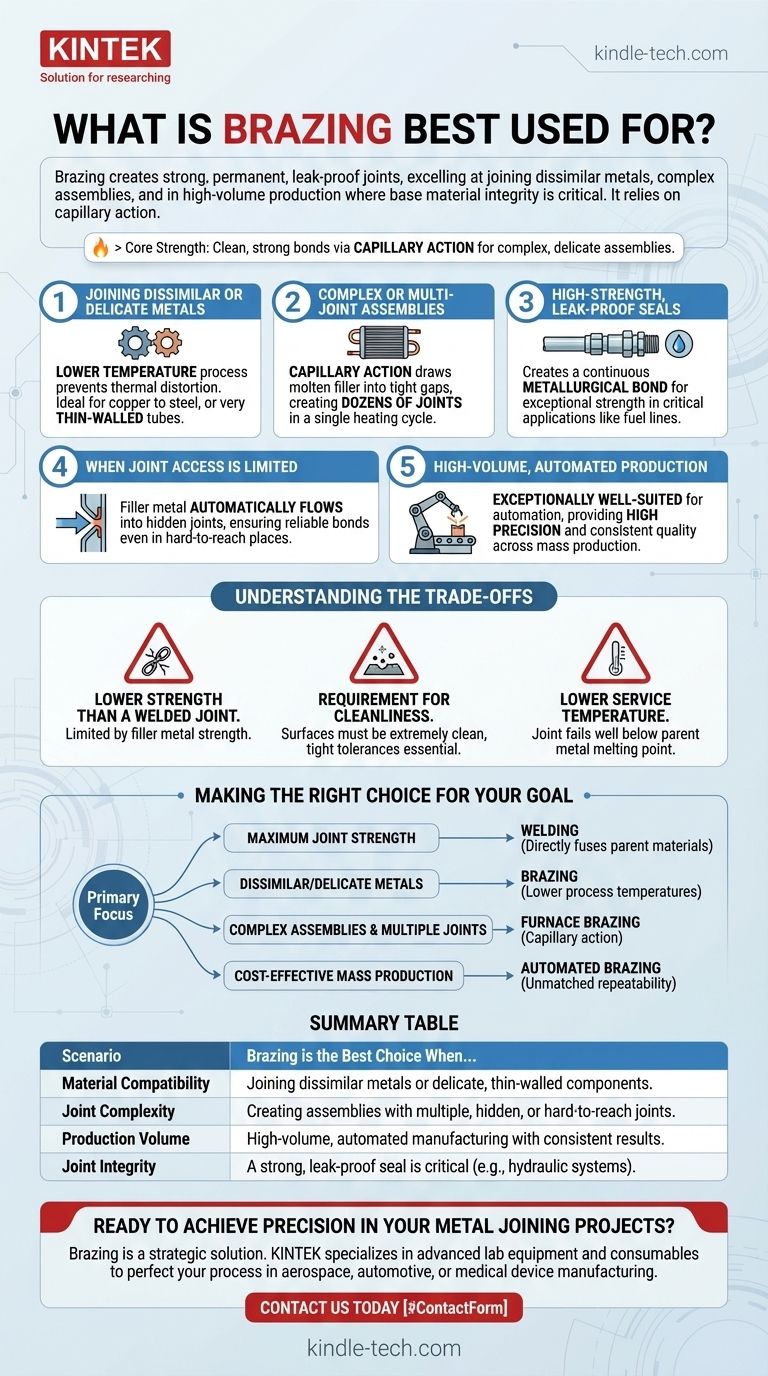
Brazing is best used for creating strong, permanent, and leak-proof joints in a wide range of applications, from automotive and HVAC components to complex aerospace and medical devices. It excels at joining dissimilar metals, creating complex assemblies with multiple or inaccessible joints, and is highly suitable for automated, high-volume production where precision is critical.
Brazing should be your go-to process when the integrity of the base materials must be preserved and the joint geometry makes welding impractical. Its core strength lies in its ability to create clean, strong bonds using capillary action, making it ideal for complex, delicate, or multi-joint assemblies.

When to Choose Brazing: Key Characteristics
Understanding the fundamental principles of brazing reveals why it is the superior choice for certain engineering challenges. It is not simply an alternative to welding, but a distinct process with unique advantages.
For Joining Dissimilar or Delicate Metals
Brazing occurs at a temperature below the melting point of the base materials being joined.
This lower-temperature process is critical because it prevents thermal distortion, stress, and damage to the base metals. This makes it the ideal method for joining dissimilar metals like copper to steel, or for joining very thin-walled tubes that would be destroyed by welding.
For Complex or Multi-Joint Assemblies
Brazing relies on capillary action, where the molten filler metal is drawn into the tight-fitting gap between the base materials, regardless of gravity.
This unique property allows a single heating cycle, often in a furnace, to create dozens or even hundreds of joints simultaneously. A perfect example is a heat exchanger, where countless fins are bonded to tubes in one operation—a task that would be impossible with welding.
For High-Strength, Leak-Proof Seals
The brazing process creates a strong, continuous metallurgical bond between the filler metal and the base materials.
This results in a sealed joint that is exceptionally strong and leak-proof, which is why it is trusted for critical applications like hydraulic fittings, fuel lines, and components for industrial gas turbines.
When Joint Access is Limited
Capillary action allows the filler metal to flow into hidden or internal joints where direct access with a welding torch or electrode is not possible.
As long as a consistent gap can be maintained, the filler metal will automatically flow and fill the entire joint area, ensuring a complete and reliable bond even in hard-to-reach places.
For High-Volume, Automated Production
The brazing process is exceptionally well-suited for automation.
Automatic brazing machines can be programmed to produce huge volumes of components with high precision and repeatability. This makes it a cost-effective solution for mass production in industries like automotive and electronics, ensuring consistent quality across thousands of parts.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No process is perfect for every situation. To use brazing effectively, you must also understand its limitations.
Lower Strength Than a Welded Joint
While a brazed joint is very strong, it is typically not as strong as a properly executed welded joint. Welding fuses the base metals themselves, creating a homogenous bond that can match the parent material's strength. A brazed joint's strength is limited by the filler metal.
Requirement for Cleanliness and Tight Tolerances
Capillary action only works if the surfaces are extremely clean and the gap between the parts is precisely controlled. Any contaminants like oil or oxides will prevent the filler metal from flowing properly. This means part preparation is a critical and non-negotiable step.
Lower Service Temperature
Because the filler metal has a lower melting point than the base materials, a brazed joint will fail at a temperature well below the melting point of the parent metals. This must be a key consideration for components used in high-temperature environments.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct joining process requires aligning the method's strengths with your project's primary objective.
- If your primary focus is maximum joint strength above all else: Welding is often the better choice, as it directly fuses the parent materials.
- If your primary focus is joining dissimilar metals or delicate, thin-walled components: Brazing is the ideal solution due to its lower process temperatures.
- If your primary focus is producing complex assemblies with multiple, inaccessible joints: Furnace brazing is uniquely suited for this task thanks to capillary action.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective mass production of strong, clean joints: Automated brazing provides unmatched repeatability and speed for high-volume manufacturing.
Understanding these core principles allows you to select brazing not just as an option, but as a strategic manufacturing solution.
Summary Table:
| Scenario | Brazing is the Best Choice When... |
|---|---|
| Material Compatibility | Joining dissimilar metals (e.g., copper to steel) or delicate, thin-walled components without damaging them. |
| Joint Complexity | Creating assemblies with multiple, hidden, or hard-to-reach joints in a single heating cycle. |
| Production Volume | High-volume, automated manufacturing requiring consistent, repeatable results. |
| Joint Integrity | A strong, leak-proof seal is critical, such as in hydraulic systems or aerospace components. |
Ready to achieve precision and reliability in your metal joining projects?
Brazing is a strategic solution for creating strong, leak-proof bonds in complex assemblies and dissimilar metals. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the advanced lab equipment and consumables needed to perfect your brazing process. Whether you're in aerospace, automotive, or medical device manufacturing, our expertise ensures your joints meet the highest standards of quality and durability.
Contact us today using the form below to discuss how KINTEK can support your laboratory's brazing and metal joining needs. Let's build something stronger together!
#ContactForm
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between welding and vacuum brazing? Choose the Right Joining Method for Your Project
- What is brazing in heat treatment? Achieve Superior Joint Quality and Efficiency
- What is the process of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Purity and Precision in High-Temp Processing
- What is the cost of a vacuum brazing furnace? A guide to key factors and investment strategy
- What are vacuum furnaces used for? Unlock Ultimate Material Purity and Performance



















