To be CVD coated means an object has had a thin, highly durable film applied to its surface through a process called Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD). This high-temperature process uses a chemical reaction to deposit the coating material from a gas, creating an exceptionally strong chemical bond with the base material. The result is a surface with superior adhesion and resistance to wear and abrasion.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is a high-temperature process that creates a chemically bonded, exceptionally hard coating. While this provides superior wear resistance and can cover complex shapes, the high heat and potential for stress fractures limit the materials it can be applied to and its suitability for high-impact applications.

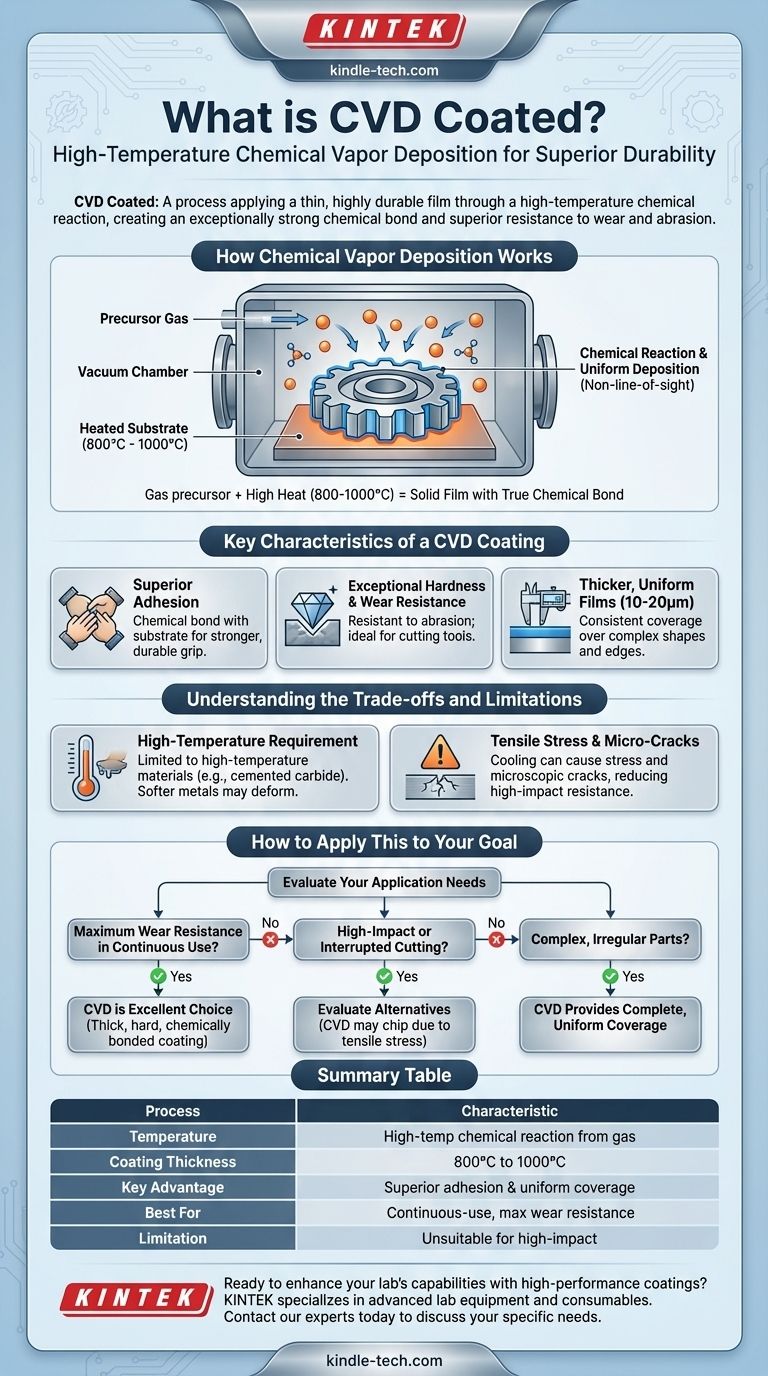
How Chemical Vapor Deposition Works
The Core Chemical Reaction
The CVD process takes place inside a vacuum chamber. A precursor gas, which contains the atoms of the desired coating material, is introduced into the chamber. The part to be coated, known as the substrate, is heated to a very high temperature. This heat triggers a chemical reaction in the gas, causing a solid film to form and deposit uniformly onto the substrate's surface.
A High-Temperature Environment
The process temperatures for CVD are significant, typically ranging from 800°C to 1000°C. This high heat is necessary to facilitate the chemical reaction that bonds the coating to the surface. It also means the substrate material must be able to withstand these temperatures without deforming, melting, or degrading.
Beyond Line-of-Sight
A key advantage of CVD is that it is not a line-of-sight process. The coating gas envelops the entire part within the chamber. This allows the coating to deposit uniformly on all surfaces, including complex, irregular shapes and internal geometries found on components like drill bits.
Key Characteristics of a CVD Coating
Superior Adhesion and Bond Strength
Because the coating is formed through a chemical reaction directly on the surface, it creates a true chemical bond with the substrate. This results in superior adhesion compared to processes that only physically deposit material.
Exceptional Hardness and Wear Resistance
CVD coatings are known for their exceptional hardness, making them highly resistant to abrasion and wear. This is why they are frequently used for cutting tools and other components that experience significant friction.
Thicker, More Uniform Films
The process allows for the creation of relatively thick films, often in the 10 to 20μm range. It also produces excellent "step coverage," meaning the coating maintains its thickness and uniformity even over sharp edges or complex surface features.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
The High-Temperature Requirement
The most significant limitation of CVD is its high processing temperature. This restricts its use to base materials with very high temperature resistance, such as cemented carbide. Softer metals or materials with lower melting points cannot be coated using this method.
The Risk of Tensile Stress
As the thick coating and the substrate cool down from the high processing temperature, differences in thermal expansion can generate significant tensile stress within the coating. This stress can lead to the formation of fine, microscopic cracks.
Unsuitability for High-Impact Forces
While these micro-cracks are not always a problem, they can become a failure point under sudden impact or non-uniform force. This makes CVD coatings less suitable for interrupted cutting processes like milling, where the tool repeatedly engages and disengages with the workpiece, as this can cause the coating to chip or peel.
Difficulty in Masking
The all-encompassing nature of the CVD process makes it difficult to mask or protect specific areas of a part from being coated.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
Before selecting a CVD-coated product, it's crucial to evaluate the specific demands of your application.
- If your primary focus is maximum wear resistance in a continuous-use environment: CVD is an excellent choice due to its thick, hard, and chemically bonded coating.
- If your primary focus is coating a complex, irregularly shaped part: CVD's non-line-of-sight process ensures complete and uniform coverage where other methods would fail.
- If your primary focus is toughness and resistance to chipping under impact: You should carefully evaluate CVD, as the inherent tensile stress can make it less suitable than alternative coatings like PVD.
Understanding these core principles allows you to select a coated material based not just on its hardness, but on its suitability for the specific stresses of your application.
Summary Table:
| Feature | CVD Coating Characteristic |
|---|---|
| Process | High-temperature chemical reaction from a gas |
| Temperature | 800°C to 1000°C |
| Coating Thickness | 10 to 20μm |
| Key Advantage | Superior adhesion & uniform coverage on complex shapes |
| Best For | Continuous-use applications requiring maximum wear resistance |
| Limitation | Unsuitable for high-impact or interrupted cutting processes |
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities with high-performance coatings?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables, including solutions for surface treatment and material analysis. Whether you're developing new tools or need coatings for demanding applications, our expertise can help you achieve superior results.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can meet your specific laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom CVD Diamond Coating for Lab Applications
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Lab and Diamond Growth
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
People Also Ask
- Is diamond coating worth it? Maximize Component Life and Performance
- How thick is CVD diamond coating? Balancing Durability and Stress for Optimal Performance
- What is CVD diamond coating? Grow a Super-Hard, High-Performance Diamond Layer
- How long does diamond coating last? Maximize Lifespan with the Right Coating for Your Application
- What is diamond coating film? A Thin Layer of Diamond for Extreme Performance



















