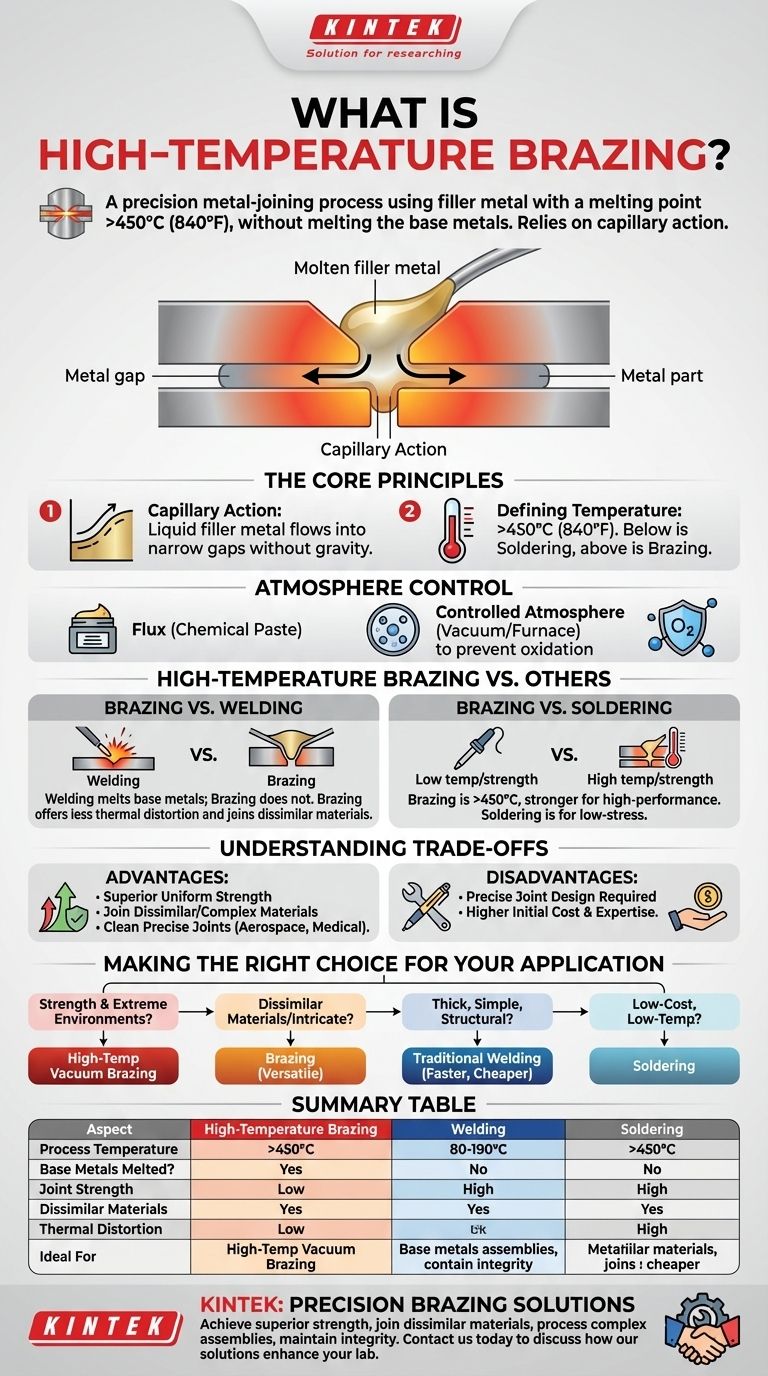
In essence, high-temperature brazing is a metal-joining process that uses a filler metal with a melting point above 450°C (840°F), but below the melting point of the base metals being joined. The process works by heating the entire assembly to melt the filler metal, which is then drawn into the tight-fitting joint by capillary action. Unlike welding, the base metals are never melted.
The critical insight is that high-temperature brazing is not just about heat; it's a precision-controlled method for creating exceptionally strong, clean, and stress-free joints, particularly in complex assemblies or between dissimilar materials where welding would fail.
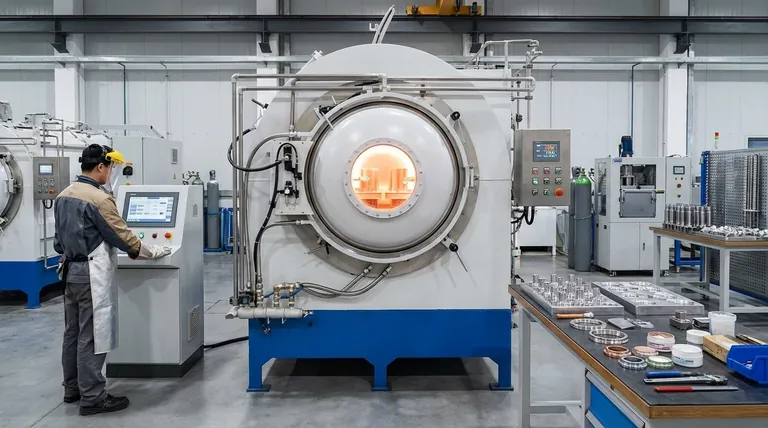

The Core Principles of the Brazing Process
To understand high-temperature brazing, it's essential to first grasp the fundamental mechanics that apply to all brazing operations.
How Brazing Fundamentally Works
Brazing relies on a phenomenon called capillary action. This is the ability of a liquid to flow into narrow spaces without assistance from, or even in opposition to, external forces like gravity.
The parts to be joined are designed with a very small, uniform gap between them. When the filler metal melts, it is naturally pulled into this gap, completely filling the joint and forming a strong metallurgical bond upon cooling.
The Defining Temperature Threshold
The internationally accepted standard that separates brazing from soldering is a temperature of 450°C (840°F).
If the filler metal melts below this point, the process is called soldering. If it melts above this point, it is called brazing.
The Critical Role of Atmosphere Control
At high temperatures, metals react rapidly with oxygen, forming oxides that prevent the filler metal from wetting the surfaces and flowing into the joint.
To ensure a clean, strong bond, these oxides must be prevented or removed. This is achieved in one of two ways:
- Flux: A chemical paste applied to the joint that melts, shields the surface from air, and dissolves oxides. This is common in torch brazing.
- Controlled Atmosphere: The entire assembly is heated in a furnace where the atmosphere is controlled, typically a vacuum or a specific gas like hydrogen. This is the standard for high-performance, high-temperature brazing.
High-Temperature Brazing vs. Other Joining Methods
Choosing the right joining method requires understanding where high-temperature brazing excels compared to its alternatives.
Brazing vs. Welding
The most significant difference is that welding melts the base metals to fuse them together. Brazing does not.
This distinction gives brazing several key advantages: it produces less thermal distortion, maintains the original metallurgical properties of the base metals, and makes it possible to join dissimilar materials (e.g., copper to steel) that are impossible to weld together.
Brazing vs. Soldering
The primary difference is temperature and strength. Brazed joints, created above 450°C, are substantially stronger and can operate at much higher service temperatures than soldered joints.
Soldering is typically used for lower-stress applications like electronics and plumbing, while brazing is used for structural, high-performance components.
Understanding the Trade-offs
High-temperature brazing is a powerful technique, but it is not the solution for every problem. Understanding its advantages and limitations is key to using it effectively.
Advantage: Superior and Uniform Strength
Because the filler metal is drawn through the entire joint via capillary action, it creates a very large bonding surface area. This results in joints that are often as strong as, or even stronger than, the base metals themselves.
Advantage: Joining Complex and Dissimilar Materials
Brazing is one of the few methods that can reliably join materials with vastly different properties, such as metals to ceramics. Furthermore, a complex assembly with dozens of joints can be brazed simultaneously in a single furnace cycle, which is impossible with welding.
Advantage: Clean and Precise Joints
High-temperature furnace brazing, particularly in a vacuum, produces extremely clean parts with neat fillets that often require no post-processing or cleaning. This is critical for applications in aerospace, medical, and semiconductor industries.
Disadvantage: Precise Joint Design is Required
Capillary action only works if the gap between the parts is small and consistent (typically 0.001" to 0.005"). This demands a higher level of precision in manufacturing the components compared to what might be required for welding.
Disadvantage: Higher Initial Cost and Expertise
The specialized filler metals (often containing nickel, silver, or gold) and the equipment (e.g., vacuum furnaces) represent a significant investment. The process also requires a higher level of technical expertise to design and execute properly.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct joining method depends entirely on the specific demands of your component and its operating environment.
- If your primary focus is strength and reliability in extreme environments (e.g., jet engine turbines, medical implants): High-temperature vacuum furnace brazing is often the superior or only viable choice.
- If your primary focus is joining dissimilar materials or intricate assemblies: Brazing provides a level of versatility that welding cannot match.
- If your primary focus is joining thick, simple sections of a common metal for structural purposes: Traditional welding is almost always faster, cheaper, and more than sufficient.
- If your primary focus is a low-cost, low-temperature assembly where high strength is not critical: Soldering is the more appropriate and economical process.
Ultimately, high-temperature brazing is a specialized tool for solving complex engineering challenges that demand the highest levels of performance and precision.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | High-Temperature Brazing | Welding | Soldering |
|---|---|---|---|
| Process Temperature | Above 450°C (840°F) | Melts base metals | Below 450°C (840°F) |
| Base Metals Melted? | No | Yes | No |
| Joint Strength | Very high, often stronger than base metals | High | Moderate to low |
| Dissimilar Materials | Excellent capability | Limited | Good |
| Thermal Distortion | Minimal | Significant | Minimal |
| Ideal For | Aerospace, medical, complex assemblies | Structural, thick sections | Electronics, plumbing |
Ready to solve your complex metal-joining challenges with precision brazing?
At KINTEK, we specialize in high-performance lab equipment and consumables for advanced metal joining processes. Our expertise in high-temperature brazing solutions can help you:
- Achieve superior joint strength for demanding applications
- Join dissimilar materials with precision and reliability
- Process complex assemblies efficiently in controlled atmospheres
- Maintain material integrity with minimal thermal distortion
Whether you're working in aerospace, medical device manufacturing, or advanced materials research, our team can provide the equipment and technical support you need for flawless brazing results.
Contact us today to discuss how our brazing solutions can enhance your laboratory's capabilities and deliver the precision your projects demand.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
People Also Ask
- What is the principle of sintering process? Transforming Powder into High-Performance Solids
- What is the importance of vacuum ovens in electrode drying? Enhance Supercapacitor Performance with Precise Thermal Control
- What are sintered components? A Guide to High-Efficiency Metal Parts Manufacturing
- What is the sintering process of stainless steel? Transform Powder into Dense, Strong Components
- How does an industrial high-temperature electric heating furnace operate to simulate engine conditions for valve steel?
- What is deposition of a vapor? A Guide to High-Precision Thin Film Coating
- Why is a multi-stage aging furnace required for gamma prime phase control in superalloys? Expert Insights.
- What is the function of the high vacuum environment in W-C-B sintering? Achieve 97%+ Density & Purity



















