In essence, Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) is an advanced manufacturing technique that uses pulsed electrical current and mechanical pressure to transform powders into a dense, solid mass. It accomplishes this with remarkable speed and at significantly lower temperatures than conventional sintering methods, making it a pivotal process for creating high-performance materials.
The defining characteristic of SPS is its unique heating mechanism. By passing a high-current, pulsed DC signal through the powder, it generates localized plasma between particles, enabling ultra-fast heating that preserves delicate microstructures which would otherwise be destroyed.
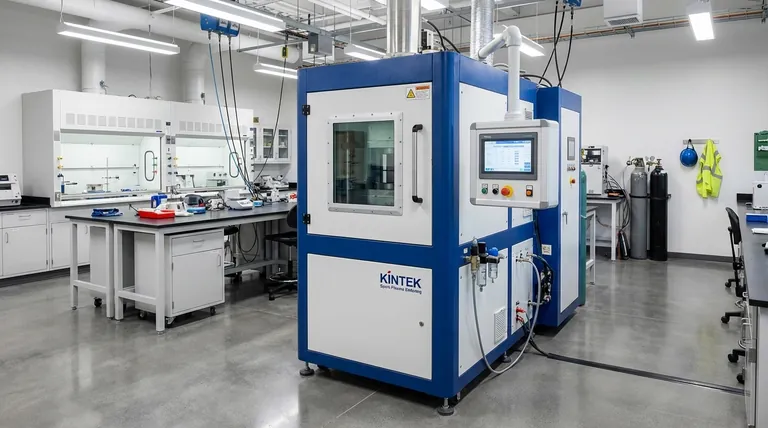

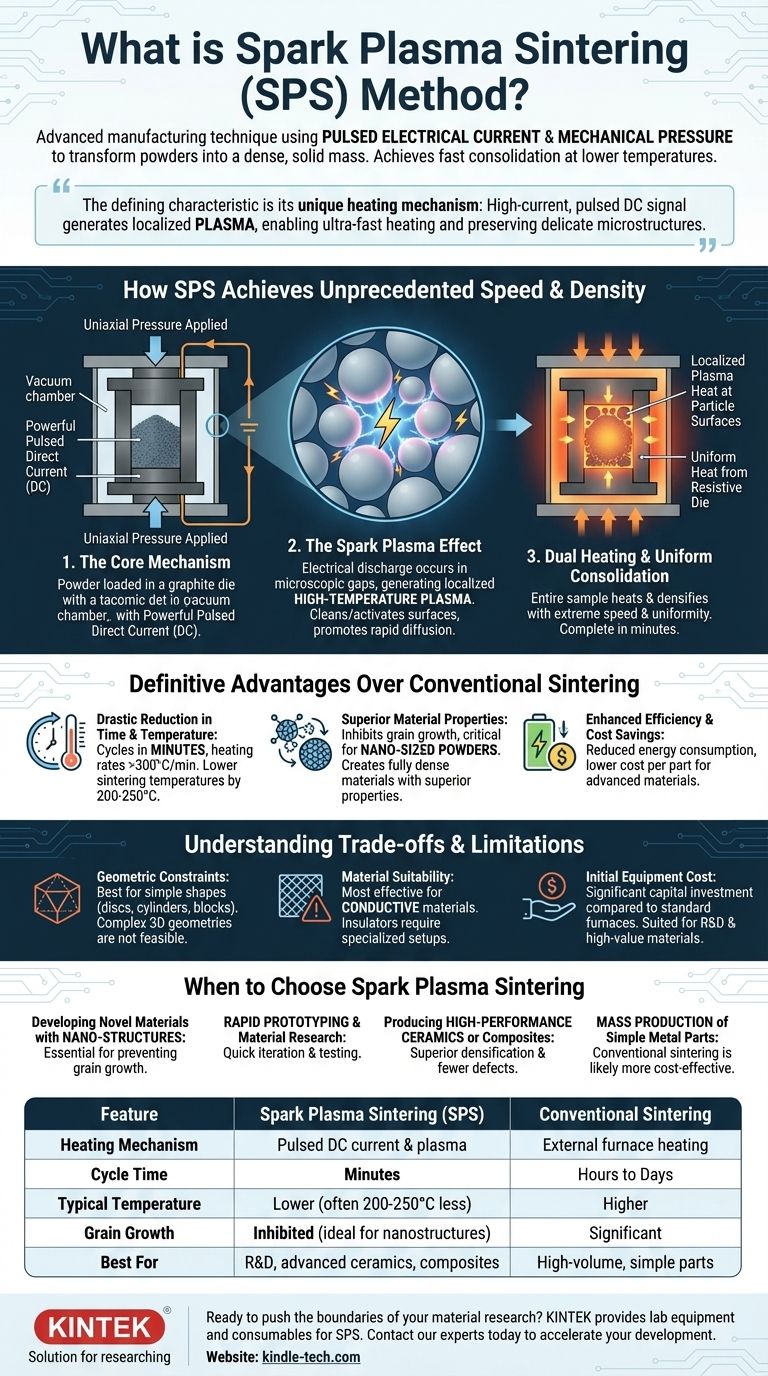
How SPS Achieves Unprecedented Speed and Density
To understand why SPS is so effective, we must look at how it fundamentally differs from a traditional furnace, which slowly bakes material from the outside in.
The Core Mechanism: Current and Pressure
The process begins by loading the powder into a conductive die, typically made of graphite. This die is placed inside a chamber under a vacuum or controlled atmosphere to prevent oxidation.
Uniaxial pressure is then applied, mechanically compressing the powder. Simultaneously, a powerful pulsed Direct Current (DC) is sent directly through the conductive die and, crucially, through the powder particles themselves.
The "Spark Plasma" Effect
The term "spark plasma" refers to the electrical discharge that occurs in the microscopic gaps between individual powder particles. This discharge generates a localized, high-temperature plasma.
This effect cleans and activates the surfaces of the particles, promoting rapid diffusion and bonding between them. It is this particle-to-particle heating that is the primary source of the system's incredible speed.
Dual Heating for Uniform Consolidation
While the plasma provides localized heating at the particle level, the electrical resistance of the graphite die causes it to heat up as well.
This dual heating model—localized plasma at the particle surfaces and uniform heat from the die—ensures the entire sample heats and densifies with extreme speed and uniformity. The process is complete once the target temperature is reached and the material has achieved maximum density, often in just a few minutes.
The Definitive Advantages Over Conventional Sintering
The unique mechanism of SPS provides several clear and compelling advantages over traditional methods like hot pressing or furnace sintering.
Drastic Reduction in Time and Temperature
The most significant advantage is speed. SPS cycles are completed in minutes, whereas conventional methods can take many hours or even days.
Heating rates often exceed 300°C per minute, compared to the 5-8°C per minute typical of conventional furnaces. This also allows for lower overall sintering temperatures, often by as much as 200-250°C.
Superior Material Properties
Because the material spends so little time at high temperatures, SPS effectively inhibits grain growth.
This is critical for sintering nano-sized powders. It allows for the creation of fully dense materials that retain their original nano-structure and its associated superior properties, something nearly impossible with slow, conventional methods. The result is a denser final product with fewer defects.
Enhanced Efficiency and Cost Savings
The combination of shorter cycle times and lower temperatures directly translates to reduced energy consumption. This makes the manufacturing process more efficient and lowers the cost per part for advanced materials.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, SPS is not a universal solution. Its specific nature introduces certain constraints that are critical to understand.
Geometric Constraints
The use of a rigid die and uniaxial pressure means SPS is best suited for producing relatively simple shapes, such as discs, cylinders, and rectangular blocks. Complex, three-dimensional geometries are not feasible with this process.
Material Suitability
The process is most effective for conductive or semi-conductive materials where current can easily pass between particles. While techniques exist to sinter insulating materials like some ceramics, they often require specialized and more complex die setups.
Initial Equipment Cost
SPS machines are sophisticated and represent a significant capital investment compared to standard industrial furnaces. This cost generally positions SPS for use in research, development, and the production of high-value, advanced materials rather than high-volume, low-cost components.
When to Choose Spark Plasma Sintering
Your choice of sintering method should be guided by your end goal. SPS is a specialized tool for specific, high-performance applications.
- If your primary focus is developing novel materials with nano-structures: SPS is the superior choice, as its rapid cycle is essential for preventing the grain growth that destroys nano-scale properties.
- If your primary focus is rapid prototyping and material research: The speed of SPS allows for quick iteration and testing, dramatically accelerating the development of new material compositions.
- If your primary focus is producing high-performance ceramics or composites: SPS achieves superior densification and fewer internal defects, leading to enhanced mechanical strength and reliability.
- If your primary focus is mass production of simple metal parts: A conventional press-and-sinter process is likely a more cost-effective solution due to lower equipment costs and established scalability.
Ultimately, Spark Plasma Sintering provides a powerful capability for pushing the boundaries of material science, enabling the creation of next-generation materials with precisely controlled, high-performance structures.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) | Conventional Sintering |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Mechanism | Pulsed DC current & plasma | External furnace heating |
| Cycle Time | Minutes | Hours to Days |
| Typical Temperature | Lower (often 200-250°C less) | Higher |
| Grain Growth | Inhibited (ideal for nanostructures) | Significant |
| Best For | R&D, advanced ceramics, composites | High-volume, simple parts |
Ready to push the boundaries of your material research?
Spark Plasma Sintering from KINTEK can help you achieve rapid prototyping and create fully dense materials with superior properties. Our lab equipment and consumables are designed to meet the precise needs of modern laboratories.
Contact our experts today to discuss how SPS can accelerate your development of next-generation materials.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Heated Vacuum Press Machine Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the uses of spark plasma sintering? Fast, Low-Temp Fabrication of Advanced Materials
- What is the heating rate of spark plasma sintering? Unlock Rapid, High-Performance Material Densification
- What is the difference between spark plasma sintering and flash sintering? A Guide to Advanced Sintering Methods
- What is the process of plasma sintering? Achieve Rapid, High-Performance Material Densification
- What is spark plasma sintering of polymers? Rapidly Create Dense, High-Performance Materials



















