At its core, an induction furnace is a powerful tool used across the metallurgical industry for melting, holding, and processing conductive metals. Its applications range from high-volume foundries melting iron and steel to specialized facilities producing high-purity alloys, investment castings, and precious metals.
The true value of an induction furnace lies not just in its ability to melt metal, but in how it does so. By using electromagnetic induction to generate heat directly within the material, it offers unparalleled speed, temperature control, and cleanliness compared to traditional fuel-fired methods.
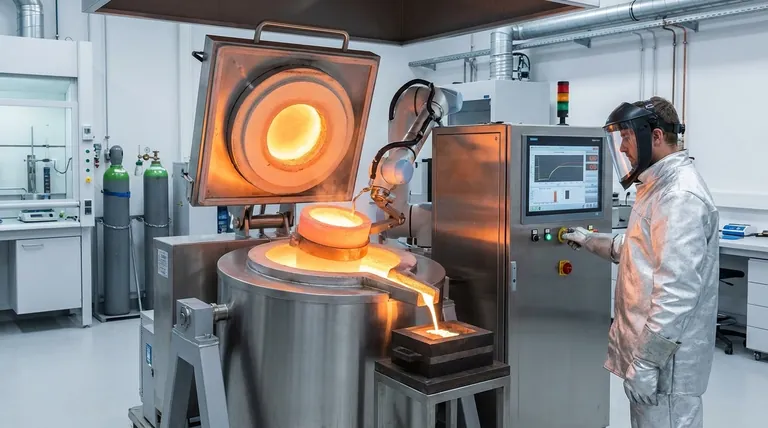

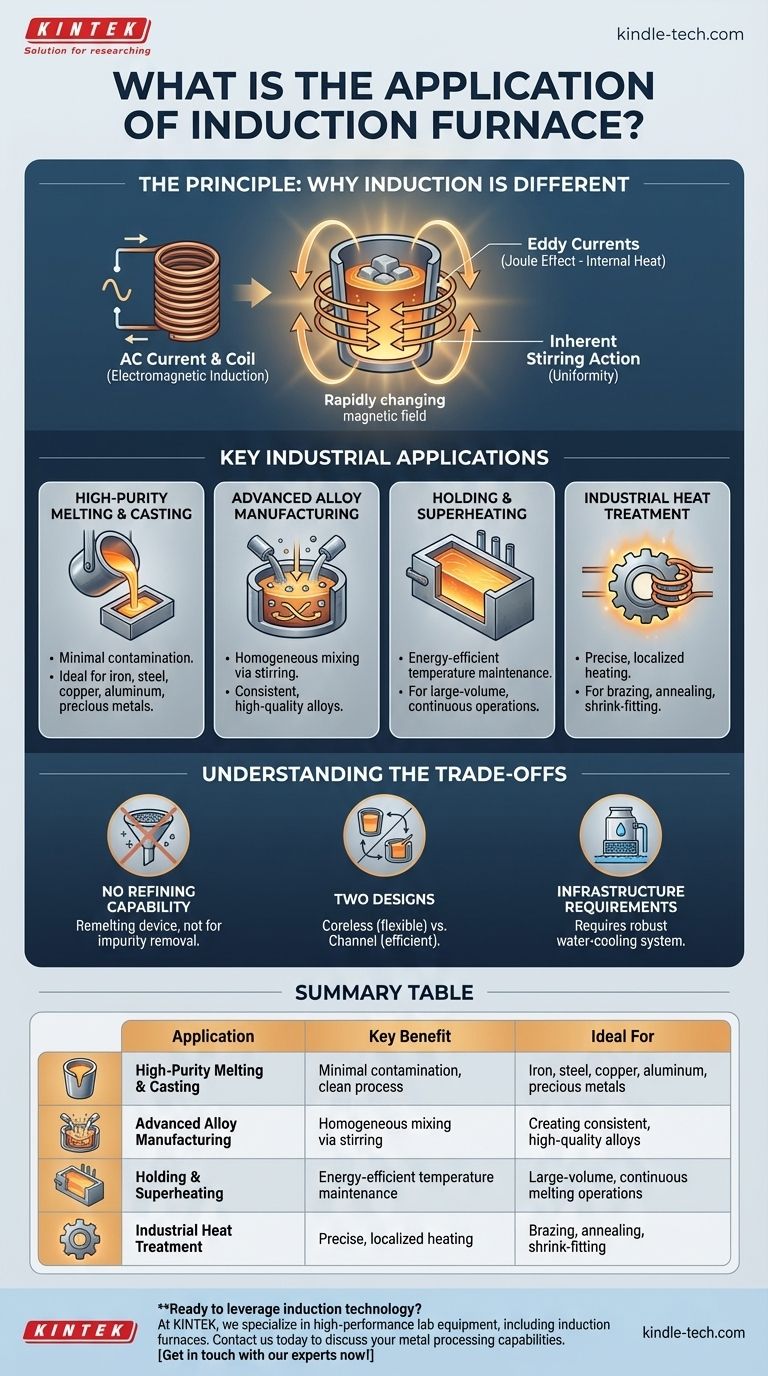
The Principle: Why Induction is Different
At the heart of every application is the furnace's unique heating method. Understanding this principle is key to understanding its value.
Electromagnetic Induction
An induction furnace uses a powerful alternating current passed through a copper coil. This creates a strong, rapidly changing magnetic field around the metal (the "charge") placed inside the furnace.
The Joule Effect
This magnetic field induces powerful electrical currents, known as eddy currents, directly within the metal charge. The metal's natural resistance to the flow of these currents generates intense heat, a phenomenon known as the Joule effect. The metal effectively becomes its own heating element.
Inherent Stirring Action
The same electromagnetic forces that generate heat also create a natural stirring or mixing effect within the molten metal bath. This is a significant advantage that promotes temperature uniformity and helps distribute alloying elements evenly.
Key Industrial Applications
The unique properties of induction heating make these furnaces indispensable for several critical processes.
High-Purity Melting and Casting
This is the most common application. Foundries use induction furnaces to melt a wide variety of metals, including iron, steel, copper, aluminum, and precious metals.
Because the heat is generated internally and there is no contact with a flame or combustion byproducts, the process introduces far less contamination. This makes it ideal for producing high-quality castings and alloys where purity is essential.
Advanced Alloy Manufacturing
The natural electromagnetic stirring action is a major benefit for creating alloys. It ensures that added elements like chromium, nickel, or manganese are homogeneously mixed into the base metal, resulting in a finished product with consistent and reliable properties.
Holding and Superheating
Some facilities use a specific type of furnace, the channel induction furnace, not for initial melting but as a holding vessel. It can efficiently maintain a large volume of molten metal at a precise temperature, ready for pouring.
This is also used for "superheating," or raising the metal's temperature just before casting to ensure it has the right fluidity to fill a complex mold.
Industrial Heat Treatment
The precise and localized nature of induction heating is perfect for surface treatments. Applications include:
- Brazing: Joining two pieces of metal together with a filler material.
- Annealing: Softening metal to make it more workable.
- Shrink-fitting: Heating a part to expand it so it can be fitted over another part, creating a tight bond as it cools and shrinks.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, induction furnaces are not a universal solution. Understanding their limitations is critical for proper application.
No Inherent Refining Capability
An induction furnace is fundamentally a remelting device. It has very little capability to refine metal or remove impurities like sulfur or phosphorus from a low-quality scrap charge. The quality of the metal produced is almost entirely dependent on the quality of the materials put in.
Two Main Designs for Different Needs
The two primary types of induction furnaces—coreless and channel—serve different functions.
- Coreless furnaces are highly flexible and excellent for melting a wide variety of metals from a solid state, making them perfect for batch-based operations.
- Channel furnaces are more energy-efficient for holding large volumes of molten metal at temperature but are less flexible and typically dedicated to a single alloy.
Infrastructure Requirements
The powerful coils generate significant waste heat and must be protected by a robust, closed-loop water-cooling system. This adds complexity to the installation and represents a critical system that must be maintained to prevent catastrophic failure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right induction process depends entirely on your end goal.
- If your primary focus is high-purity batch melting or creating diverse alloys: A coreless induction furnace provides the flexibility and cleanliness required for high-quality, varied production.
- If your primary focus is large-volume holding or continuous melting of a single metal: A channel induction furnace offers superior energy efficiency for maintaining large liquid baths at a stable temperature.
- If your primary focus is precise component manufacturing or heat treatment: The targeted, non-contact heating of an induction system is unmatched for processes like brazing, annealing, or shrink-fitting.
Ultimately, the strategic application of induction technology hinges on leveraging its precise, clean, and efficient heating to meet specific metallurgical goals.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Benefit | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| High-Purity Melting & Casting | Minimal contamination, clean process | Iron, steel, copper, aluminum, precious metals |
| Advanced Alloy Manufacturing | Homogeneous mixing via electromagnetic stirring | Creating consistent, high-quality alloys |
| Holding & Superheating | Energy-efficient temperature maintenance | Large-volume, continuous melting operations |
| Industrial Heat Treatment | Precise, localized heating for surface treatments | Brazing, annealing, shrink-fitting |
Ready to leverage the power of induction technology in your lab or foundry?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-performance lab equipment, including induction furnaces, tailored to meet the precise needs of laboratories and metallurgical facilities. Whether you require high-purity melting, advanced alloy production, or efficient metal holding, our solutions deliver unparalleled temperature control, cleanliness, and operational efficiency.
Contact us today to discuss how our induction furnaces can enhance your metal processing capabilities and drive your projects forward. Get in touch with our experts now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is an Alumina Ceramic Tube Support Necessary for 1100°C Experiments? Ensure Data Accuracy and Chemical Inertness
- How do you clean a tube furnace tube? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe and Effective Cleaning
- What are the advantages of using an alumina liner in a tube furnace for biomass combustion corrosion simulations?
- What is the ceramic tube high temperature? From 1100°C to 1800°C, Choose the Right Material
- What is the primary advantage of using a tube furnace? Achieve Superior Temperature and Atmosphere Control



















