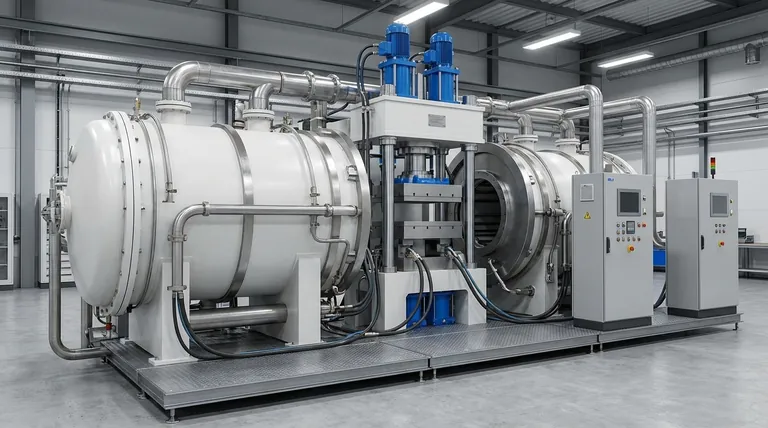
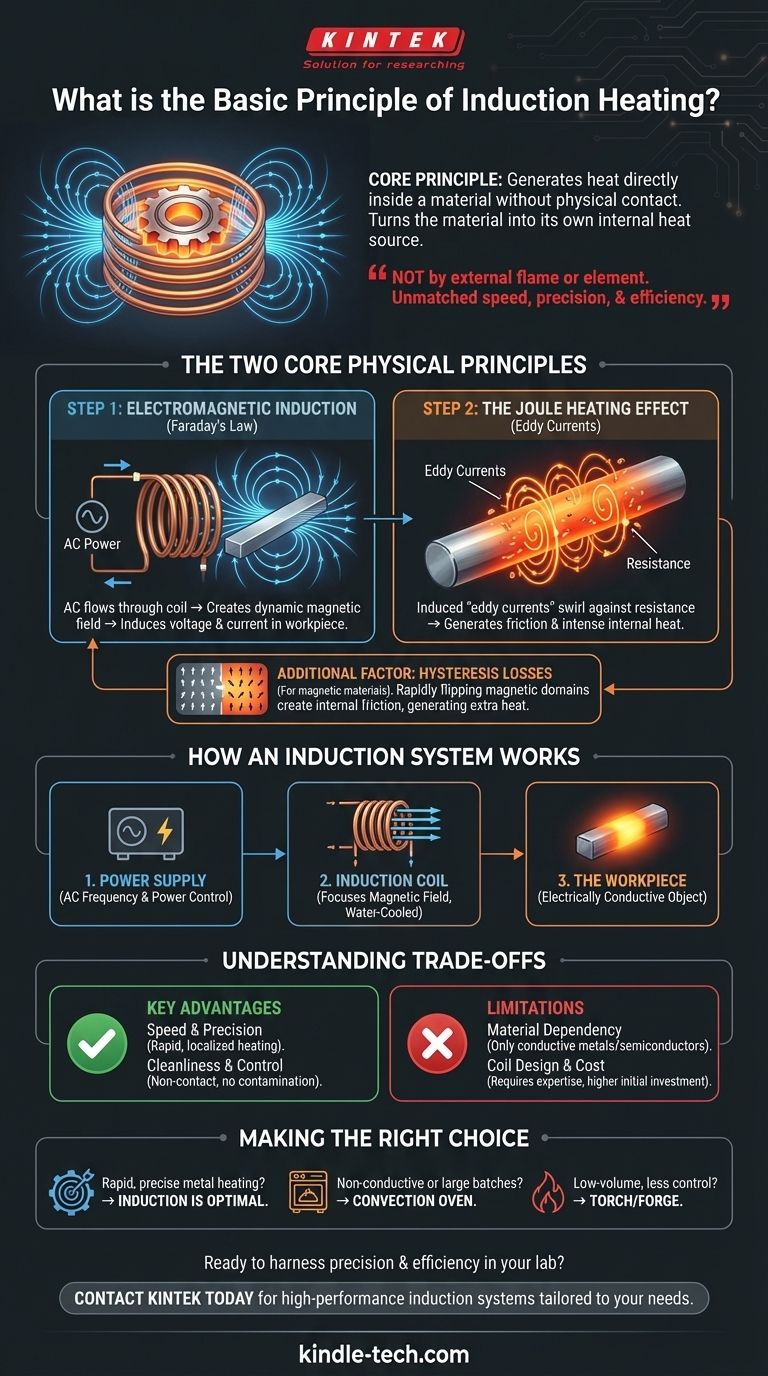
At its core, induction heating is a method of generating heat directly inside a material without any physical contact. It achieves this by using a powerful, rapidly changing magnetic field to create internal electrical currents within a conductive object. The object's natural resistance to these swirling currents, called eddy currents, instantly generates intense and precise heat through a process known as Joule heating.
The central principle to grasp is that induction heating does not heat a material with an external flame or element. Instead, it effectively turns the material itself into its own internal heat source, leading to unmatched speed, precision, and efficiency.

The Two Core Physical Principles
Induction heating is a direct application of two fundamental laws of physics: electromagnetic induction and the Joule effect. These two principles work in tandem to convert electrical energy into heat.
Step 1: Electromagnetic Induction
An induction heating system begins by passing a high-frequency alternating current (AC) through a copper coil, often called an inductor.
According to Faraday's Law of Induction, this AC flow generates a dynamic and powerful magnetic field in the space around the coil.
When an electrically conductive workpiece (like a piece of steel) is placed inside this magnetic field, the field induces a voltage directly within the workpiece, causing an electrical current to flow.
Step 2: The Joule Heating Effect
The current induced inside the workpiece does not flow in a straight line but rather in continuous, swirling loops called eddy currents.
As these eddy currents flow, they encounter the material's inherent electrical resistance. This opposition to the current's flow generates friction on an atomic scale, converting the electrical energy directly into heat.
This conversion is known as the Joule heating effect. Because the heat is generated inside the material, the heating process is exceptionally fast and efficient.
An Additional Factor: Hysteresis Losses
For magnetic materials like iron and steel, there is a secondary heating mechanism. The rapidly alternating magnetic field causes the magnetic domains within the material to rapidly flip their polarity back and forth.
This internal friction, called magnetic hysteresis, also generates a significant amount of heat in addition to the Joule effect, making induction particularly effective for ferrous metals.
How an Induction System Works
A typical induction heating system is composed of three primary parts that work together to execute this process.
The Power Supply
This is an electronic unit that takes standard line power and converts it into a high-frequency alternating current. The frequency and power level can be precisely controlled to manage the heating process.
The Induction Coil (Inductor)
This is typically a water-cooled copper tube that has been formed into a specific shape. It acts as an antenna, focusing the magnetic field onto the workpiece. The coil's design is critical for determining the location, pattern, and intensity of the heat.
The Workpiece
This is the object to be heated. It must be electrically conductive for eddy currents to be generated. Metals and semiconductors are the most common materials heated with induction.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Advantages
While powerful, induction heating is not a universal solution. Understanding its advantages and limitations is key to using it effectively.
Key Advantage: Speed and Precision
Because heat is generated directly within the part, heating is incredibly rapid. Furthermore, by shaping the coil, you can precisely heat a specific zone of a part—like the tip of a screwdriver or the teeth on a gear—without affecting the rest of the material.
Key Advantage: Cleanliness and Control
Induction is a non-contact process. The coil never touches the part, eliminating any risk of contamination. With no combustion gases or external elements, it is an extremely clean process ideal for medical, aerospace, and cleanroom applications.
Limitation: Material Dependency
The most significant limitation is that induction heating only works on electrically conductive materials. It cannot be used to directly heat insulators like most plastics, glass, or ceramics.
Limitation: Coil Design and Cost
The efficiency of the process is heavily dependent on the design of the induction coil. Creating custom coils for complex part geometries requires expertise. Additionally, the initial investment in a high-frequency power supply can be higher than for a simple convection oven or forge.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Understanding the core principle empowers you to decide when induction is the optimal choice.
- If your primary focus is rapid, precise, and repeatable heating of metals: Induction heating is often the superior technology for tasks like hardening, brazing, or annealing.
- If your primary focus is heating non-conductive materials or large, simple batches with less precision: A conventional convection or radiation oven may be a more practical and cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is low-volume metal heating without strict process control: Simpler methods like a torch or forge might be sufficient, but they lack the control and efficiency of induction.
By turning the part into its own heat source, induction heating provides a level of control that few other technologies can match.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Core Principle | Uses electromagnetic induction to create internal eddy currents in conductive materials, generating heat via the Joule effect. |
| How It Works | High-frequency AC passes through a copper coil, creating a magnetic field that induces currents in the workpiece. |
| Key Advantages | Rapid heating, precise control, non-contact process, high efficiency, and cleanliness. |
| Limitations | Only works on electrically conductive materials; requires custom coil design and higher initial investment. |
| Ideal For | Metal hardening, brazing, annealing, and applications needing localized, repeatable heat without contamination. |
Ready to harness the precision and efficiency of induction heating in your lab?
At KINTEK, we specialize in high-performance lab equipment, including induction heating systems tailored for your specific needs—whether you're working with metals, semiconductors, or other conductive materials. Our solutions deliver rapid, clean, and controlled heating to enhance your research, manufacturing, or quality control processes.
Contact us today via our contact form to discuss how KINTEK’s induction heating technology can optimize your workflow and deliver unmatched results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the primary role of the Vacuum Hot Pressing Sintering Furnace? Prepare High-Purity W-Si Alloy Targets
- How does the degassing stage in a vacuum hot press (VHP) optimize diamond/aluminum composite performance?
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing furnace over HIP? Optimize Fiber-Foil Composite Production
- How does a vacuum hot press furnace achieve the densification of ZrB2–SiC–TaC? Unlock Ultra-High Ceramic Density
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot press for CuCr50? Achieve Superior Density & Purity in Alloy Production



















