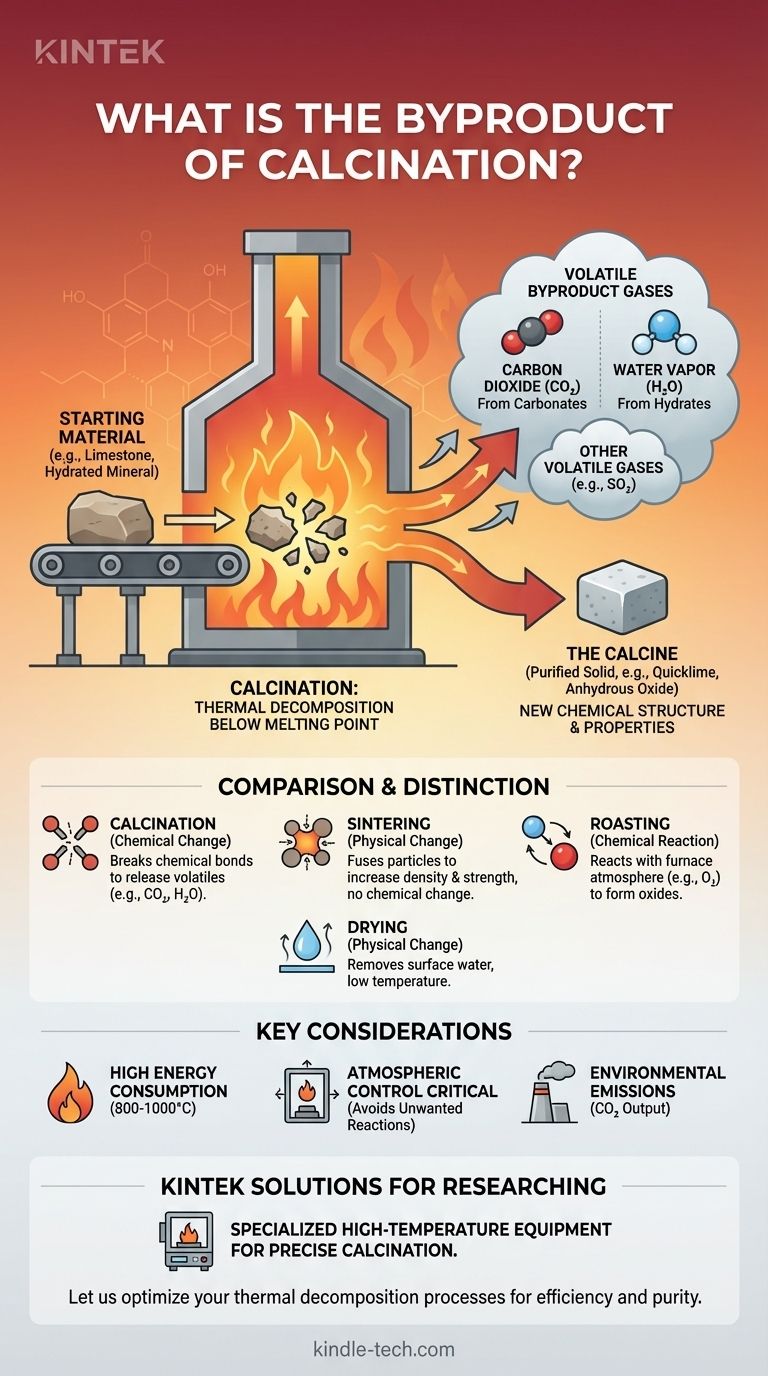
In almost all cases, the primary byproduct of calcination is a gas. This is most commonly carbon dioxide (CO2) when heating carbonates like limestone, or water vapor (H2O) when heating hydrated minerals. The process is a form of thermal decomposition, where intense heat breaks down a compound into a purified solid and volatile gases that are driven off.
Calcination is a process of chemical transformation, not simply purification. It uses high heat below the melting point to decompose a material, fundamentally changing its chemical structure by driving off volatile byproducts like carbon dioxide or water vapor.

What is Calcination? A Deeper Look
Calcination is a foundational process in metallurgy and materials science, particularly in the production of cement, lime, and the refining of certain ores. Understanding the mechanism is key to understanding its purpose.
The Core Principle: Thermal Decomposition
At its heart, calcination is about breaking chemical bonds with heat. The energy applied causes the starting material to decompose into two or more new substances.
One of these substances is the desired solid product, often called the "calcine." The other substances are the gaseous byproducts that are removed.
Common Byproducts Explained
The specific byproduct depends entirely on the chemical composition of the material being heated.
- Carbon Dioxide (CO2): This is the most famous example. When calcium carbonate (CaCO3, limestone) is calcined, it breaks down into calcium oxide (CaO, quicklime) and releases CO2 gas. This is the central reaction in cement manufacturing.
- Water Vapor (H2O): Many minerals exist as hydrates, meaning they have water molecules locked into their crystal structure. Calcining bauxite (aluminum ore) or gypsum removes this chemically bound water as steam.
- Other Volatile Gases: In more specific applications, other gases can be released. For instance, heating certain sulfates can release sulfur dioxide (SO2), though this process often overlaps with a related technique called roasting.
The Desired Product: The Calcine
The solid material left after the volatile byproducts have been driven off is the primary goal. This resulting calcine now has different chemical and physical properties.
For example, the quicklime produced from calcining limestone is highly reactive, which is essential for making cement and other industrial chemicals.
How Calcination Differs from Other Heat Treatments
The term "calcination" is often confused with other high-temperature processes. The distinction lies in the underlying chemical or physical goal.
Calcination vs. Sintering
Calcination changes a material's chemical composition. It breaks down one compound into another by removing volatile components.
Sintering, as the reference correctly notes, changes a material's physical form. It uses heat to fuse small particles together into a single, solid piece without melting them, increasing its strength and density. The chemical composition remains unchanged.
Calcination vs. Roasting
This is a very common point of confusion. Calcination is typically performed in a controlled or inert atmosphere to cause decomposition.
Roasting, by contrast, is a process that involves a chemical reaction with the furnace's atmosphere, specifically with oxygen. It is a form of oxidation, often used to convert metal sulfide ores into metal oxides.
Calcination vs. Drying
Drying is a low-temperature process that removes physically absorbed water from a substance's surface.
Calcination is a high-temperature process that removes chemically bonded water or other volatile compounds from within the material's crystal structure, requiring significantly more energy to break those chemical bonds.
Understanding the Pitfalls and Context
While powerful, calcination is an industrial process with significant operational considerations that must be managed.
High Energy Consumption
Reaching and maintaining the high temperatures required to break chemical bonds (often 800-1000°C or higher) makes calcination an extremely energy-intensive and costly process.
Atmospheric Control is Crucial
The composition of the gas inside the kiln is critical. Unwanted reactions, such as oxidation from excess air, can occur if the atmosphere is not carefully controlled, leading to an impure final product.
Environmental Emissions
The gaseous byproducts are a primary output. The calcination of limestone for cement production is one of the largest single industrial sources of global CO2 emissions, a critical factor in environmental management and regulation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding calcination allows you to recognize its specific role in creating the materials that shape our world.
- If your primary focus is producing cement or lime: Calcination is the core process used to decompose limestone (CaCO3) into reactive quicklime (CaO) by driving off CO2.
- If your primary focus is preparing a catalyst or adsorbent: Calcination is used to remove water and volatile precursors, creating a pure, high-surface-area material ready for use.
- If your primary focus is strengthening a ceramic or metal powder part: You are thinking of sintering, which compacts particles to increase density, not calcination which changes their chemistry.
Ultimately, calcination is a fundamental tool for chemically altering a solid material by using heat to release its volatile components.
Summary Table:
| Calcination Material | Common Byproduct Gas | Primary Solid Product |
|---|---|---|
| Limestone (CaCO₃) | Carbon Dioxide (CO₂) | Quicklime (CaO) |
| Hydrated Minerals (e.g., Bauxite, Gypsum) | Water Vapor (H₂O) | Anhydrous Oxide |
| Certain Sulfates | Sulfur Dioxide (SO₂) | Metal Oxide |
Need precise thermal processing for your materials?
Calcination is a critical step in producing everything from cement to catalysts. KINTEK specializes in high-temperature laboratory equipment, including furnaces ideal for controlled calcination processes. Our solutions help you achieve the exact chemical transformations you need, with a focus on efficiency and purity.
Whether you are developing new materials, refining ores, or preparing catalysts, KINTEK's expertise in lab equipment can support your R&D and quality control. Let us help you optimize your thermal decomposition processes.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific calcination needs and discover the right equipment for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
People Also Ask
- What are the industrial applications of pyrolysis? Transform Waste into Energy and Valuable Products
- What is the purpose of a calciner? Boost Efficiency in High-Temperature Processing
- What are the zones in rotary kiln in cement production? Master the Core Process for High-Quality Clinker
- What are the types of pyrolysis reactors used in industry? Choose the Right Technology for Your Product
- What equipment is used in pyrolysis? Choosing the Right Reactor for Your Feedstock and Products



















