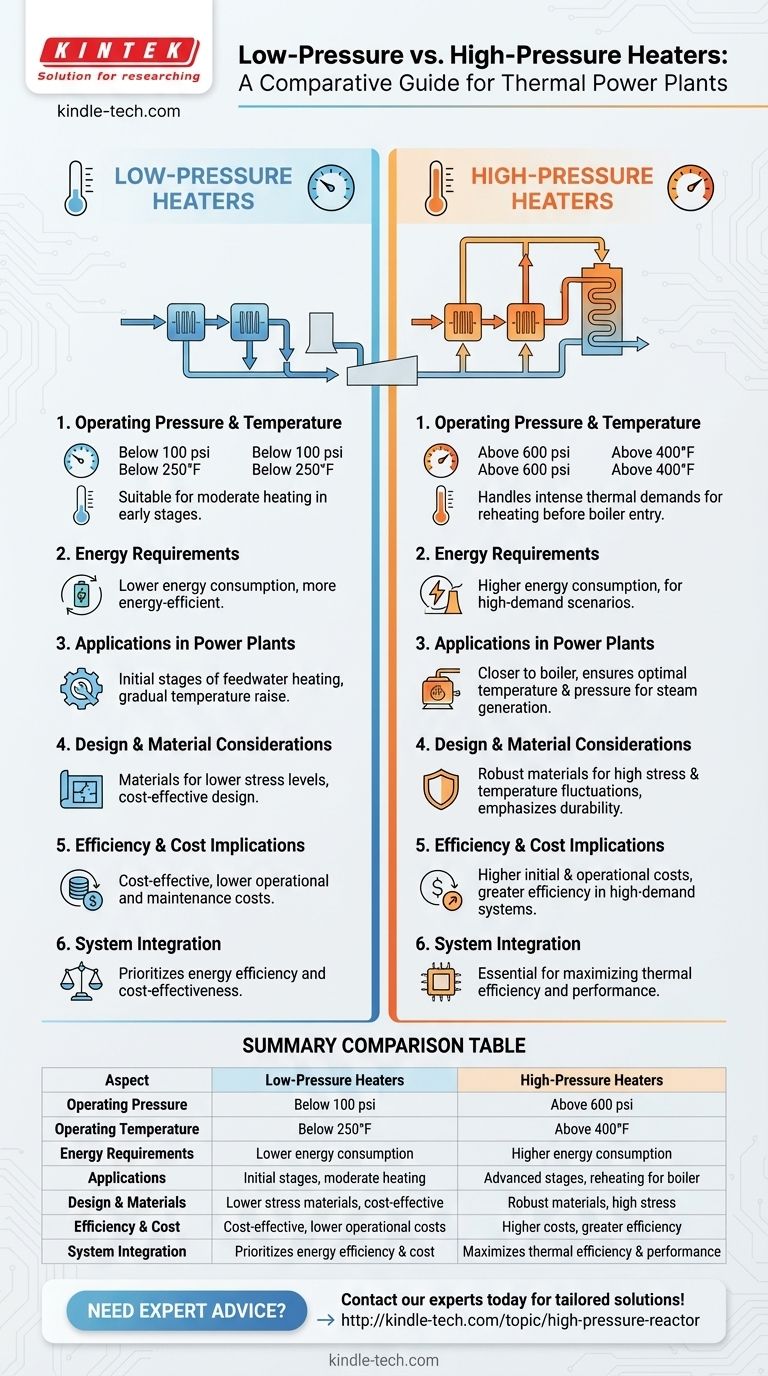
Low-pressure and high-pressure heaters are essential components in thermal power plants, primarily used to heat feedwater before it enters the boiler. The primary difference lies in their operating pressure, temperature, and energy requirements. Low-pressure heaters operate at lower pressures and temperatures, making them more energy-efficient for specific applications, while high-pressure heaters operate at higher pressures and temperatures, enabling them to handle greater thermal loads. Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting the right equipment based on system requirements, energy efficiency, and operational goals.

Key Points Explained:
-
Operating Pressure and Temperature:
- Low-Pressure Heaters: Operate at lower pressures (typically below 100 psi) and temperatures (below 250°F). These conditions make them suitable for applications where moderate heating is required, such as preheating feedwater in the early stages of a thermal cycle.
- High-Pressure Heaters: Operate at significantly higher pressures (often above 600 psi) and temperatures (above 400°F). They are designed to handle the intense thermal demands of advanced stages in the power generation process, such as reheating feedwater before it enters the boiler.
-
Energy Requirements:
- Low-Pressure Heaters: Require less energy to operate due to their lower pressure and temperature settings. This makes them more energy-efficient for applications where excessive heat is unnecessary.
- High-Pressure Heaters: Demand more energy to achieve and maintain higher pressures and temperatures. This increased energy input is necessary to ensure efficient heat transfer in high-demand scenarios.
-
Applications in Power Plants:
- Low-Pressure Heaters: Commonly used in the initial stages of the feedwater heating process. They help raise the temperature of the feedwater gradually, improving overall system efficiency without excessive energy consumption.
- High-Pressure Heaters: Positioned closer to the boiler, these heaters ensure the feedwater reaches the optimal temperature and pressure required for efficient steam generation. They are critical for maximizing thermal efficiency in high-pressure systems.
-
Design and Material Considerations:
- Low-Pressure Heaters: Typically constructed with materials that can withstand lower stress levels, reducing manufacturing costs. Their design focuses on efficiency and reliability under moderate operating conditions.
- High-Pressure Heaters: Built with robust materials capable of withstanding high stress and temperature fluctuations. Their design emphasizes durability and performance under extreme conditions.
-
Efficiency and Cost Implications:
- Low-Pressure Heaters: Offer cost savings in terms of energy consumption and maintenance. Their simpler design and lower operating conditions contribute to reduced operational costs.
- High-Pressure Heaters: While more expensive to operate and maintain, they provide significant efficiency gains in high-demand systems, justifying their higher initial and operational costs.
-
System Integration:
- Low-Pressure Heaters: Often integrated into systems where energy efficiency and cost-effectiveness are prioritized over high thermal output. They work well in conjunction with other low-pressure components.
- High-Pressure Heaters: Integrated into systems requiring high thermal efficiency and performance. They are essential in modern power plants aiming to maximize energy output and minimize waste.
By understanding these key differences, equipment purchasers can make informed decisions based on the specific needs of their thermal systems, balancing energy efficiency, operational requirements, and cost considerations.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Low-Pressure Heaters | High-Pressure Heaters |
|---|---|---|
| Operating Pressure | Below 100 psi | Above 600 psi |
| Operating Temperature | Below 250°F | Above 400°F |
| Energy Requirements | Lower energy consumption, more energy-efficient | Higher energy consumption, designed for high-demand scenarios |
| Applications | Initial stages of feedwater heating, moderate heating needs | Advanced stages, reheating feedwater for boiler entry |
| Design & Materials | Materials for lower stress levels, cost-effective | Robust materials for high stress and temperature fluctuations |
| Efficiency & Cost | Cost-effective, lower operational costs | Higher initial and operational costs, but greater efficiency in high-demand systems |
| System Integration | Prioritizes energy efficiency and cost-effectiveness | Essential for maximizing thermal efficiency and performance |
Need help selecting the right heater for your thermal power plant? Contact our experts today for tailored solutions!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Stainless High Pressure Autoclave Reactor Laboratory Pressure Reactor
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Integrated Manual Heated Plates for Lab Use
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
People Also Ask
- How is high pressure generated in an autoclave? Unlock the Science of Sterilization & Synthesis
- What are autoclaves used in the chemical industry? High-Pressure Reactors for Synthesis & Curing
- What is a high pressure autoclave? A Complete Guide to High-Temp, High-Pressure Reactors
- How high pressure is created in a lab? Master Safe and Precise Pressure Generation
- Does pressure affect melting and boiling? Master Phase Changes with Pressure Control



















