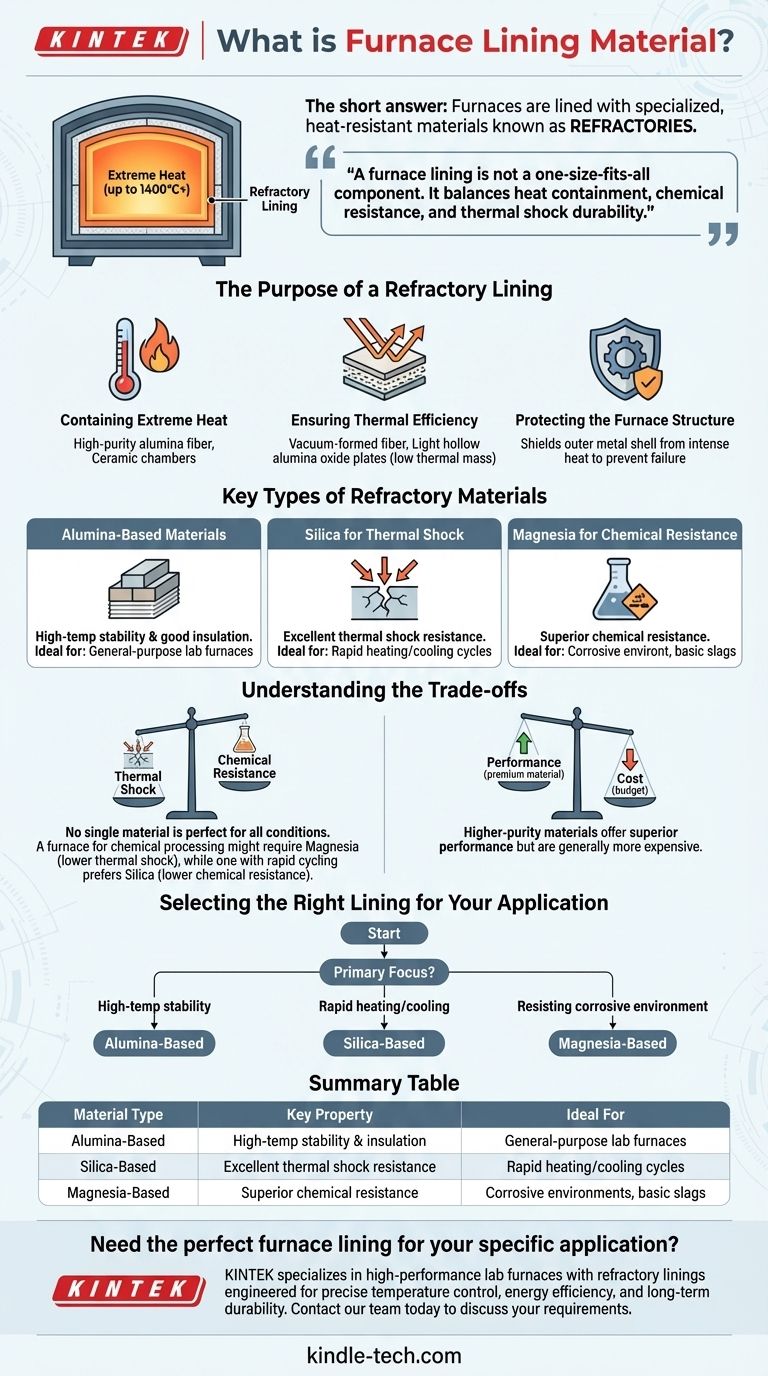
The short answer is that furnaces are lined with specialized, heat-resistant materials known as refractories. The most common types include materials based on alumina (aluminum oxide), silica (silicon dioxide), and magnesia (magnesium oxide), often in the form of fibers, boards, or bricks. The specific material chosen depends entirely on the furnace's maximum temperature, its chemical environment, and how quickly it heats and cools.
The core principle to understand is that a furnace lining is not a one-size-fits-all component. It is a critical engineering choice that balances heat containment, chemical resistance, and thermal shock durability to protect the furnace structure and ensure operational efficiency.

The Purpose of a Refractory Lining
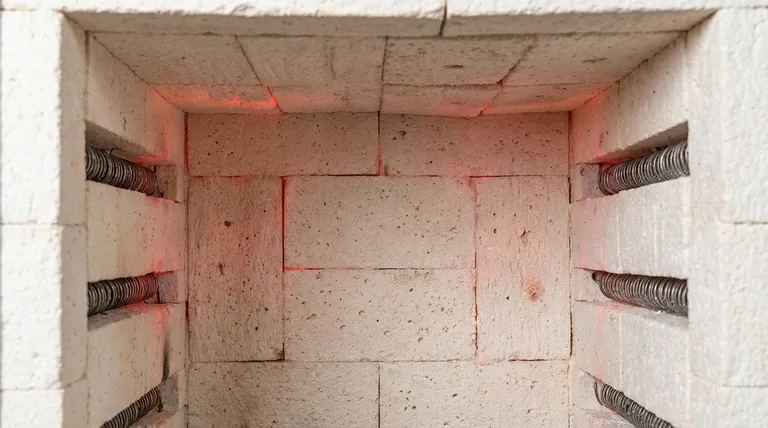
A furnace lining does more than just get hot. It serves as a multi-functional barrier that is essential for the furnace's safety, performance, and longevity.
Containing Extreme Heat
The primary job of the lining is to withstand the furnace's internal operating temperature, which can exceed 1400°C, without melting or degrading.
Materials like high-purity alumina fiber and ceramic chambers are selected specifically for their ability to remain stable at these extreme temperatures.
Ensuring Thermal Efficiency
A good lining minimizes heat loss, which is critical for energy efficiency and stable temperature control.
Materials like vacuum-formed fiber and light hollow aluminum oxide plates have low thermal mass and excellent insulation properties. This means they heat up quickly and don't "store" a lot of heat, preventing it from escaping through the furnace walls.
Protecting the Furnace Structure
The lining acts as a shield, protecting the outer metal shell—typically made of steel—from the intense internal heat.
Without this refractory layer, the structural steel would quickly overheat, deform, and fail.
Key Types of Refractory Materials
The choice of material is dictated by the specific demands of the furnace's application. Each type of refractory offers a unique set of properties.
Alumina-Based Materials
These are excellent general-purpose refractories known for high-temperature stability and good insulation.
High-purity alumina fibers and boards are common choices for electric lab furnaces due to their high service temperature and resistance to cracking or shedding slag.
Silica for Thermal Shock
Silica (silicon dioxide) is the material of choice when a furnace must endure rapid changes in temperature.
If a process requires fast heating and cooling cycles, a silica lining helps prevent the material from cracking due to thermal shock.
Magnesia for Chemical Resistance
Magnesia (magnesium oxide) excels in environments where the lining is exposed to corrosive chemicals, such as basic slags in steelmaking.
It is used specifically for its ability to resist chemical attack at high temperatures, which would quickly erode other types of refractories.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a lining material always involves balancing competing priorities. An expert decision requires understanding these compromises.
Lining vs. Shell
It is crucial to distinguish between the inner lining and the outer structure.
Materials like carbon steel or stainless steel are used for the external shell because of their structural strength at ambient temperatures. They are completely unsuitable for the hot face lining.
Thermal Shock vs. Chemical Resistance
No single material is perfect for all conditions. The very properties that make a material strong in one area can be a weakness in another.
A furnace designed for chemical processing might require a magnesia lining at the expense of optimal thermal shock resistance. Conversely, a furnace with rapid cycling will prioritize a silica lining, even if it has lower chemical resistance.
Performance vs. Cost
Higher-purity materials that offer superior performance, such as high-purity alumina, are generally more expensive. The selection must align with both the technical requirements and the project budget.
Selecting the Right Lining for Your Application
Your choice should be driven by the primary function of your furnace.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature stability and general-purpose use: An alumina-based ceramic fiber or board is a reliable and versatile choice.
- If your primary focus is rapid heating and cooling cycles: A silica-based refractory is necessary to prevent cracking from thermal shock.
- If your primary focus is resisting a corrosive chemical environment: A magnesia-based lining is the correct choice to ensure longevity.
Ultimately, understanding the properties of these key refractory materials is the foundation for designing a safe, efficient, and durable high-temperature system.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Key Property | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Alumina-Based | High-temperature stability & insulation | General-purpose lab furnaces |
| Silica-Based | Excellent thermal shock resistance | Rapid heating/cooling cycles |
| Magnesia-Based | Superior chemical resistance | Corrosive environments, basic slags |
Need the perfect furnace lining for your specific application?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab furnaces with refractory linings engineered for precise temperature control, energy efficiency, and long-term durability. Whether you require the high-temperature stability of alumina, the thermal shock resistance of silica, or the chemical resistance of magnesia, our experts will help you select the ideal solution.
Contact our team today to discuss your furnace requirements and ensure optimal performance and safety for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the primary characteristic of a muffle furnace? Unlock Pure, Contamination-Free Heating
- What construction features contribute to the practicality and reliability of a muffle furnace? Key Design Elements for Lab Success
- How is the ash content determined in a muffle furnace? Master the Gravimetric Analysis Method
- What is done by ashing in muffle furnace? A Guide to Precise Inorganic Content Analysis
- What is the difference between a muffle furnace and a normal furnace? Ensuring Sample Purity with Indirect Heating



















