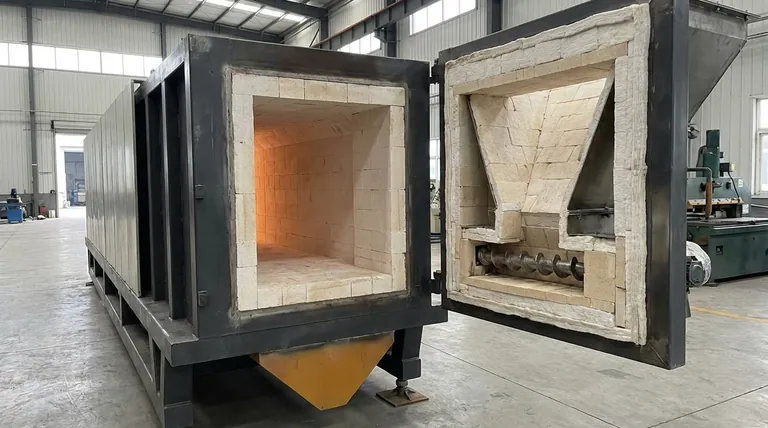
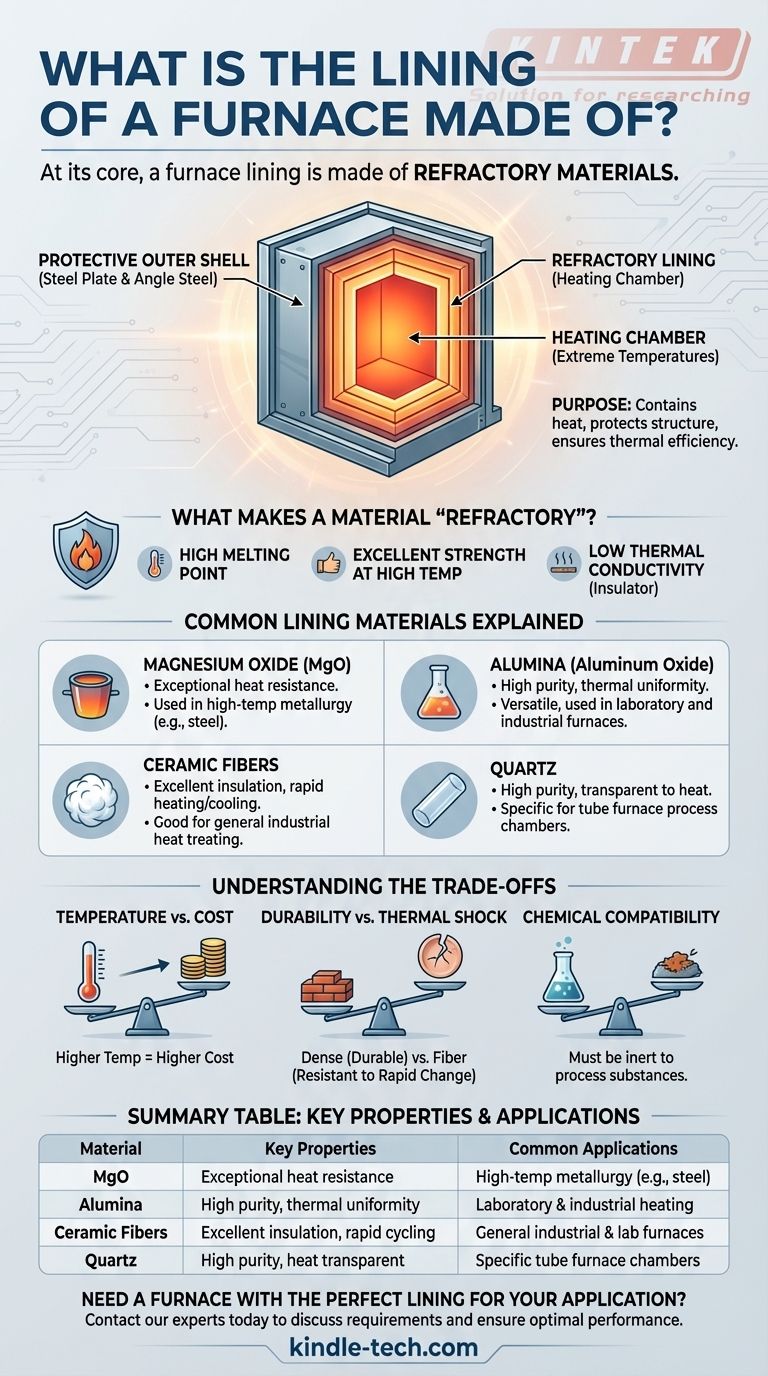
At its core, a furnace lining is made of refractory materials. These are specialized substances, most commonly magnesium oxide (MgO), alumina (aluminum oxide), and various ceramic fibers, chosen specifically for their ability to resist extreme heat and maintain their structural integrity at very high temperatures.
The specific material used for a furnace lining is not a one-size-fits-all solution. The choice is a critical engineering decision dictated by the furnace's maximum operating temperature, its intended application, and the need to balance durability with thermal efficiency.

The Purpose of Refractory Materials
The lining is the functional heart of a furnace's heating chamber. It must contain extreme temperatures while protecting the furnace's external structure. This requires materials with a unique set of properties.
What Makes a Material "Refractory"?
A refractory is a material that is chemically and physically stable at high temperatures. These materials are the only viable option for containing processes that can reach thousands of degrees.
Their key characteristics include high melting points, excellent strength at high temperatures, and low thermal conductivity, which makes them effective insulators.
Common Lining Materials Explained
Different furnace types and applications call for different refractory materials.
- Magnesium Oxide (MgO): Often found in furnaces for steel manufacturing, MgO is prized for its exceptionally high resistance to heat.
- Alumina (Aluminum Oxide): This is a highly versatile material used in many laboratory and industrial furnaces, such as tube furnaces. It can be found as high-purity fiber, light hollow plates, or as the core material for the heating tube itself.
- Ceramic Fibers: These materials, often based on alumina, provide excellent thermal insulation. Their low heat storage capacity allows for rapid heating and cooling cycles without cracking or degrading.
- Quartz: In certain tube furnaces, a high-purity quartz tube serves as the process chamber. While the chamber is surrounded by other insulating refractories, the quartz tube is the component directly containing the heat and the sample.
How the Lining Integrates into Furnace Construction
The lining doesn't exist in isolation. It works as part of a system to provide structural integrity, thermal containment, and operational efficiency.
The Protective Outer Shell
The entire furnace assembly is housed within a heavy-duty outer shell, typically fabricated from welded angle steel and high-quality steel plate. This shell provides the primary structural support and a cool, safe exterior.
Forming the Heating Chamber
The refractory lining sits inside the steel shell and forms the actual heating chamber. In a box furnace, this might be a brick-like construction. In a tube furnace, the heating chamber is often a cylinder made of alumina ceramic fiber that surrounds the central process tube.
The Critical Role of Insulation
The primary function of the lining is to keep the heat inside the chamber. This ensures the furnace can reach and maintain its target temperature efficiently and protects the outer shell and surrounding environment from the extreme internal heat.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a furnace lining involves balancing competing priorities. No single material is perfect for every situation.
Temperature vs. Cost
As a general rule, materials capable of withstanding higher temperatures are more expensive. High-purity alumina or specialized refractory alloys cost significantly more than standard ceramic fibers.
Durability vs. Thermal Shock
Dense, brick-like refractories can be very durable against physical wear. However, they can be brittle and prone to cracking during rapid temperature changes (thermal shock). Lighter ceramic fibers excel at resisting thermal shock but may be less resistant to physical abrasion.
Chemical Compatibility
The lining material must be chemically inert to the substances being heated inside the furnace. An incompatible lining can contaminate the sample or be corroded by the process, leading to premature furnace failure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The ideal lining is determined entirely by the furnace's intended use.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature metallurgy (e.g., steel): Your furnace will likely rely on robust materials like magnesium oxide (MgO) for maximum heat containment.
- If your primary focus is controlled laboratory research: You will encounter high-purity alumina, ceramic fibers, and quartz tubes, which provide excellent thermal uniformity and a clean environment.
- If your primary focus is general industrial heat treating: Vacuum-formed ceramic fiber linings offer an effective balance of insulation, rapid cycling, and cost-efficiency.
Ultimately, the furnace lining is a critical component where the material is precisely engineered to meet the extreme demands of its specific application.
Summary Table:
| Material | Key Properties | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Magnesium Oxide (MgO) | Exceptional heat resistance | High-temperature metallurgy (e.g., steel) |
| Alumina (Aluminum Oxide) | High purity, thermal uniformity, versatile | Laboratory tube furnaces, industrial heating |
| Ceramic Fibers | Excellent insulation, rapid heating/cooling | General industrial heat treating, lab furnaces |
| Quartz | High purity, transparent to heat | Specific tube furnace process chambers |
Need a Furnace with the Perfect Lining for Your Application?
The right refractory lining is critical for your process's success, whether you're in high-temperature research, metallurgy, or industrial heat treatment. KINTEK specializes in providing laboratory equipment with precisely engineered furnace linings tailored to your specific needs for temperature, durability, and chemical compatibility.
Contact our experts today to discuss your requirements and ensure you get a furnace that delivers optimal performance, efficiency, and longevity.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
People Also Ask
- What is the meaning of rotary furnace? Achieve Superior Uniformity in Continuous Heat Treatment
- How does a rotary extractor work? Master Continuous High-Volume Solid Processing
- What are the zones in rotary kiln in cement production? Master the Core Process for High-Quality Clinker
- How are composites processed using sintering? Engineered Material Solutions Through Advanced Thermal Bonding
- What is the principle of rotary kiln? Mastering Continuous Thermal Processing



















