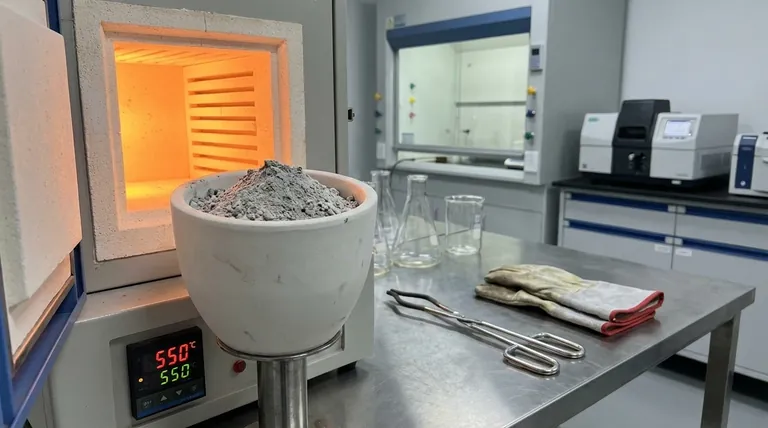
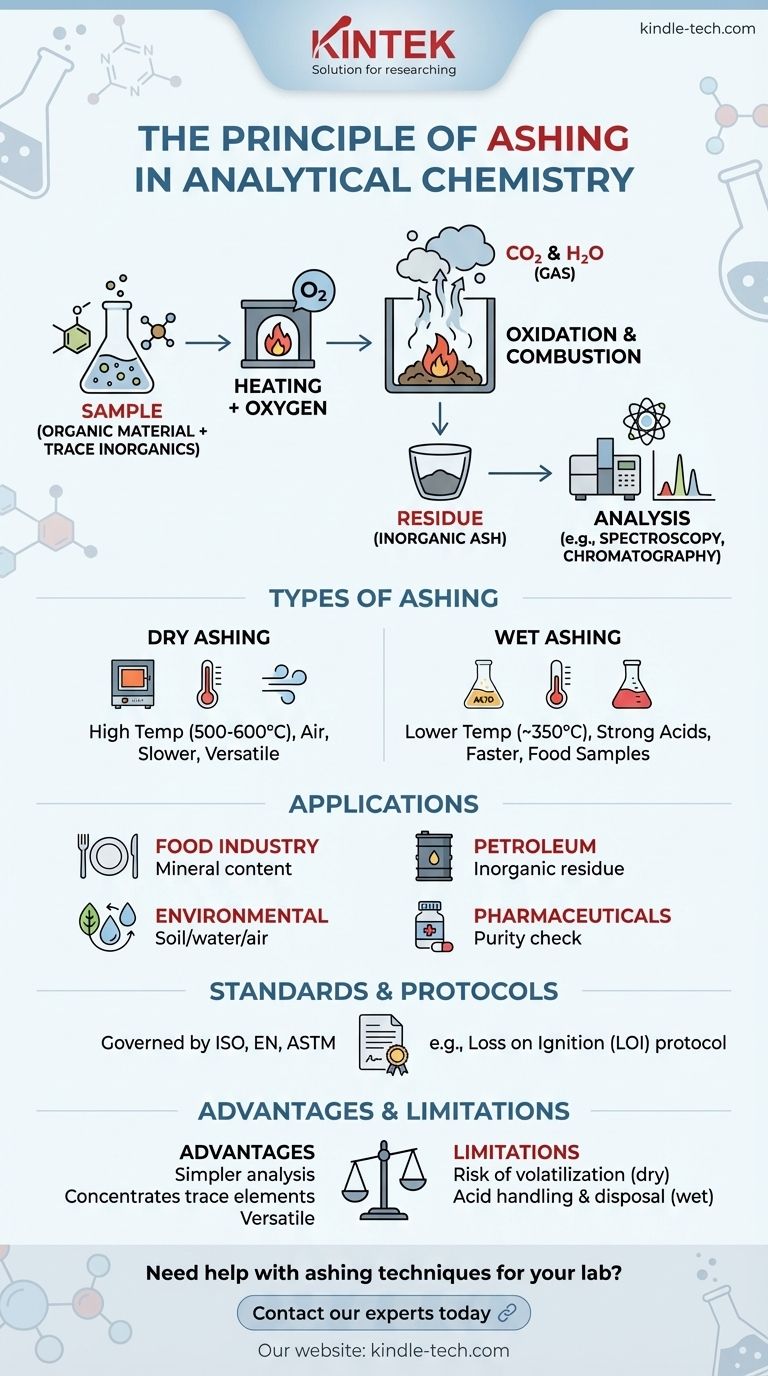
Ashing is a fundamental process in analytical chemistry used to remove organic material from a sample, leaving behind inorganic, non-combustible ash for further analysis. This technique is crucial for preconcentrating trace substances and determining elemental composition. The process involves heating a sample in the presence of oxygen, causing organic compounds to combust and oxidize, while inorganic residues remain as ash. Ashing is widely applied in industries such as food, petroleum, and environmental testing, and it can be governed by international standards like ISO, EN, or ASTM. The resulting ash can be analyzed using techniques like chromatography or spectroscopy to determine the sample's elemental makeup.

Key Points Explained:
-
Definition and Purpose of Ashing:
- Ashing is the process of heating a sample to remove organic material, leaving behind inorganic ash.
- The primary purpose is to preconcentrate trace substances for chemical or optical analysis, such as chromatography or spectroscopy.
- It is widely used in industries like food, petroleum, and environmental testing to determine elemental composition.
-
Mechanism of Ashing:
- The sample is heated in the presence of oxygen, causing organic compounds to combust and oxidize.
- This oxidation process breaks down organic materials into gases (e.g., CO₂ and H₂O), leaving behind inorganic residues (ash).
- The ash consists of non-combustible compounds, such as metal oxides, salts, and minerals, which can be analyzed for their elemental composition.
-
Types of Ashing:
- Dry Ashing: Involves heating the sample in a muffle furnace at high temperatures (typically 500–600°C) in the presence of air. This method is slower but suitable for many types of samples.
- Wet Ashing: Uses strong acids (e.g., nitric acid or sulfuric acid) to oxidize organic material at lower temperatures (around 350°C). This method is faster and often used for food samples.
- Both methods aim to achieve complete combustion of organic material, but the choice depends on the sample type and analysis requirements.
-
Applications of Ashing:
- Food Industry: Used to determine ash content, which indicates the mineral content in food products.
- Petroleum Industry: Helps analyze the inorganic residue in fuels and lubricants.
- Environmental Testing: Used to assess the mineral content in soil, water, and air samples.
- Pharmaceuticals: Ensures the purity of raw materials and finished products by analyzing inorganic residues.
-
Standards and Protocols:
- Ashing processes are often governed by international standards such as ISO, EN, or ASTM.
- These standards define specific procedures, including temperature ranges, heating durations, and sample preparation methods.
- For example, Loss on Ignition (LOI) is a common protocol where samples are weighed before and after ashing to determine mass reduction.
-
Advantages of Ashing:
- Removes unwanted organic material, simplifying the analysis of inorganic components.
- Provides a concentrated sample of trace elements, improving the sensitivity of subsequent analytical techniques.
- Can be applied to a wide range of sample types, from solids to liquids.
-
Limitations and Considerations:
- High temperatures in dry ashing can cause volatilization of certain elements, leading to inaccurate results.
- Wet ashing, while faster, requires careful handling of corrosive acids and proper disposal of chemical waste.
- The choice of ashing method must consider the sample's properties and the elements of interest.
-
Practical Example: Wet Ashing in Food Analysis:
- A food sample is heated at 350°C in the presence of acids until organic material is fully oxidized.
- The remaining ash is weighed, and the ash content is calculated based on the weight difference before and after the process.
- This method is particularly useful for determining mineral content in foods like cereals, dairy products, and beverages.
By understanding the principles and applications of ashing, analysts can effectively prepare samples for accurate elemental analysis, ensuring reliable results in various industries.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | Heating a sample to remove organic material, leaving inorganic ash. |
| Purpose | Preconcentrate trace substances for chemical or optical analysis. |
| Types | Dry Ashing (500–600°C) and Wet Ashing (350°C with acids). |
| Applications | Food, petroleum, environmental testing, pharmaceuticals. |
| Standards | ISO, EN, ASTM (e.g., Loss on Ignition protocol). |
| Advantages | Simplifies inorganic analysis, improves sensitivity, versatile application. |
| Limitations | Risk of volatilization in dry ashing; acid handling in wet ashing. |
Need help with ashing techniques for your lab? Contact our experts today for tailored solutions!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How hot does a furnace get in Celsius? From 1100°C to 1800°C for Your Lab Needs
- What is the range of a muffle furnace? Choose the Right Temperature for Your Lab
- What is the power requirement for a muffle furnace? Ensure Safe and Efficient Operation
- What is the difference between a lab oven and a muffle furnace? A Guide to Temperature Applications
- What is the temperature range of a furnace? From 1100°C to Over 2000°C Explained



















