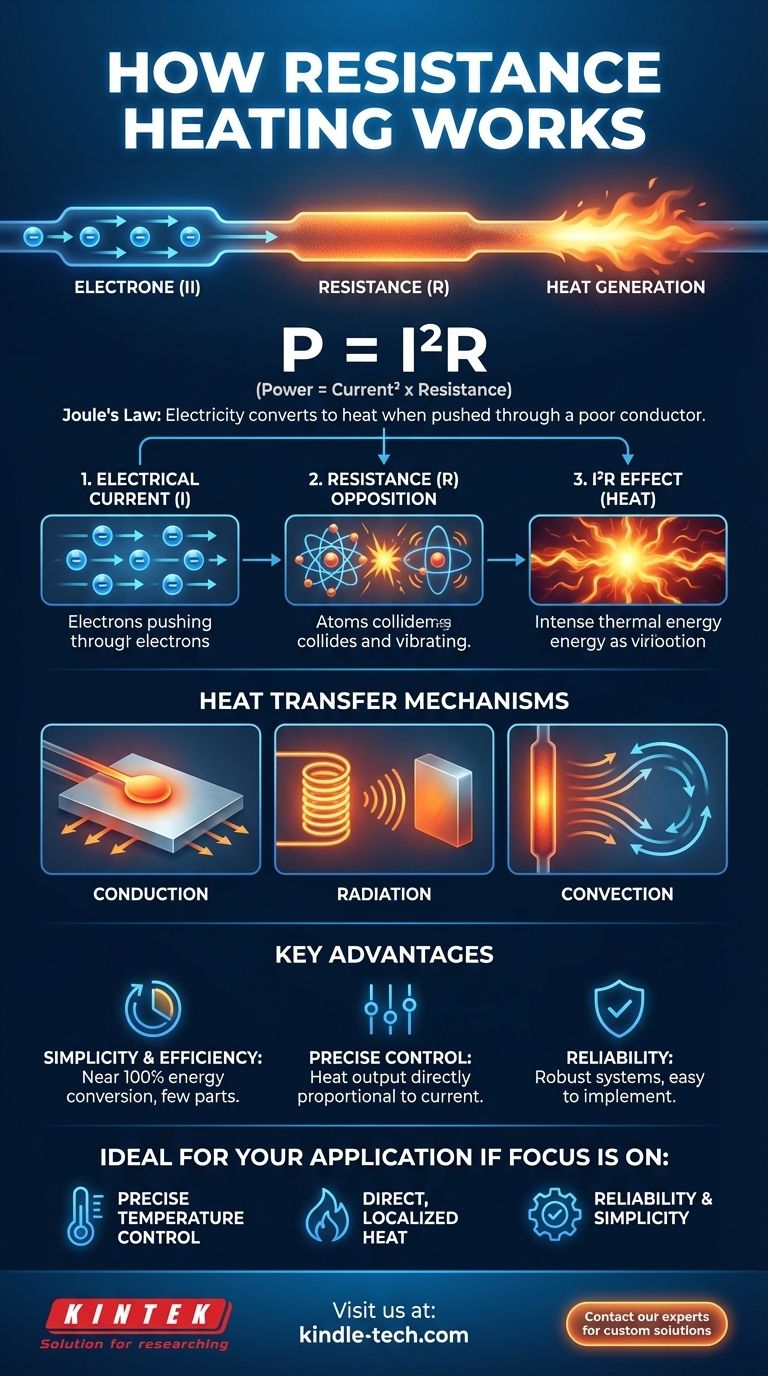
At its core, resistance heating is the process of generating heat by passing an electric current through a material that resists its flow. This principle, known as Joule's law or the I²R effect, is a fundamental method for converting electrical energy directly into thermal energy. The material's opposition to the electrical current causes friction at a microscopic level, releasing energy in the form of heat.
The central concept is simple: electricity is converted into heat when it is forced to travel through a poor conductor. The more the material resists the flow of electrons, the more heat it will generate.

The Fundamental Principle: Joule Heating
To understand how resistance heating works, we must look at the relationship between electrical current, material resistance, and the energy they produce.
The Role of Electrical Current (I)
An electric current is simply the flow of electrons through a material. A power source provides the voltage necessary to push these electrons through a circuit.
The Importance of Resistance (R)
Resistance is a material's inherent opposition to the flow of electric current. At the atomic level, as electrons are pushed through the material, they collide with its atoms.
These collisions transfer kinetic energy from the electrons to the atoms, causing the atoms to vibrate more intensely. This increased atomic vibration is what we perceive as heat.
The I²R Effect
The amount of heat generated is defined by the formula P = I²R, where P is power (heat), I is current, and R is resistance. This means the heat produced increases exponentially with the current and linearly with the resistance.
Materials chosen for heating elements, such as specific metal alloys or ceramics, are selected precisely because they have a high electrical resistance.
How It Works in Practice
A practical resistance heating system consists of a few key components and relies on basic principles of heat transfer to be effective.
The Heating Element
This is the core component. It is a specially designed material, often a high-temperature-resistant alloy, that has both high electrical resistance and the ability to withstand extreme temperatures without degrading.
When current passes through this element, it glows hot, becoming the source of thermal energy for the system.
Heat Transfer Mechanisms
Once the element is hot, the heat must be transferred to the object or space you intend to warm. This happens in three primary ways:
- Conduction: Heat transfers through direct physical contact, like a heating element touching a metal plate.
- Radiation: Heat is emitted as electromagnetic waves, warming objects without direct contact, similar to how the sun warms the Earth.
- Convection: Heat is transferred through the movement of a fluid (like air or water). A heating element warms the air around it, and that warm air then circulates to heat a room.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, resistance heating has distinct advantages and limitations that make it suitable for specific applications.
Key Advantage: Simplicity and Efficiency
Resistance heating systems are mechanically simple, often with no moving parts. The conversion of electrical energy to heat at the point of use is nearly 100% efficient, as virtually all the resisted electrical energy becomes thermal energy.
Key Advantage: Precise Control
The heat output is directly and immediately proportional to the amount of electrical current applied. This allows for extremely precise and responsive temperature control.
Common Limitation: Heating Time
In systems using indirect heating—where the element heats a chamber, which then heats the target object via convection—the process can be slow. It takes time for the entire chamber and the air within it to reach the target temperature.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Understanding these principles allows you to determine where resistance heating is the most effective solution.
- If your primary focus is precise temperature control: Resistance heating is ideal due to its direct and instantaneous response to electrical input.
- If your primary focus is direct, localized heat: This method excels at applying heat exactly where it's needed through elements designed for conduction or radiation.
- If your primary focus is reliability and simplicity: The lack of complex or moving parts makes resistance heating systems exceptionally robust and easy to implement.
Ultimately, resistance heating is a foundational technology that provides a reliable and controllable source of heat for countless applications.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Core Principle | Joule Heating (I²R Effect) |
| Heat Generation | Current flow through a high-resistance material |
| Primary Advantage | Near 100% efficiency & precise temperature control |
| Heat Transfer Methods | Conduction, Radiation, Convection |
| Ideal For | Applications requiring reliability and localized heat |
Need a reliable and precise heating solution for your lab or process? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including custom resistance heating systems. Our expertise ensures you get the exact thermal control your application demands, enhancing efficiency and reproducibility. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube Tubular Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What are the properties of molybdenum heating element? Choose the Right Type for Your Furnace Atmosphere
- What is the temperature range of molybdenum disilicide heating elements? Choose the Right Grade for Your High-Temp Needs
- What is the temperature range of a MoSi2 heating element? Unlock 1900°C Performance for Your Lab
- What is the thermal expansion coefficient of molybdenum disilicide? Understanding its role in high-temperature design
- What material is used for furnace heating? Select the Right Element for Your Process



















