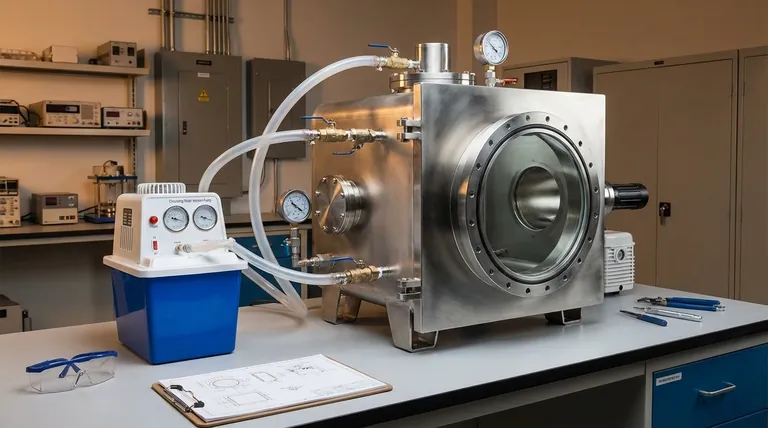
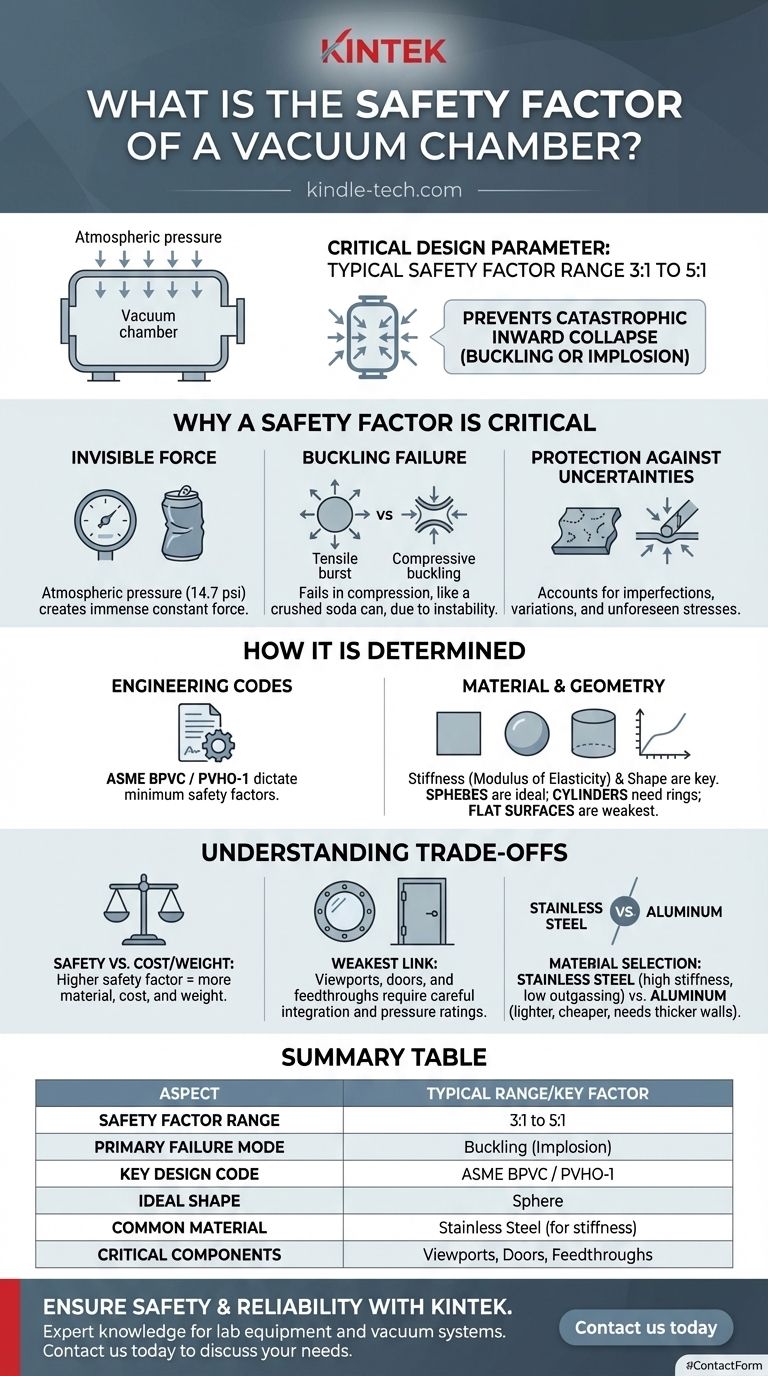
In engineering practice, a vacuum chamber does not have one single, universally mandated safety factor. Instead, the safety factor is a critical design parameter determined by engineering codes, the materials used, and the chamber's geometry, typically resulting in a factor of safety between 3:1 and 5:1 against material yielding or buckling failure under external atmospheric pressure. This ensures the vessel can withstand forces far greater than it will ever experience in operation.
The core purpose of a vacuum chamber's safety factor is not to prevent it from bursting, but to prevent a catastrophic inward collapse, known as buckling or implosion. This is a fundamentally different failure mode driven by the immense, constant force of external atmospheric pressure.

Why a Safety Factor is Critical for Vacuum Chambers
The Invisible Force of the Atmosphere
At sea level, the atmosphere exerts a pressure of approximately 14.7 pounds per square inch (psi), or 1 bar, on every surface. While this seems small, it creates an enormous total force on the large surface area of a vacuum chamber.
For example, a flat 12x12 inch section of a chamber wall experiences a constant inward force of over 2,100 pounds. The safety factor ensures the chamber can resist this crushing force without deforming.
The Primary Failure Mode: Buckling
Unlike a pressurized tank that fails in tension (bursting outward), a vacuum vessel fails in compression. When the compressive stress from external pressure exceeds the chamber's structural stability, it will suddenly and catastrophically collapse inward.
This failure, known as buckling, is an instability problem. Think of crushing an empty soda can—it holds its shape until a critical point, then collapses instantly. The safety factor provides a buffer against reaching this critical buckling point.
What the Safety Factor Protects Against
The designed safety factor is a margin of safety that accounts for real-world uncertainties that could compromise the chamber's integrity.
These include minor imperfections in the material, variations in wall thickness from manufacturing, and unforeseen stresses during handling or operation.
How the Safety Factor is Determined
The Role of Engineering Codes
For high-risk or human-occupied applications, vacuum chamber design is governed by strict codes. The most prominent is the ASME (American Society of Mechanical Engineers) Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code (BPVC).
Specifically, ASME PVHO-1 (Pressure Vessels for Human Occupancy) provides rigorous standards that are often adopted for high-performance scientific chambers even when not used for humans. These codes dictate the minimum required safety factors.
Material Properties and Geometry
The calculation for buckling resistance is complex, depending heavily on the material's stiffness (Modulus of Elasticity) and the chamber's shape.
Stiffness is often more important than pure strength for preventing buckling. This is why geometry is paramount:
- Spheres are the ideal shape for resisting external pressure.
- Cylinders are very common but require sufficient wall thickness or external stiffening rings to prevent collapse.
- Flat surfaces, such as doors and viewports, are the weakest points and require significant reinforcement or thickness to avoid being pushed in.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Safety vs. Cost and Weight
A higher safety factor requires thicker walls or more reinforcement. This directly increases the amount of material needed, which in turn raises the cost, weight, and manufacturing complexity of the chamber.
Engineering for a stationary lab system involves a different set of trade-offs than designing a lightweight chamber for a space application.
The Weakest Link: Viewports and Feedthroughs
A vacuum chamber is only as strong as its weakest component. The safety factor of the overall system must account for features like doors, seals, and ports.
Glass or acrylic viewports, electrical feedthroughs, and access doors are all potential points of failure. These components have their own pressure ratings and must be chosen and integrated carefully to maintain the safety of the entire vessel.
Material Selection
Stainless steel is a common choice for its high stiffness, strength, and excellent vacuum properties (low outgassing). However, aluminum may be used to reduce weight or cost.
Because aluminum is less stiff than steel, an aluminum chamber must have significantly thicker walls or more structural reinforcement to achieve the same safety factor against buckling as a steel one.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing or designing a vacuum chamber requires balancing safety with operational requirements. Your primary goal will determine your focus.
- If your primary focus is fundamental research: Prioritize chambers built to established codes like ASME, as operational reliability and the safety of personnel and equipment are paramount.
- If your primary focus is industrial production: Emphasize durability and designs that minimize stress at high-use points like doors and seals to ensure a long service life and repeatable performance.
- If you are designing a custom chamber: Always engage a qualified mechanical engineer to perform a structural analysis, such as a Finite Element Analysis (FEA), to definitively verify the design against buckling failure before fabrication.
Ultimately, a vacuum chamber's safety factor is the engineered guarantee against the immense, invisible force of the atmosphere.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Typical Range / Key Factor |
|---|---|
| Safety Factor Range | 3:1 to 5:1 (against yield/buckling) |
| Primary Failure Mode | Buckling (Implosion) |
| Key Design Code | ASME BPVC / PVHO-1 |
| Ideal Shape | Sphere |
| Common Material | Stainless Steel (for stiffness) |
| Critical Components | Viewports, Doors, Feedthroughs |
Ensure the safety and reliability of your vacuum processes with KINTEK.
Designing or selecting a vacuum chamber requires expert knowledge to balance safety factors, material selection, and operational demands. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment, including vacuum systems and components. Our expertise ensures you get a solution that is safe, durable, and perfectly suited for your research or industrial application.
Contact us today to discuss your specific needs and let our engineers help you build a secure foundation for your work.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Circulating Water Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- Oil Free Diaphragm Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- Benchtop Laboratory Vacuum Freeze Dryer
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
People Also Ask
- What types of gases can a water circulating vacuum pump handle? Safely Manage Flammable, Condensable & Dirty Gases
- What determines the vacuum degree achievable by a water circulating vacuum pump? Unlock the Physics of Its Limits
- How does a water circulating vacuum pump operate? Discover the Efficient Liquid Piston Principle
- What can I use a vacuum pump for? Powering Industrial Processes from Packaging to Automation
- What is the purpose of the compression chamber in a vacuum pump? The Heart of Vacuum Generation



















