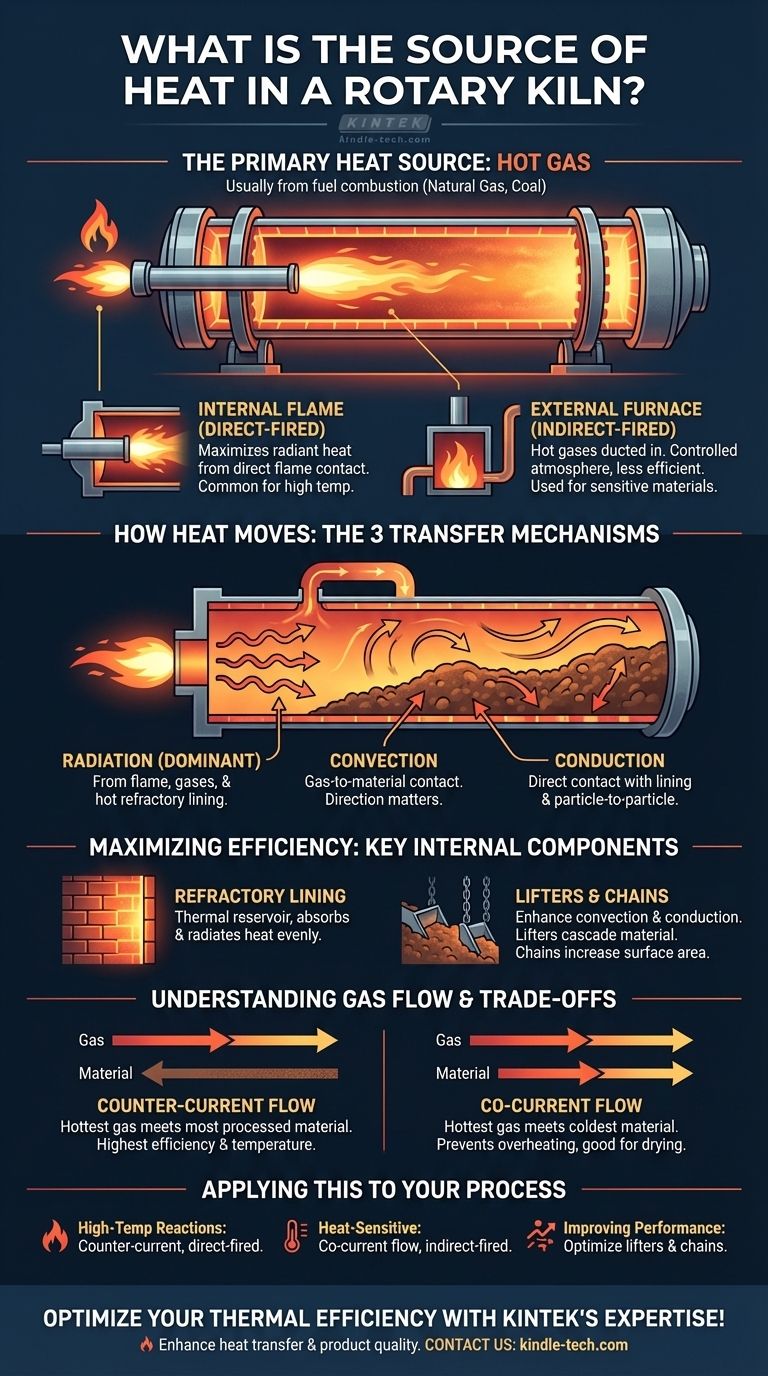
The primary source of heat in a rotary kiln is hot gas. This gas is almost always generated by the combustion of fuel, such as natural gas or coal. The flame and resulting hot gases can be generated either directly inside the kiln vessel by a large burner-pipe or in a separate, external furnace before being ducted into the kiln.
A rotary kiln’s function is not just to generate heat, but to transfer that heat into a moving bed of material with maximum efficiency. Therefore, the true "source" of processing heat involves the entire system—the fuel burner, the gas flow, the refractory lining, and internal heat exchangers—all working together to manage radiation, convection, and conduction.

Generating the Heat: The Burner System
A rotary kiln is fundamentally a thermal processing device. The initial energy input comes from the combustion of fuel, which can be configured in one of two primary ways.
The Internal Flame (Direct-Fired)
This is the most common configuration. A large, powerful burner-pipe is mounted at one end of the kiln, projecting a long, controlled flame down the central axis.
This method directly exposes the material and the kiln's internal surfaces to the flame, maximizing radiant heat transfer from the combustion process itself.
The External Furnace (Indirect-Fired)
In some applications, hot gases are generated in a separate, stationary furnace and then piped into the kiln.
This approach is used when direct flame impingement on the material is undesirable. It allows for greater control over the atmosphere inside the kiln but is generally less common and less thermally efficient than direct firing.
How Heat Moves: The Three Transfer Mechanisms
Once heat is generated, it must be transferred to the material being processed. This occurs through three distinct but interconnected mechanisms.
Radiation: The Dominant Force
Heat radiates from the flame, the hot combustion gases, and, critically, from the hot refractory brick lining the kiln's inner shell. As the kiln rotates, the refractory heats up as it passes through the hot gas space and then radiates that heat down onto the material bed.
Convection: Gas-to-Material Contact
Convection is the transfer of heat from the hot gases as they flow over the surface of the material bed. The direction of this gas flow—either with or against the flow of material—is a critical design parameter.
Conduction: Direct Physical Touch
Heat is also conducted directly to the material where it makes physical contact with the hot refractory wall. Furthermore, heat conducts between the individual particles within the processing bed itself.
Maximizing Efficiency: Key Internal Components
A bare, rotating tube is an inefficient heat exchanger. Kilns employ sophisticated internal components to dramatically improve the heat transfer process.
The Refractory Lining
The refractory brick lining the kiln's steel shell does more than just protect the steel from extreme temperatures. It acts as a thermal reservoir, absorbing massive amounts of heat and radiating it evenly into the material bed.
Internal Heat Exchangers (Lifters & Chains)
These components are designed to enhance convection and conduction.
- Lifters are fins or scoops that pick up material and cascade it through the hot gas stream, dramatically increasing the surface area exposed to convective heat transfer.
- Chains are curtains of heavy chain that hang in the gas stream, typically at the cooler feed end of the kiln. They become coated in material and serve as an enormous surface area for heat exchange between the gas and the solid feed.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Gas Flow Direction
The relationship between the flow of hot gas and the flow of material fundamentally changes the kiln's thermal profile.
Counter-Current Flow
The hot gas is introduced at the material discharge end and flows uphill against the moving material. This is the most common and thermally efficient setup. It ensures the hottest gases meet the most processed material, allowing for the highest possible final product temperatures.
Co-Current Flow
The hot gas is introduced at the material feed end and flows in the same direction. This is often used for drying or for processing heat-sensitive materials. The hottest, most intense gas meets the coldest, wettest material, which provides a protective cooling effect and prevents thermal shock or damage.
Applying This to Your Process
Your choice of kiln design and operation depends entirely on the material you are processing and your desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is maximum thermal efficiency for high-temperature reactions (like cement clinkering): A direct-fired, counter-current kiln with an extensive chain system and optimized lifters is the standard for maximizing heat transfer.
- If your primary focus is processing heat-sensitive or volatile materials (like drying sludges): A co-current flow configuration is often preferred to prevent overheating or uncontrolled reactions at the material feed end.
- If your primary focus is improving an existing kiln's performance: Evaluating and optimizing internal heat exchangers, like lifters and chains, often yields the greatest improvement in heat transfer and overall efficiency.
Understanding how heat is generated, transferred, and managed is the key to mastering the performance of any rotary kiln system.
Summary Table:
| Heat Source & Transfer Method | Key Features | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Direct-Fired (Internal Flame) | Burner inside kiln, maximizes radiant heat | Cement clinkering, high-temperature calcination |
| Indirect-Fired (External Furnace) | Separate furnace, controlled atmosphere | Processing sensitive or volatile materials |
| Radiation | Heat from flame, gases, and refractory lining | Dominant in high-temperature zones |
| Convection | Heat transfer via gas flow over material bed | Enhanced by lifters and chains |
| Conduction | Direct contact with hot refractory or material particles | Critical in material bed heating |
Optimize your rotary kiln’s thermal efficiency with KINTEK’s expertise! Whether you're processing cement, minerals, or specialty materials, our lab equipment and consumables are designed to enhance heat transfer, reduce energy costs, and improve product quality. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your laboratory’s unique thermal processing needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
People Also Ask
- What is the principle of rotary kiln? Mastering Continuous Thermal Processing
- What equipment is used in pyrolysis? Choosing the Right Reactor for Your Feedstock and Products
- What are the industrial applications of pyrolysis? Transform Waste into Energy and Valuable Products
- What are the products of pyrolysis of wood? A Guide to Biochar, Bio-oil, and Syngas Yields
- What biomass is used in pyrolysis? Selecting the Optimal Feedstock for Your Goals



















