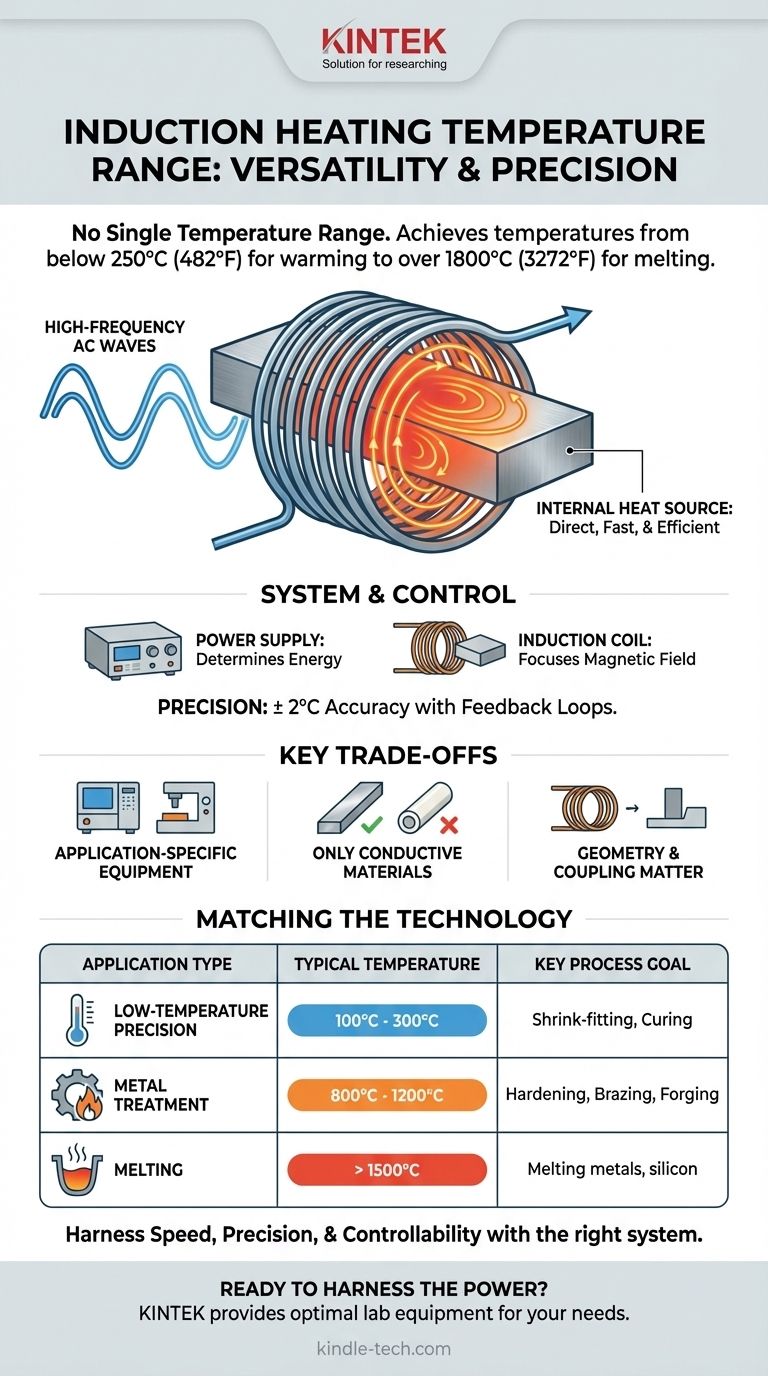
There is no single temperature range for induction heating. The technology is highly versatile, capable of everything from gentle warming for shrink-fitting bearings at temperatures below 250°C (482°F) to extreme heat for melting metals in industrial furnaces that can exceed 1800°C (3272°F). The achievable temperature is not a fixed property but a direct result of the equipment's design and the material being heated.
The core takeaway is that induction heating's true value lies not in a specific temperature range, but in its exceptional speed, precision, and controllability across a vast thermal spectrum. The specific range is engineered for the application.

How Induction Heating Achieves Its Temperature
Induction heating is fundamentally different from conventional methods. Instead of applying heat from an external source like a flame or heating element, it generates heat directly inside the material itself. This principle is key to its speed and efficiency.
The Core Mechanism: An Internal Heat Source
The process begins with a coil that has a high-frequency alternating current (AC) flowing through it. This AC creates a powerful and rapidly changing magnetic field around the coil.
When an electrically conductive workpiece, such as a piece of metal, is placed within this field, the magnetic field induces electrical currents within the part. These circulating currents are known as eddy currents.
The material's natural resistance to the flow of these eddy currents generates intense, localized heat. Because this happens inside the part, heating is incredibly fast and efficient, with no wasted energy heating the surrounding air.
The Role of System Design
The final temperature is determined by the system's components. The power supply dictates the amount of energy available, while the design of the induction coil focuses the magnetic field onto the specific area of the workpiece that needs heating. A more powerful system with a highly coupled coil can deliver more energy, resulting in higher temperatures achieved more quickly.
Precision and Control
Modern induction systems offer extremely fine control. Using feedback from temperature probes (such as K-type thermocouples), the system can self-regulate to maintain a target temperature with high accuracy, often within ± 2°C. Many systems also feature time-based controls, allowing for consistent, repeatable heating cycles measured in minutes or even seconds.
Understanding the Key Trade-offs
While powerful, induction heating is not a universal solution. Its effectiveness is highly dependent on matching the right equipment to the specific material and process goal.
Equipment is Application-Specific
An induction heater designed for low-temperature applications, like mounting bearings at 110°C, is fundamentally different from an induction furnace built to melt steel. The power supply, coil construction, and control systems are engineered for vastly different thermal ranges and cannot be used interchangeably.
It Only Works on Conductive Materials
The primary requirement for induction heating is that the material must be electrically conductive. It is exceptionally effective on metals and some semiconductors. However, it cannot be used to directly heat non-conductive materials like most ceramics, plastics, or glass.
Geometry and Coupling Matter
The efficiency of the heating process depends heavily on the shape of the workpiece and its proximity to the coil—a factor known as coupling. Irregularly shaped parts or parts that cannot be placed close to the coil may heat less efficiently or unevenly.
Matching the Technology to Your Goal
Choosing the right induction system requires a clear understanding of your final objective. The process is defined by the temperature you need to achieve for a specific task.
- If your primary focus is low-temperature precision (e.g., shrink-fitting, curing): You need a system with precise temperature control and feedback, typically operating in the 100°C to 300°C range.
- If your primary focus is metal treatment (e.g., hardening, brazing, forging): You require a mid-to-high power system capable of rapidly reaching temperatures between 800°C and 1200°C.
- If your primary focus is melting materials (e.g., steel, silicon): You need a specialized, high-power induction furnace designed to safely exceed the material's melting point, often operating well above 1500°C.
Ultimately, induction heating offers unparalleled control over temperature, but only when the system is correctly specified for the job at hand.
Summary Table:
| Application Type | Typical Temperature Range | Key Process Goal |
|---|---|---|
| Low-Temperature Precision | 100°C - 300°C | Shrink-fitting, Curing |
| Metal Treatment | 800°C - 1200°C | Hardening, Brazing, Forging |
| Melting | > 1500°C | Melting metals, silicon |
Ready to Harness the Power of Induction Heating?
Induction heating's versatility means the right system must be precisely matched to your material and process goals. KINTEK specializes in providing the optimal lab equipment and consumables for your specific laboratory needs.
Our experts will help you select the perfect induction heating solution to achieve the speed, precision, and controllability your work demands.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your application and discover how we can enhance your lab's efficiency and results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Anti-Cracking Press Mold for Lab Use
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Aluminum Oxide Al2O3 Heat Sink for Insulation
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the maximum temperature for a SiC heating element? Unlock the Key to Longevity and Performance
- What is silicon carbide rod heated to high temperature used as? A Premier Heating Element for Extreme Environments
- What are the uses of silicon carbide rod? The Ultimate Heating Solution for Extreme Temperatures
- What is SiC melting point? Discover the Extreme Thermal Stability of Silicon Carbide
- What are silicon carbide heating elements used for? Reliable High-Temp Heating for Industrial Processes



















