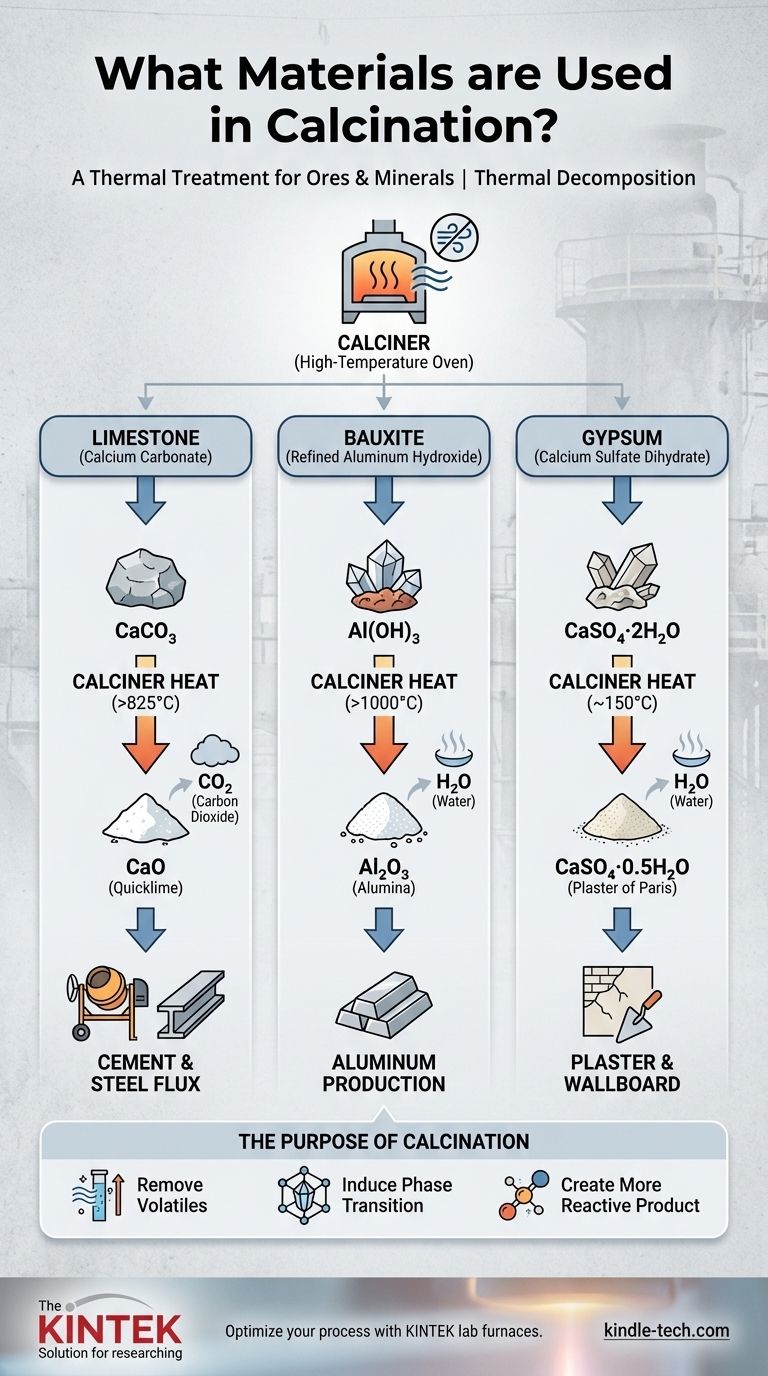
In essence, calcination is a thermal treatment process applied to a wide range of raw materials, most notably ores and minerals. Common examples include limestone (calcium carbonate), bauxite (aluminum ore), and gypsum, which are heated to high temperatures to trigger chemical decomposition and create a new, purified substance.
Calcination is not defined by a single material but by a specific outcome: using intense heat, below the melting point and with limited air, to break down a compound and drive off a volatile component like carbon dioxide or water.
What is Calcination? The Core Principle
Calcination is a fundamental process in materials science and metallurgy. It is a form of thermal decomposition, meaning it uses heat to break down a complex material into simpler ones.
The process is conducted in a specialized high-temperature oven or kiln, often called a calciner.
Crucially, this is done in the absence or with a very limited supply of air. This prevents combustion and distinguishes it from other heat treatments like roasting, which involves reacting the material with air.
Common Materials Processed by Calcination
The materials used in calcination are typically mineral compounds that contain a volatile component, such as carbonates or hydrates.
Limestone (Calcium Carbonate)
This is the most classic example of calcination. Limestone (CaCO₃) is heated to over 825°C (1517°F).
The heat drives off carbon dioxide (CO₂), leaving behind calcium oxide (CaO), commonly known as quicklime. This is a vital ingredient for making cement and is used as a flux in steel manufacturing.
Bauxite (Aluminum Hydroxide)
To produce aluminum, the raw ore (bauxite) is first refined into aluminum hydroxide (Al(OH)₃).
This refined material is then calcined at temperatures exceeding 1,000°C (1832°F). The process drives off water (H₂O) to produce pure aluminum oxide (Al₂O₃), or alumina, the primary feedstock for smelting aluminum metal.
Gypsum (Calcium Sulfate Dihydrate)
When gypsum (CaSO₄·2H₂O) is gently calcined at around 150°C (302°F), it loses most of its bound water.
The resulting fine white powder is calcium sulfate hemihydrate (CaSO₄·0.5H₂O), better known as plaster of Paris.
Other Ores and Minerals
Calcination is also used to process other materials like magnesite (MgCO₃) to produce magnesium oxide (MgO), and to prepare certain catalysts and pigments by driving off water or other volatile organic precursors.
The Purpose: What Calcination Achieves
The goal of calcination is to fundamentally alter the chemical or physical state of a material to make it suitable for a subsequent process.
To Remove Volatiles
The primary purpose is purification by removal. Driving off CO₂ from limestone or water from bauxite and gypsum leaves behind a more concentrated and useful base material.
To Induce a Phase Transition
Heat can change the crystalline structure of a material, altering its properties like hardness, density, or reactivity without changing its chemical formula.
To Create a More Reactive Product
The product of calcination is often more chemically reactive than the starting material. For example, quicklime (CaO) reacts vigorously with water, a property that is essential for its use in cement and other chemical processes.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
- If your primary focus is producing cement or flux for steel: Your key material is limestone, which is calcined to produce quicklime.
- If your primary focus is manufacturing aluminum: Your key material is refined bauxite (aluminum hydroxide), which is calcined to produce pure alumina.
- If your primary focus is creating plaster or wallboard: Your key material is gypsum, which is calcined to drive off water.
Understanding calcination means recognizing it as a key transformation step used to prepare raw minerals for their final industrial applications.
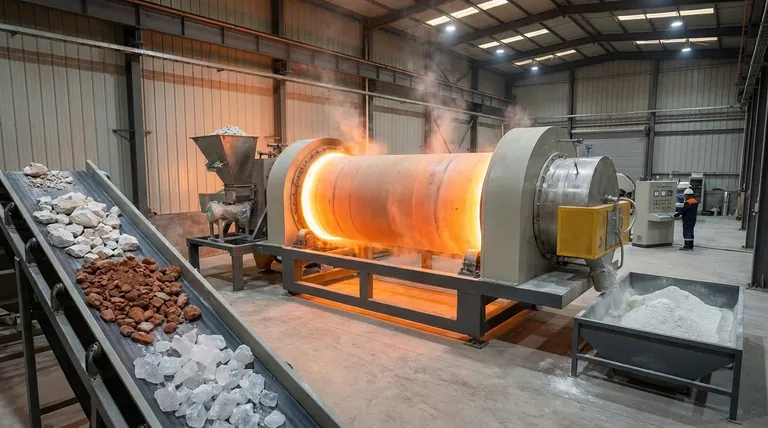

Summary Table:
| Material | Chemical Formula | Product After Calcination | Primary Industrial Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Limestone | CaCO₃ | Quicklime (CaO) | Cement, Steel Flux |
| Bauxite (Refined) | Al(OH)₃ | Alumina (Al₂O₃) | Aluminum Production |
| Gypsum | CaSO₄·2H₂O | Plaster of Paris (CaSO₄·0.5H₂O) | Plaster, Wallboard |
Ready to optimize your calcination process? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab furnaces and kilns (calciners) designed for precise thermal decomposition of ores and minerals. Whether you're processing limestone for cement or refining bauxite for aluminum, our equipment ensures the uniform heating and temperature control critical for successful outcomes. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific material processing needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the equipment for pyrolysis laboratory? Choosing the Right Reactor for Your Research
- What is a rotary kiln reactor? A Guide to Industrial Thermal Processing
- How does precision temperature control impact TiAl alloy sintering? Master Microstructure Development
- How does a rotary extractor work? Master Continuous High-Volume Solid Processing
- What is the drying zone in a rotary kiln? Boost Efficiency with Modern Drying Solutions



















