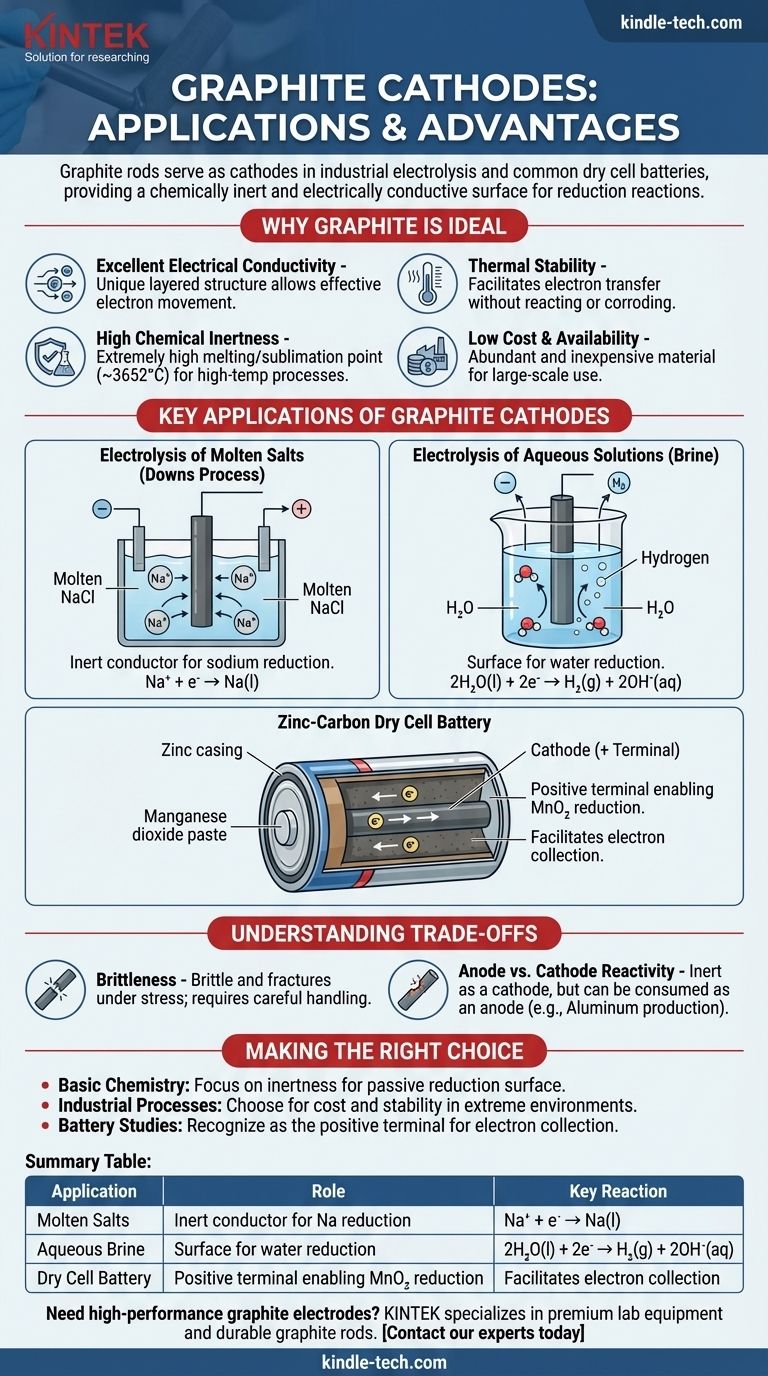
Graphite rods serve as cathodes in several key electrochemical processes, most notably in the industrial electrolysis of salts and within common dry cell batteries. In these applications, the graphite rod's primary function is not to be consumed or react, but to act as a chemically inert and electrically conductive surface where a reduction reaction can take place.
Graphite is chosen as a cathode material not because it participates in the primary reaction, but because it is an excellent inert conductor. Its unique combination of electrical conductivity, chemical resistance, high thermal stability, and low cost makes it an ideal platform for the reduction half-reaction to occur.

Why Graphite is an Ideal Cathode Material
The selection of a material for an electrode is a critical design choice in any electrochemical cell. Graphite (a specific form of carbon) possesses a set of properties that make it exceptionally well-suited for the role of a cathode.
Excellent Electrical Conductivity
Graphite has a unique layered, planar structure. Within these layers, delocalized electrons are free to move, allowing graphite to conduct electricity very effectively, a necessary trait for any electrode.
High Chemical Inertness
As a cathode, the electrode must facilitate the transfer of electrons to a substance in the electrolyte without reacting itself. Carbon is relatively unreactive, especially compared to most metals, meaning it won't corrode or interfere with the desired chemical process.
Thermal Stability
Graphite has one of the highest melting/sublimation points of all elements (around 3652°C or 6606°F). This makes it perfect for high-temperature electrochemical processes, like the electrolysis of molten salts, where metal electrodes would melt.
Low Cost and Availability
From an industrial perspective, graphite is an abundant and inexpensive material. This makes large-scale electrochemical production, which requires large electrodes, economically feasible.
Key Applications of Graphite Cathodes
Understanding the specific use cases clarifies the theory. In each example, the graphite cathode is simply the location where electrons are delivered to cause a chemical change.
Electrolysis of Molten Salts (Downs Process)
In the production of pure sodium metal from molten sodium chloride (NaCl), a graphite rod is often used as the cathode. Positively charged sodium ions (Na⁺) are attracted to the negatively charged cathode, where they gain an electron and are reduced to liquid sodium metal.
Na⁺ + e⁻ → Na(l)
The graphite cathode merely provides the surface and the electrons for this reaction.
Electrolysis of Aqueous Solutions (Brine)
When electrolyzing an aqueous solution of sodium chloride (brine), the graphite cathode plays a similar role. However, in this case, water is easier to reduce than sodium ions.
Therefore, water molecules are reduced at the graphite cathode's surface, producing hydrogen gas and hydroxide ions.
2H₂O(l) + 2e⁻ → H₂(g) + 2OH⁻(aq)
The Zinc-Carbon Dry Cell Battery
In a common "heavy-duty" battery, the central rod is made of graphite and acts as the cathode (the positive terminal). It is surrounded by a moist paste of manganese dioxide (MnO₂) and other chemicals.
The graphite rod collects electrons from the external circuit. The reduction reaction occurs in the paste adjacent to the rod, where manganese dioxide is reduced. The graphite simply facilitates this process.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, graphite is not a perfect material. Recognizing its limitations is key to understanding its applications.
Brittleness
Unlike metals, which are ductile, graphite is brittle and can fracture under mechanical shock or stress. This requires careful handling and support in industrial designs.
Anode vs. Cathode Reactivity
While graphite is very inert as a cathode, it can be consumed when used as an anode (the site of oxidation) in certain processes. For example, in aluminum production, the carbon anode reacts with the oxygen produced to form CO₂ gas and is slowly eaten away.
Confusion Between Cell Types
A common point of confusion is electrode polarity. The cathode is always the site of reduction, but its sign changes depending on the cell type.
- In an electrolytic cell (like for salt electrolysis), the cathode is the negative terminal.
- In a galvanic cell (like a battery), the cathode is the positive terminal.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your reason for asking about graphite cathodes determines which aspect is most important to focus on.
- If your primary focus is basic chemistry: Remember that graphite is an inert conductor, providing a passive surface for a reduction reaction to occur without reacting itself.
- If your primary focus is industrial processes: Choose graphite for its cost-effectiveness and unmatched stability in high-temperature or corrosive environments where most metals would fail.
- If your primary focus is studying batteries: Recognize that the graphite rod in a zinc-carbon cell acts as the positive terminal (cathode), serving as the electron collector that enables the reduction of the surrounding chemical paste.
Ultimately, understanding graphite's role as a cathode is about recognizing the power of an inert, conductive material that enables chemistry without interfering with it.
Summary Table:
| Application | Role of Graphite Cathode | Key Reaction |
|---|---|---|
| Electrolysis of Molten Salts (Downs Process) | Inert conductor for sodium reduction | Na⁺ + e⁻ → Na(l) |
| Electrolysis of Aqueous Brine | Surface for water reduction | 2H₂O(l) + 2e⁻ → H₂(g) + 2OH⁻(aq) |
| Zinc-Carbon Dry Cell Battery | Positive terminal enabling MnO₂ reduction | Facilitates electron collection |
Need high-performance graphite electrodes for your electrochemical processes? KINTEK specializes in premium lab equipment and consumables, including durable graphite rods designed for superior conductivity and thermal stability. Whether you're running industrial electrolysis or developing battery technologies, our materials ensure reliable, inert performance. Contact our experts today to find the perfect graphite solution for your laboratory needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Carbon Graphite Plate Manufactured by Isostatic Pressing Method
- Electrode Polishing Material for Electrochemical Experiments
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Large Vertical Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does convection play in heat transfer? Understanding Heat Movement in Fluids
- Does graphite lead electricity? Unlocking the Secrets of Its Atomic Structure
- What are the applications of radioactive substances? From Medical Imaging to Nuclear Power
- How can different materials have different heat capacity? Unlocking the Microscopic Secrets of Energy Storage
- What are the advantages disadvantages and uses of sheet metal? The Ultimate Guide to Material Selection



















