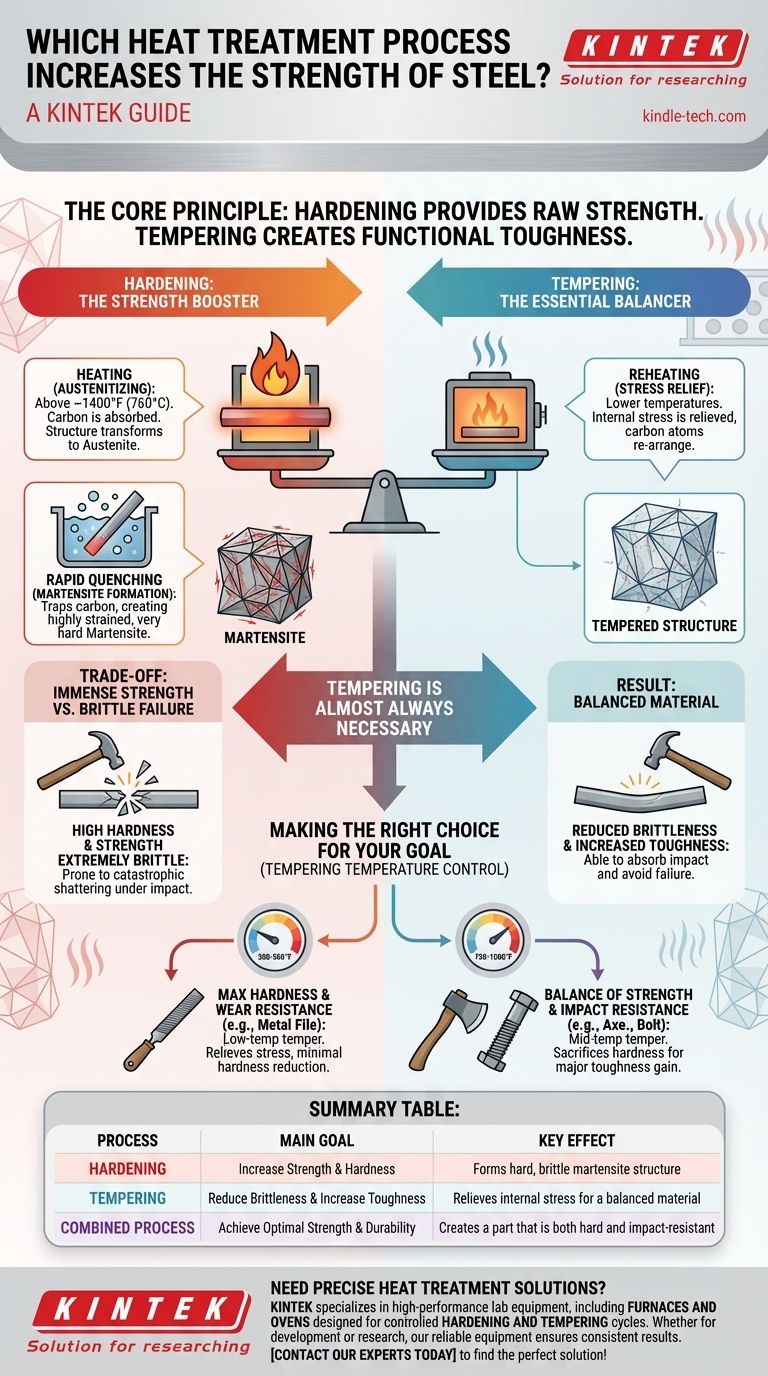
The primary heat treatment for increasing the strength of steel is hardening. This process involves heating the metal to a critical temperature to alter its internal crystal structure, followed by a rapid cooling process known as quenching. While this significantly boosts strength and hardness, it also makes the steel extremely brittle and prone to shattering under impact.
The core principle to understand is that true functional strength is a balance between hardness and toughness. Hardening provides the initial, raw strength, but a second process called tempering is almost always necessary to reduce the resulting brittleness and create a durable, usable final product.

The Mechanics of Hardening
Hardening is not a single action but a precise, two-stage process that fundamentally changes steel's internal structure. Understanding these stages is key to controlling the final properties of the material.
The Role of Temperature
First, the steel is heated to a specific "austenitizing" temperature, typically above 1400°F (760°C). At this temperature, the steel's crystal structure transforms into a phase called austenite, which has the unique ability to absorb carbon atoms from within the steel.
The Critical Quench
Once the steel is uniformly heated, it is rapidly cooled—or quenched—in a medium like water, oil, or even air. This rapid cooling does not give the crystal structure time to change back to its soft state.
Instead, the carbon atoms are trapped within the crystal lattice, creating a new, highly strained, and very hard structure called martensite.
Why Martensite Increases Strength
The formation of martensite is the direct cause of increased strength and hardness. Its distorted and stressed internal structure is extremely resistant to deformation, which we measure as strength.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Strength vs. Brittleness
The immense strength gained through hardening is not a free lunch. It comes with a significant and often dangerous trade-off that must be managed.
The Inevitable Consequence
The martensitic structure that makes steel so strong also makes it incredibly brittle. The internal stress that resists bending and scratching also prevents the material from absorbing any impact.
Brittleness in Practice
A piece of fully hardened, untempered steel behaves much like glass. It can withstand immense pressure, but a sharp blow will cause it to fracture and shatter catastrophically rather than bend or deform.
Why Brittleness is a Critical Failure
For nearly all applications—from tools and gears to structural components—brittleness is a critical point of failure. A brittle part can break without warning, leading to equipment damage or unsafe conditions. This is why hardening alone is rarely the final step.
Tempering: The Essential Second Step
To make the hardened steel useful, its brittleness must be reduced. This is accomplished through tempering, a secondary heat treatment that fine-tunes the material's final properties.
Reclaiming Toughness
Tempering involves reheating the hardened steel to a much lower temperature, well below the critical austenitizing point. The part is held at this temperature for a specific time to allow for internal changes.
How Tempering Works
This reheating gives the trapped carbon atoms just enough energy to move slightly and relieve some of the extreme internal stress within the martensite. This process reduces hardness and strength slightly but provides a dramatic increase in toughness—the material's ability to absorb impact.
The Final, Balanced Material
The final result is a material that retains a significant portion of the hardness gained from quenching but is also ductile and tough enough to withstand the shocks and stresses of its intended application.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The balance between hardness and toughness is controlled by the tempering temperature. By understanding this relationship, you can tailor the steel's properties to a specific need.
- If your primary focus is maximum hardness and wear resistance (e.g., a metal file): Use hardening followed by a low-temperature temper to relieve internal stress without significantly reducing hardness.
- If your primary focus is a balance of high strength and impact resistance (e.g., an axe or a structural bolt): Use hardening followed by a mid-range temperature temper to sacrifice some hardness for a major gain in toughness.
By mastering the interplay between hardening and tempering, you gain precise control over your material's final mechanical properties.
Summary Table:
| Process | Main Goal | Key Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Hardening | Increase Strength & Hardness | Forms hard, brittle martensite structure |
| Tempering | Reduce Brittleness & Increase Toughness | Relieves internal stress for a balanced material |
| Combined Process | Achieve Optimal Strength & Durability | Creates a part that is both hard and impact-resistant |
Need precise heat treatment solutions for your laboratory or manufacturing process? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including furnaces and ovens designed for controlled hardening and tempering cycles. Whether you're developing tools, components, or conducting materials research, our reliable equipment ensures consistent results. Contact our experts today to find the perfect heat treatment solution for your specific steel strength requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- How do you clean a quartz tube furnace? Prevent Contamination & Extend Tube Lifespan
- What is the difference between upflow and horizontal furnace? Find the Perfect Fit for Your Home's Layout
- What is quartz tube heating? Achieve Instant, Targeted Heat with Infrared Radiation
- What is the temperature of a quartz tube furnace? Master the Limits for Safe, High-Temp Operation
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost



















