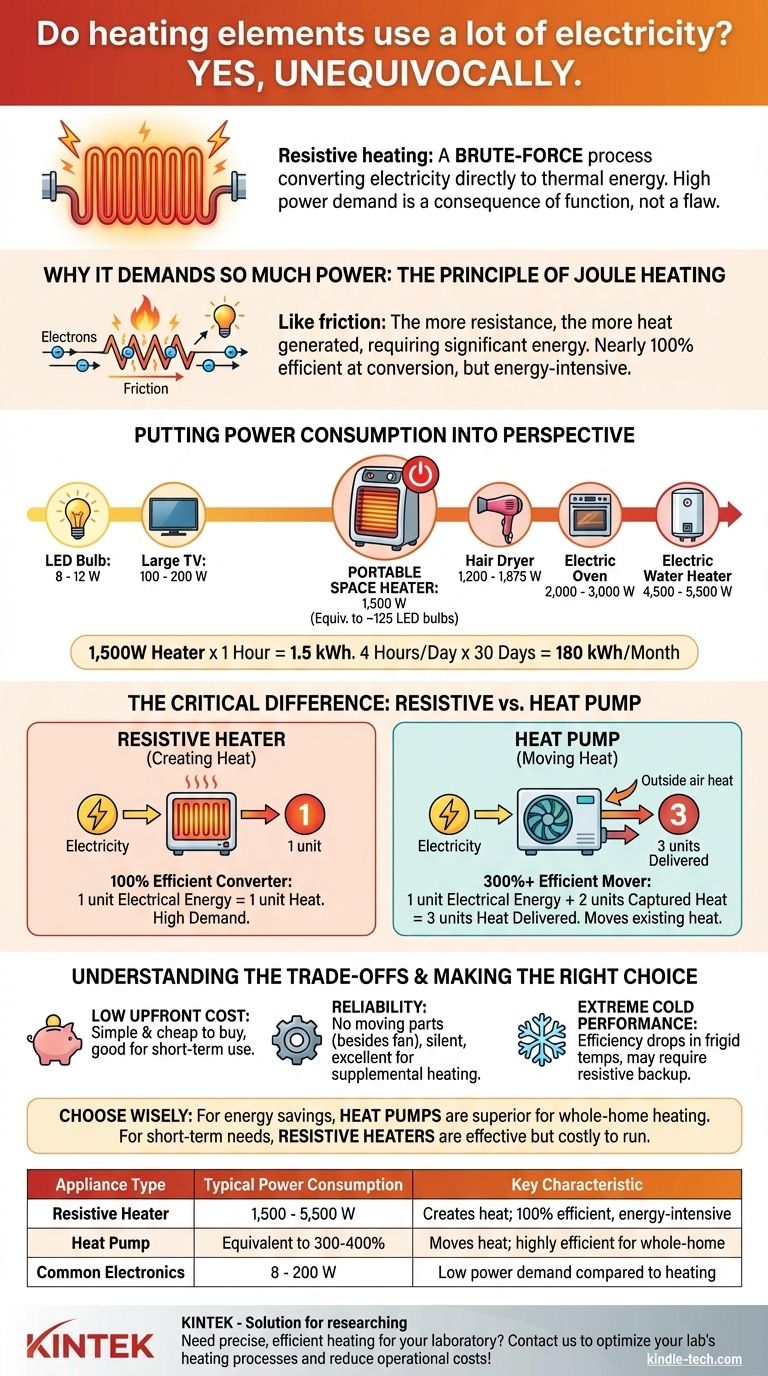
Yes, unequivocally. Devices that use resistive heating elements are among the most power-hungry appliances in any home. This is not a design flaw but a direct consequence of their function: to convert electrical energy directly into thermal energy (heat). The amount of electricity required to generate a meaningful amount of heat is substantial by its very nature.
While a heating element is nearly 100% efficient at converting electricity to heat, this is a brute-force process. The crucial insight is that modern technology allows us to move heat far more efficiently than we can create it from electricity, leading to dramatic differences in overall energy consumption.
Why Resistive Heating Demands So Much Power
To understand the high energy use, we must look at the fundamental principle at work. It's a simple and direct, but energy-intensive, process.
The Principle of Joule Heating
A standard heating element is a resistor. When electricity is forced to flow through a material that resists it, the electrical energy is converted into heat. This physical law is known as Joule heating.
Think of it like friction. The more friction you have, the more heat is generated, but it takes more energy to overcome it. A heating element is designed to have high electrical "friction."
No Wasted Energy, Just High Demand
Technically, a resistive heater is almost 100% efficient. Nearly every watt of electricity it draws is converted directly into heat, with very little lost to light or sound.
However, this efficiency is misleading. The problem isn't the conversion process; it's the sheer amount of energy required to heat a physical space. Resistive heating meets this high demand by drawing a large and continuous flow of electricity.
Putting Power Consumption into Perspective
The numbers on appliance labels clearly illustrate the difference in power demand. Power is measured in watts (W), and your utility bill is based on kilowatt-hours (kWh)—or 1,000 watts used for one hour.
Common Appliance Wattage
Comparing a heating device to other common household items reveals the scale of its consumption:
- LED Light Bulb: 8 - 12 Watts
- Large TV: 100 - 200 Watts
- Portable Space Heater: 1,500 Watts
- Hair Dryer: 1,200 - 1,875 Watts
- Electric Oven (one element): 2,000 - 3,000 Watts
- Electric Water Heater: 4,500 - 5,500 Watts
A single space heater on its high setting demands the same power as about 125 LED light bulbs.
From Watts to Kilowatt-Hours (kWh)
Your electricity bill is determined by how many watts an appliance uses and for how long. A 1,500W space heater running for just one hour consumes 1.5 kWh.
If you run that heater for 4 hours a day, it uses 6 kWh daily. Over a month, that's 180 kWh from a single appliance, which can significantly impact your utility bill.
The Critical Difference: Resistive vs. Heat Pump Technology
The most important concept for understanding heating and electricity is the difference between creating heat and moving it.
Resistive Heaters: The 100% Efficient Converter
As discussed, these devices create heat from electricity. The ratio is fixed: 1 unit of electrical energy produces 1 unit of heat. This includes space heaters, electric furnaces, water heaters, toasters, and ovens.
Heat Pumps: The 300%+ Efficient Mover
A heat pump works like an air conditioner in reverse. It doesn't create heat; it captures existing heat from the outside air (even when it's cold) and moves it inside.
Because it's moving heat rather than generating it, its efficiency can be well over 100%. A modern heat pump can often produce 3 units of heat for every 1 unit of electrical energy it consumes. This is why its efficiency is often rated at 300% or higher (expressed as a Coefficient of Performance or COP of 3.0+).
Understanding the Trade-offs
If heat pumps are so much more efficient, why do resistive heaters still exist? The answer lies in their simplicity and cost.
Upfront Cost and Simplicity
Resistive heating elements are incredibly cheap to manufacture and mechanically simple. An electric space heater can be purchased for a low price, while a heat pump system is a major home investment.
Reliability and Niche Uses
Resistive heaters have no moving parts (aside from a fan), making them very reliable and silent. They are excellent for supplemental or occasional use, such as warming a small bathroom for 15 minutes or taking the chill off a single room.
Performance in Extreme Cold
While modern heat pumps have improved, their efficiency decreases as the outdoor temperature drops to extreme lows. Many heat pump systems even include resistive "emergency heat" strips to take over when the heat pump can no longer extract enough heat from the frigid outside air.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your decision should be guided by your specific heating need, balancing upfront cost against long-term operational expense.
- If your primary focus is low upfront cost and occasional use: A portable resistive space heater is an effective and economical choice for short-term, targeted heating.
- If your primary focus is energy savings for whole-home heating: A heat pump is overwhelmingly superior and will result in dramatically lower electricity bills over its lifespan.
- If you are evaluating everyday appliances: Be aware that any device designed to produce high heat quickly (kettle, toaster, hair dryer) will, by necessity, be a high-wattage device with a large impact on energy use.
Understanding the difference between creating heat and moving it gives you direct control over your energy consumption and costs.
Summary Table:
| Appliance Type | Typical Power Consumption | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|
| Resistive Heater (Space Heater, Oven) | 1,500 - 5,500 Watts | Creates heat directly; 100% efficient but energy-intensive |
| Heat Pump | Equivalent to 300-400% efficiency | Moves existing heat; highly efficient for whole-home heating |
| Common Electronics (LED Bulb, TV) | 8 - 200 Watts | Low power demand compared to heating devices |
Need precise, efficient heating for your laboratory? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including energy-efficient ovens, furnaces, and heating solutions tailored to your specific research and testing needs. Our expertise ensures you get reliable temperature control without unnecessary energy waste. Contact us today to optimize your lab's heating processes and reduce operational costs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Platinum Sheet Electrode for Laboratory and Industrial Applications
- Reference Electrode Calomel Silver Chloride Mercury Sulfate for Laboratory Use
- Gold Disc Electrode
People Also Ask
- What happens when tungsten is heated? Harnessing Extreme Heat for Demanding Applications
- What is molybdenum disilicide used for? Powering High-Temperature Furnaces Up to 1800°C
- What are the causes of failure of heating elements? Prevent Downtime with Proper Operation
- What is molybdenum highest melting point? 2622°C for Extreme Heat Applications
- Which is a disadvantage of electric resistance heating systems? High Operating Costs Explained
- How do I know if my furnace heating element is bad? Spot the Signs and Test for Failure
- What factors affect the resistance of a heating element? Master the 4 Key Variables for Precise Thermal Design
- Which element is best for heating? Match the Right Material to Your Application for Optimal Performance
















