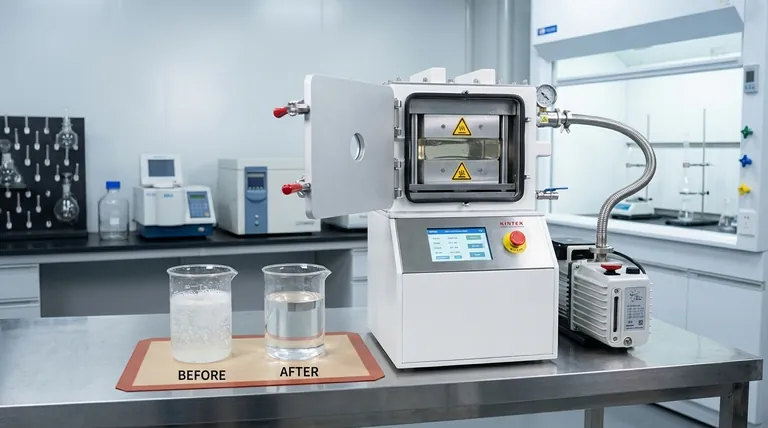
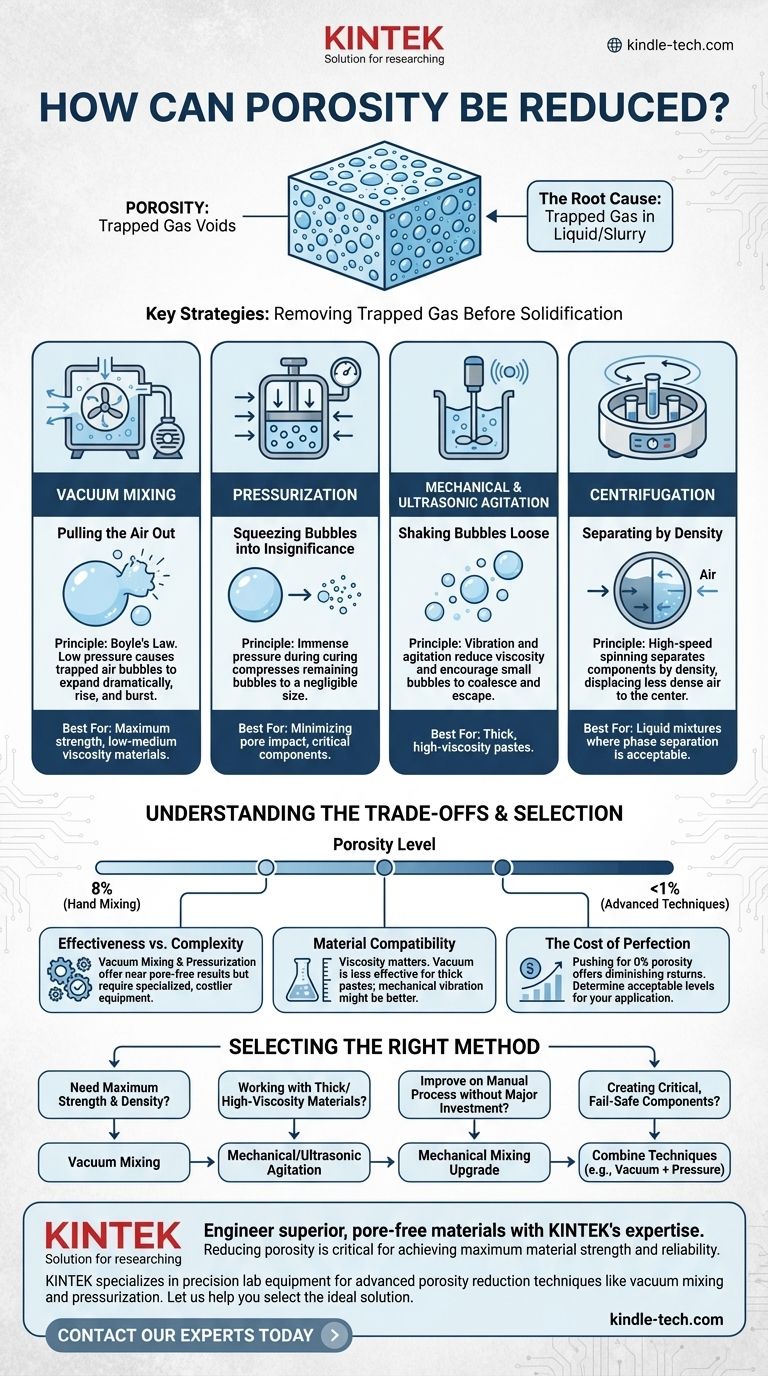
To reduce porosity, you must actively remove trapped gases from a liquid or slurry before it solidifies. The most effective methods involve vacuum mixing, pressurization during curing, mechanical or ultrasonic agitation, and centrifugation. These techniques can dramatically decrease pore volume, often reducing it from nearly 10% in a hand-mixed material to less than 1%.
The fundamental challenge in reducing porosity is not the material itself, but the air trapped within it during processing. Each reduction technique is simply a different physical strategy for forcing that trapped air out or minimizing its volume before the material sets.

The Root Cause of Porosity: Trapped Gas
Porosity is the presence of small voids or pores within a solid material. In many applications, especially with cements, resins, or metal castings, these pores are defects that weaken the final structure.
The primary cause of this porosity is the entrapment of air. When powders and liquids are combined and mixed, air is inevitably folded into the slurry, creating countless microscopic bubbles that become trapped as the material's viscosity increases.
Key Strategies for Porosity Reduction
The most successful strategies are applied while the material is still in its liquid or paste-like state. Each method uses a different physical principle to deal with the trapped gas bubbles.
Vacuum Mixing: Pulling the Air Out
Vacuum mixing is widely considered the gold standard for eliminating porosity. The process involves mixing the components inside a chamber where the air pressure has been significantly lowered.
According to Boyle's Law, decreasing the pressure on a gas causes its volume to increase. In a vacuum, trapped air bubbles expand dramatically, making them more buoyant. This forces them to rise to the surface and burst, effectively de-gassing the mixture.
This method is highly effective for low-to-medium viscosity materials like resins and some specialized cements.
Pressurization: Squeezing Bubbles into Insignificance
Pressurization works on the opposite principle. Instead of removing the air, it minimizes its impact. After the material is mixed and placed in its mold, it is cured under high atmospheric pressure.
This immense pressure compresses any remaining air bubbles, shrinking them to a fraction of their original size. While the pores technically still exist, they are so small that their negative impact on the material's strength and integrity becomes negligible.
Mechanical & Ultrasonic Agitation: Shaking Bubbles Loose
This strategy uses energy to help trapped bubbles escape. Gentle vibration, vigorous mechanical mixing, or high-frequency ultrasonic waves are introduced into the liquid mixture.
This agitation serves two purposes. It reduces the material's temporary viscosity (a property known as thixotropy), allowing bubbles to move more freely. It also encourages small bubbles to coalesce into larger, more buoyant ones that can rise to the surface and escape.
Centrifugation: Separating by Density
Centrifugation involves spinning the mixed material at high speed. The resulting centrifugal force separates the components based on their density.
The denser liquid or slurry is forced to the outer edge of the container, while the less dense air bubbles are displaced and migrate toward the center, where they can be removed. This technique is highly effective but can be unsuitable for mixtures where you want to avoid separating the solid and liquid phases.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a method requires balancing effectiveness with cost, complexity, and the specific properties of your material. No single technique is perfect for every scenario.
Effectiveness vs. Complexity
Vacuum mixing and pressurization are exceptionally effective, capable of producing nearly pore-free parts. However, they require specialized equipment like vacuum chambers, pumps, and pressure vessels, which adds significant cost and complexity to the process.
Material Compatibility
The ideal technique depends on your material's viscosity. Vacuum degassing is less effective on very thick pastes, as bubbles cannot rise easily. In such cases, mechanical vibration may be a more practical choice to aid in air release. Centrifugation can also cause undesirable separation of fillers in some composite materials.
The Cost of Perfection
As noted, conventional hand mixing may result in 8% porosity, while advanced techniques can achieve less than 1%. Pushing from 1% to near 0% porosity offers diminishing returns and may not be necessary for all applications. You must determine the acceptable level of porosity for your specific performance requirements.
Selecting the Right Method for Your Application
Your choice should be driven by your final goal, budget, and material constraints.
- If your primary focus is maximum material strength and density: Vacuum mixing is the most reliable method for creating a virtually void-free product.
- If you are working with thick, high-viscosity materials: Mechanical or ultrasonic vibration is essential to help release trapped air that cannot escape on its own.
- If your primary focus is improving on a manual process without major investment: Upgrading from hand mixing to a high-quality mechanical mixer will yield a significant reduction in porosity.
- If you are creating a critical component that cannot fail: Combine techniques, such as vacuum mixing the material first and then curing it under pressure for maximum reliability.
By understanding the principles behind porosity, you can move from simply mixing a material to truly engineering its final properties.
Summary Table:
| Method | Key Principle | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Vacuum Mixing | Expands & removes bubbles under low pressure | Maximum strength, low-medium viscosity materials |
| Pressurization | Compresses bubbles during curing | Minimizing pore impact, critical components |
| Mechanical/Ultrasonic Agitation | Shakes bubbles loose via vibration | Thick, high-viscosity pastes |
| Centrifugation | Separates air by density using spin force | Liquid mixtures where phase separation is acceptable |
Engineer superior, pore-free materials with KINTEK's expertise.
Reducing porosity is critical for achieving maximum material strength and reliability in your laboratory products. Whether you're working with resins, cements, or composites, the right equipment and method make all the difference.
KINTEK specializes in precision lab equipment and consumables that enable advanced porosity reduction techniques like vacuum mixing and pressurization. Our solutions help R&D teams, material scientists, and quality control labs produce consistently dense, high-performance parts.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific material challenges. Let us help you select the ideal mixing, degassing, or curing equipment to minimize defects and optimize your process.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Heated Hydraulic Vacuum Heat Press for Lab
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Vacuum Box Laboratory Hot Press
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
People Also Ask
- What are hot presses used for? Transforming Materials with Heat and Pressure
- What is the function of a hydraulic heat press? Perfecting Solid-State Battery Polymer Membranes
- What does hot-pressing do? Transform Materials with High-Temperature, High-Pressure Densification
- What is a vacuum heat press machine? The Ultimate Tool for 3D Product Decoration
- How does temperature affect vacuum pressure? Master the Key to System Control



















