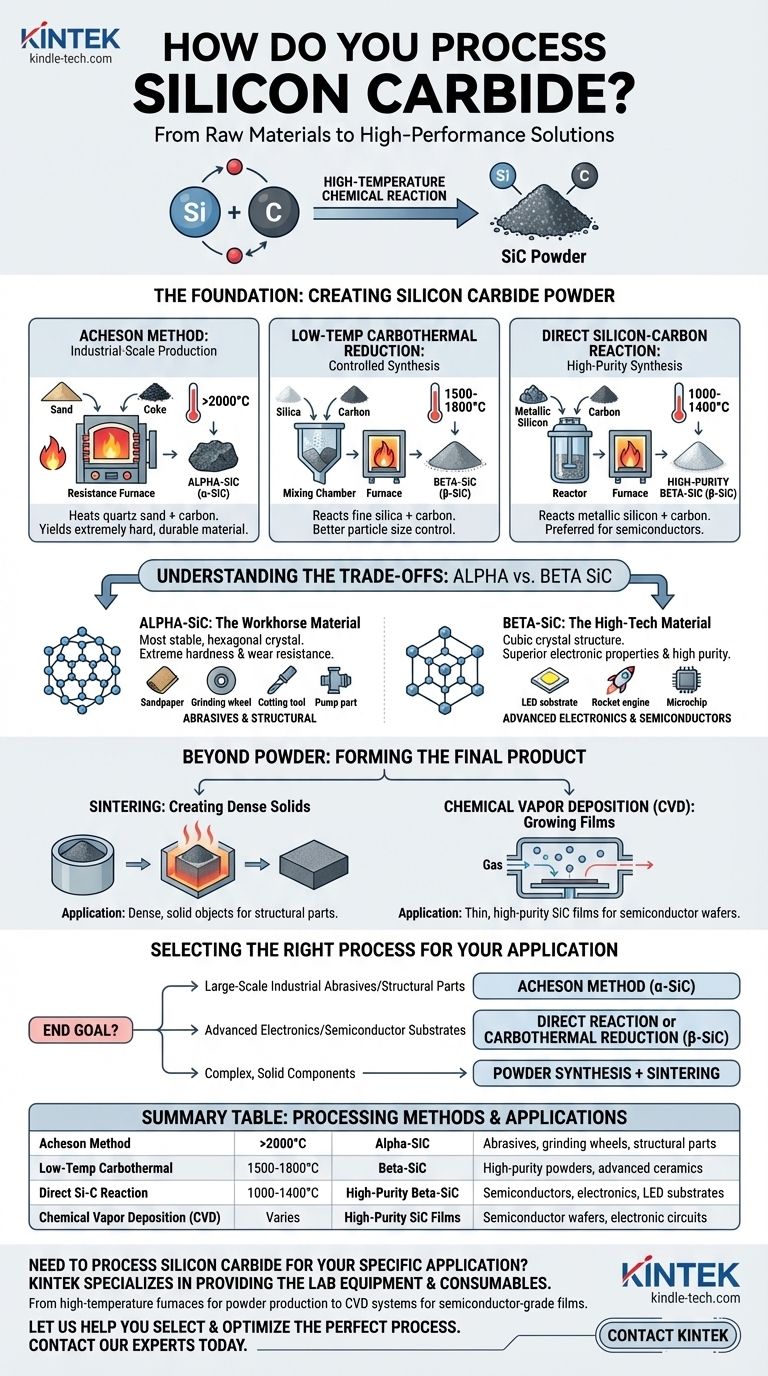
At its core, processing silicon carbide begins with a high-temperature chemical reaction to create SiC powder. The three main industrial methods are the Acheson method, low-temperature carbothermal reduction, and the direct reaction of silicon and carbon. Each method operates at a different temperature range and is chosen based on the desired purity and crystal structure of the final material.
The method used to process silicon carbide is a strategic choice, not just a manufacturing step. It directly determines whether you produce the harder alpha-SiC for abrasives or the high-purity beta-SiC required for advanced electronics, dictating the material's final cost and performance.

The Foundation: Creating Silicon Carbide Powder
The first and most critical phase of processing is synthesizing the raw silicon carbide powder. The method chosen here defines the fundamental properties of the material.
The Acheson Method: Industrial-Scale Production
This is the oldest and most common method for mass production. It involves heating a mixture of high-purity quartz sand and carbon (typically from petroleum coke) in a large resistance furnace to temperatures exceeding 2000°C.
This process primarily yields alpha-silicon carbide (α-SiC), an extremely hard and durable material ideal for industrial applications.
Low-Temperature Carbothermal Reduction: Controlled Synthesis
This method reacts fine silica powder with carbon powder at a lower temperature range, typically between 1500°C and 1800°C.
The result is beta-silicon carbide (β-SiC) powder. This approach offers better control over the final particle size and properties compared to the Acheson method.
Direct Silicon-Carbon Reaction: High-Purity Synthesis
For applications demanding the highest purity, metallic silicon powder is reacted directly with carbon powder. This reaction occurs at even lower temperatures, between 1000°C and 1400°C.
This process is the preferred route for generating high-purity β-SiC powder, which is essential for the semiconductor industry.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Alpha vs. Beta SiC
The distinction between the processing methods is critical because they produce different crystal structures, or "polymorphs," of silicon carbide. The two most important are Alpha (α) and Beta (β).
The Significance of Crystal Structure
Alpha-SiC is the most stable and common polymorph, characterized by a hexagonal crystal structure. It is exceptionally hard and forms at very high temperatures.
Beta-SiC has a cubic crystal structure and forms at lower temperatures. While still very hard, its primary advantage lies in its superior electronic properties and the ability to be synthesized with very high purity.
Alpha-SiC: The Workhorse Material
Produced primarily by the Acheson method, α-SiC is valued for its mechanical properties. Its extreme hardness and wear resistance make it the standard for abrasive and structural applications.
Common uses include sandpaper, grinding wheels, cutting tools, and durable components like pump parts and furnace heating elements.
Beta-SiC: The High-Tech Material
Synthesized via carbothermal reduction or direct reaction, β-SiC is prized for its purity and semiconductor characteristics.
Its unique electronic bandgap makes it indispensable for high-power, high-frequency electronic devices. Key applications include substrates for LEDs and components for rocket engines where high thermal conductivity and purity are paramount.
Beyond Powder: Forming the Final Product
Creating powder is only the first step. To be useful in applications like rocket nozzles or electronic wafers, this powder must be consolidated into a solid form.
Sintering: Creating Dense Solids
Sintering involves compacting the SiC powder in a mold and heating it to a high temperature, causing the individual particles to bond together into a dense, solid object.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD): Growing Films
For semiconductor applications, CVD is often used. This process grows a thin, crystalline film of high-purity SiC directly onto a substrate, creating the foundational wafer for building electronic circuits.
Selecting the Right Process for Your Application
Your choice of processing method depends entirely on your end goal, balancing cost, volume, and required material properties.
- If your primary focus is large-scale industrial abrasives or structural parts: The Acheson method is the most cost-effective path for producing durable α-SiC.
- If your primary focus is advanced electronics or semiconductor substrates: Direct reaction or low-temperature carbothermal reduction is necessary to create the high-purity β-SiC required.
- If your primary focus is creating complex, solid components: Remember that powder synthesis is just the first stage; a secondary process like sintering will be needed to form the final part.
Understanding the link between the initial synthesis method and the final material properties is the key to successfully leveraging silicon carbide's unique capabilities.
Summary Table:
| Processing Method | Temperature Range | Primary Output | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acheson Method | >2000°C | Alpha-SiC (α-SiC) | Abrasives, grinding wheels, structural parts |
| Low-Temperature Carbothermal Reduction | 1500-1800°C | Beta-SiC (β-SiC) | High-purity powders, advanced ceramics |
| Direct Silicon-Carbon Reaction | 1000-1400°C | High-Purity Beta-SiC (β-SiC) | Semiconductors, electronics, LED substrates |
| Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) | Varies | High-Purity SiC Films | Semiconductor wafers, electronic circuits |
Need to Process Silicon Carbide for Your Specific Application?
Whether you're developing advanced semiconductors, high-performance abrasives, or durable structural components, the right processing method is critical to achieving your material's desired properties. KINTEK specializes in providing the lab equipment and consumables needed for precise silicon carbide synthesis and processing—from high-temperature furnaces for powder production to CVD systems for semiconductor-grade films.
Let us help you select and optimize the perfect process for your needs. Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK's solutions can enhance your silicon carbide processing efficiency and final product performance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular RTP Heating Furnace
People Also Ask
- Are all lab grown diamonds CVD? Understanding the Two Main Methods
- What is the floating catalyst method? A Guide to High-Yield CNT Production
- How does chirality affect carbon nanotubes? It Determines If They Are Metal or Semiconductor
- What is a CVD tube furnace? A Complete Guide to Thin-Film Deposition
- Why are carbon nanotubes important in industry? Unlocking Next-Generation Material Performance



















