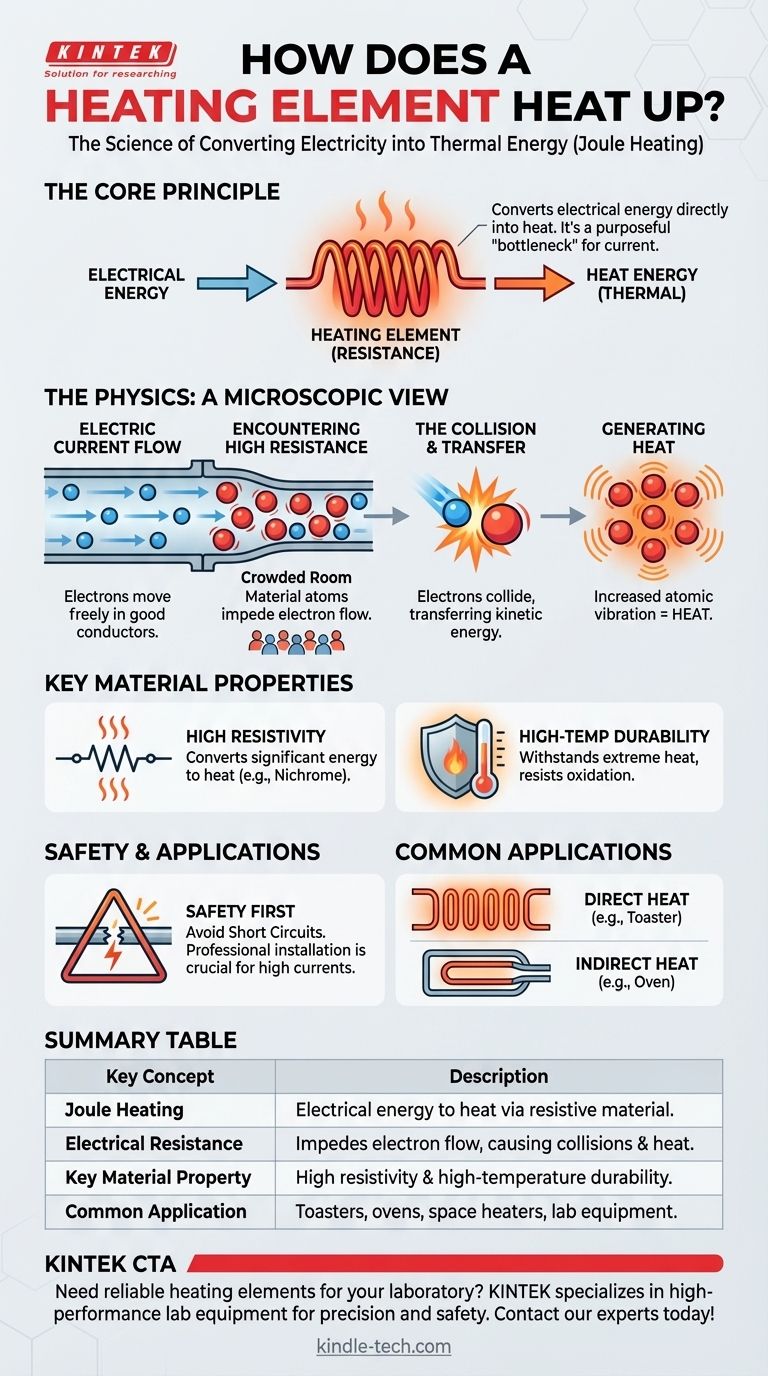
At its core, a heating element works by converting electrical energy directly into heat. When an electric current is passed through a material with high electrical resistance, the material obstructs the flow of electricity. This "friction" on the moving electrons generates thermal energy in a process known as Joule heating.
The essential principle is simple: a heating element is designed to be a purposefully inefficient conductor of electricity. By intentionally creating a bottleneck for the electrical current, it forces energy that would otherwise be electrical to be released as heat.

The Physics Behind the Heat
To understand how this conversion happens, we need to look at the flow of electricity at a microscopic level. It's a simple, elegant process driven by a single key property.
The Role of Electric Current
An electric current is nothing more than a flow of electrons moving through a material. In a good conductor, like a copper wire, these electrons can move relatively freely with little opposition.
The Critical Factor: Electrical Resistance
A heating element, however, is made from a material with high electrical resistance. This means the material's atomic structure actively impedes the flow of electrons.
Imagine trying to run through a crowded room. The people are like the atoms in the resistive material, and you are an electron. You can't move in a straight line; you constantly bump into people, transferring your energy to them.
How Collisions Generate Heat
This is precisely what happens inside a heating element. As electrons are forced through the resistive material, they collide with the atoms of that material.
Each collision transfers kinetic energy from the electron to the atom, causing the atom to vibrate more intensely. This increased atomic vibration is what we perceive and measure as heat.
Designing the Perfect Heating Element
Not just any resistive material will work. An effective heating element must have specific properties to function safely and reliably over long periods.
Property 1: High Resistivity
The primary requirement is high electrical resistivity. This ensures that the material converts a significant amount of electrical energy into heat rather than just passing the current along. This is why elements are often made from alloys like Nichrome (nickel and chromium), not highly conductive metals like copper.
Property 2: High-Temperature Durability
The material must be able to withstand getting extremely hot without melting or degrading. It also needs to resist oxidation (reacting with oxygen in the air), which would cause it to quickly break down, especially when glowing red-hot.
Common Pitfalls and Safety Considerations
While the principle is straightforward, its application involves significant energy and requires careful engineering to be safe.
The Danger of a Short Circuit
If a heating element breaks or touches a conductive surface, it can create a short circuit. This allows the current to bypass the intended resistance, leading to a massive, uncontrolled surge of electricity that can cause fires or electrical shocks.
Why Professional Installation is Crucial
As noted, heating elements are connected to the mains electrical supply. They draw a large amount of current to generate the necessary heat. This is why they must be installed by a qualified electrician who understands proper wiring, circuit protection, and grounding to ensure safe operation.
How This Applies to Everyday Devices
You can see this principle in action all around you, though the design may differ based on the goal.
- If your goal is visible, direct heat (like a toaster or space heater): The heating element is often a coil of Nichrome wire that glows red-hot, maximizing radiant heat output.
- If your goal is contained, indirect heat (like an oven or water heater): The resistive wire is typically encased in a protective metal sheath. This prevents electric shock and allows for safe heat transfer to the surrounding air or water.
Understanding Joule heating reveals that the warmth from these devices isn't magic; it's the direct, physical result of controlling electrical friction.
Summary Table:
| Key Concept | Description |
|---|---|
| Joule Heating | The process of converting electrical energy into heat as current flows through a resistive material. |
| Electrical Resistance | The property of a material that impedes electron flow, generating heat through collisions. |
| Key Material Property | High resistivity and high-temperature durability (e.g., Nichrome alloy). |
| Common Application | Found in toasters, ovens, space heaters, and water heaters. |
Need a reliable heating element for your laboratory equipment? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including durable heating elements designed for precision and safety. Our products ensure efficient and consistent heat generation for your critical applications. Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your lab's needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Rotating Platinum Disk Electrode for Electrochemical Applications
- RRDE rotating disk (ring disk) electrode / compatible with PINE, Japanese ALS, Swiss Metrohm glassy carbon platinum
- Platinum Auxiliary Electrode for Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- Is molybdenum disulfide a heating element? Discover the best material for high-temperature applications.
- What is the temperature range of molybdenum disilicide heating elements? Choose the Right Grade for Your High-Temp Needs
- What are the heating elements for high temperature furnaces? Select the Right Element for Your Atmosphere
- What is the temperature range of a MoSi2 heating element? Unlock 1900°C Performance for Your Lab
- What material is used for furnace heating? Select the Right Element for Your Process

















