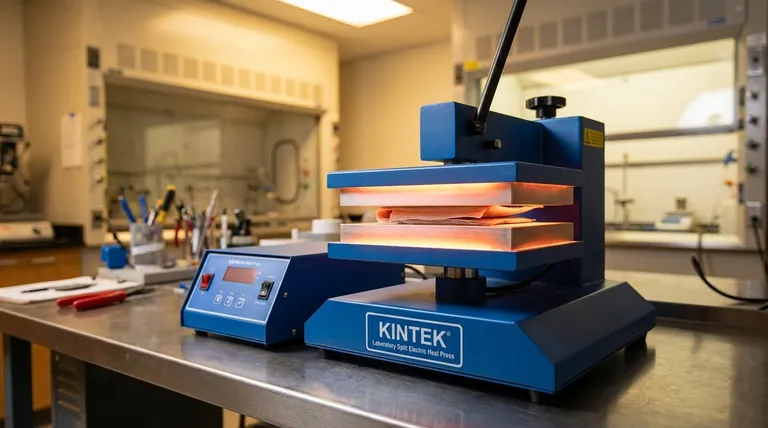
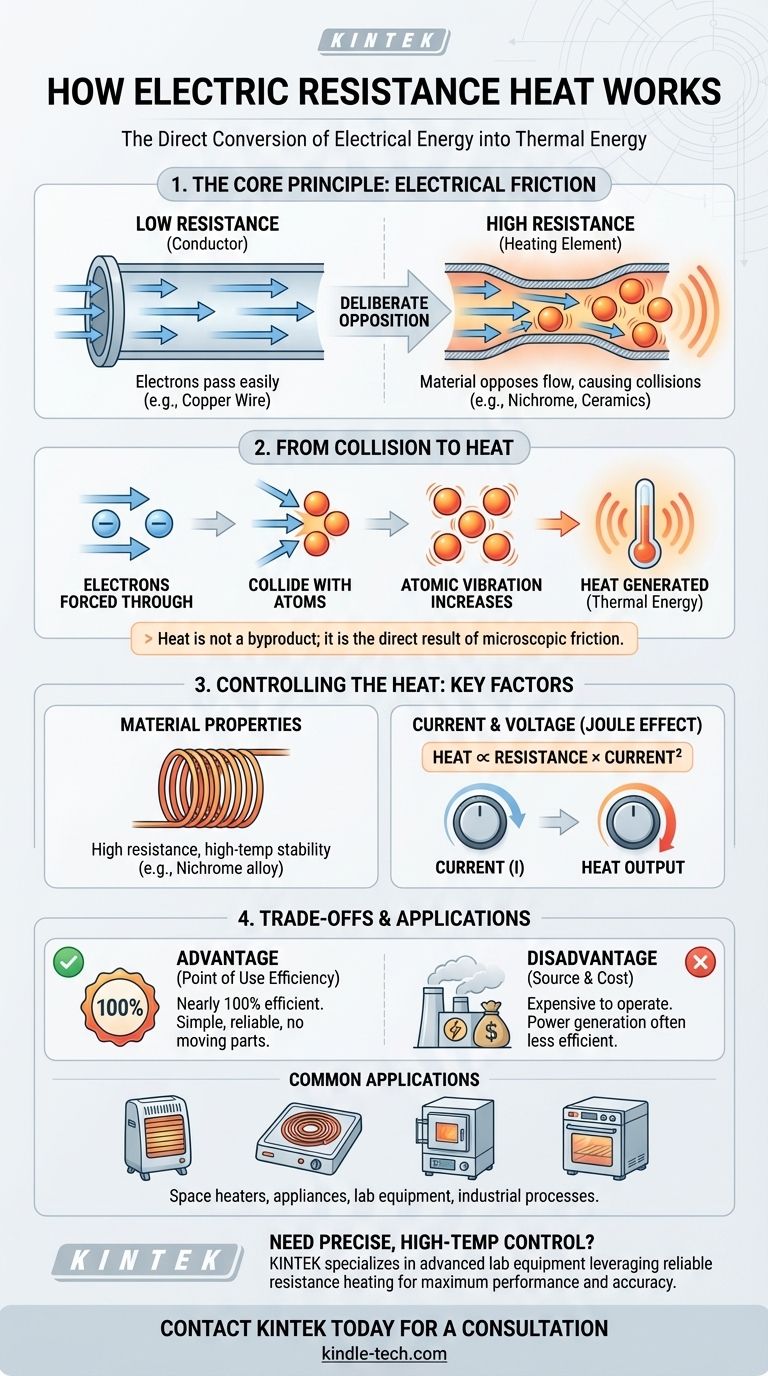
At its core, electric resistance heating is the process of converting electrical energy directly into thermal energy. This happens when an electric current is passed through a material that deliberately opposes its flow, known as a resistor or heating element. The energy lost by the electrical current as it pushes through this resistance is released in the form of heat.
The key principle to understand is that heat is not a byproduct of this process; it is the intended and direct result of friction at a microscopic level. As electrons are forced through a resistant material, they collide with atoms, transferring their kinetic energy and causing the material to heat up.

The Fundamental Principle: Current, Resistance, and Heat
To grasp how resistance heating works, we must look at the three core components involved: the electric current, the material it flows through, and the interaction between them.
The Flow of Electrons (Current)
An electric current is simply the movement of charged particles, typically electrons, through a conductor. Think of it as water flowing through a pipe. The amount of current (amperage) is like the volume of water flowing.
The Role of the Material (Resistance)
Electrical resistance is a material's inherent opposition to the flow of that electric current. Materials like copper have very low resistance, allowing electricity to pass easily, making them ideal for wires.
Materials used for heating elements, such as nichrome or certain ceramics, have very high resistance. They act like a narrow, constricted section in the pipe, making it much harder for the "water" to get through.
The Collision That Creates Heat
When electrons are forced through a high-resistance material, they don't pass through unimpeded. They constantly collide with the atoms that make up the material.
Each of these countless collisions transfers kinetic energy from the moving electron to the atom. This energy transfer causes the atoms to vibrate more rapidly. This increased atomic vibration is what we perceive and measure as heat.
Key Factors Influencing Heat Generation
The amount of heat produced by an electric resistor is not arbitrary. It is governed by precise physical laws and can be controlled by manipulating a few key variables.
Material Properties
The choice of material is critical. The ideal heating element has a high resistance to generate heat effectively but can also withstand very high temperatures without melting or degrading. This is why alloys like nichrome (nickel-chromium) are so common in heating devices.
Current and Voltage
The amount of heat generated is directly related to the amount of electric current flowing and the voltage applied. According to the principle known as the Joule effect, the heat produced is proportional to the resistance multiplied by the square of the current. Doubling the current, therefore, quadruples the heat output.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While incredibly simple and reliable, electric resistance heating has distinct advantages and disadvantages that are important to understand.
The Advantage: Simplicity and Efficiency
The primary benefit of resistance heating is its simplicity. There are no moving parts, and the conversion of electrical energy into heat at the point of use is nearly 100% efficient. Every watt of electricity consumed by the heating element is converted directly into a watt of thermal energy.
The Disadvantage: Cost and Source Inefficiency
The key trade-off is the high cost of electricity. While the device itself is 100% efficient, the power plant that generated the electricity was likely not. This makes resistance heating one of the more expensive forms of heating compared to alternatives.
For example, a modern heat pump doesn't create heat; it moves existing heat from one place to another. This allows it to achieve an effective efficiency of 300-400%, delivering 3 to 4 units of heat for every 1 unit of electricity consumed.
Common Applications
You can find resistance heating in countless devices, including:
- Portable space heaters
- Electric furnaces and baseboard heaters
- Electric water heaters
- Stovetops, ovens, and toasters
- Industrial process heaters and environmental remediation systems
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the core principle allows you to evaluate its application based on your specific needs.
- If your primary focus is simplicity and low upfront cost: Resistance heating is often the best choice for portable or supplemental heating due to its simple design and reliability.
- If your primary focus is whole-home heating efficiency: A heat pump will almost always provide significantly lower running costs, though the initial investment is much higher.
- If your primary focus is precise, high-temperature control: For applications like lab equipment, industrial ovens, or even a kitchen stove, the direct and immediate control of resistance heat is unmatched.
By understanding that heat is the direct result of controlled electrical friction, you can better appreciate the role this fundamental technology plays in our daily lives.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Core Principle | Converts electrical energy directly into heat via electron-atom collisions in a resistant material. |
| Efficiency | Nearly 100% efficient at the point of use. |
| Primary Advantage | Simple, reliable design with precise temperature control. |
| Primary Disadvantage | Can be expensive to operate due to electricity costs. |
| Common Applications | Space heaters, stovetops, industrial ovens, laboratory furnaces. |
Need precise, high-temperature control for your laboratory or industrial process?
At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced lab equipment that leverages the reliability of electric resistance heating. Our ovens, furnaces, and heating systems are engineered for maximum performance, safety, and accuracy.
Let our experts help you select the perfect heating solution for your specific application.
Contact KINTEK today for a consultation and discover how our expertise in lab equipment can enhance your workflow.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Automatic Laboratory Heat Press Machine
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Integrated Manual Heated Plates for Lab Use
- Automatic High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Automatic Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
People Also Ask
- Why use KBr for IR? Achieve Clear, Unobstructed Spectra for Solid Samples
- What is the pellet technique in IR? Master Solid Sample Preparation for Clear Spectroscopy
- What is the pressed powder pellet method? A Guide to Accurate FTIR Sample Preparation
- Are hydraulic presses powered by water? Discover the critical role of hydraulic oil.
- How does a laboratory hydraulic press improve XRF accuracy for catalyst samples? Enhance Precision & Signal Stability



















