The duration of heat treatment is not a single number but a calculated variable, ranging from under an hour for small, simple parts to several days for large, complex alloy components. The total time is dictated by a precise recipe involving the metal's composition, its thickness, and the desired final properties.
The core principle to understand is that heat treatment time is a function of three distinct phases: heating to temperature, soaking at temperature, and cooling back to room temperature. The soaking phase, which allows the metal's internal structure to transform, is often the most critical and time-consuming element.

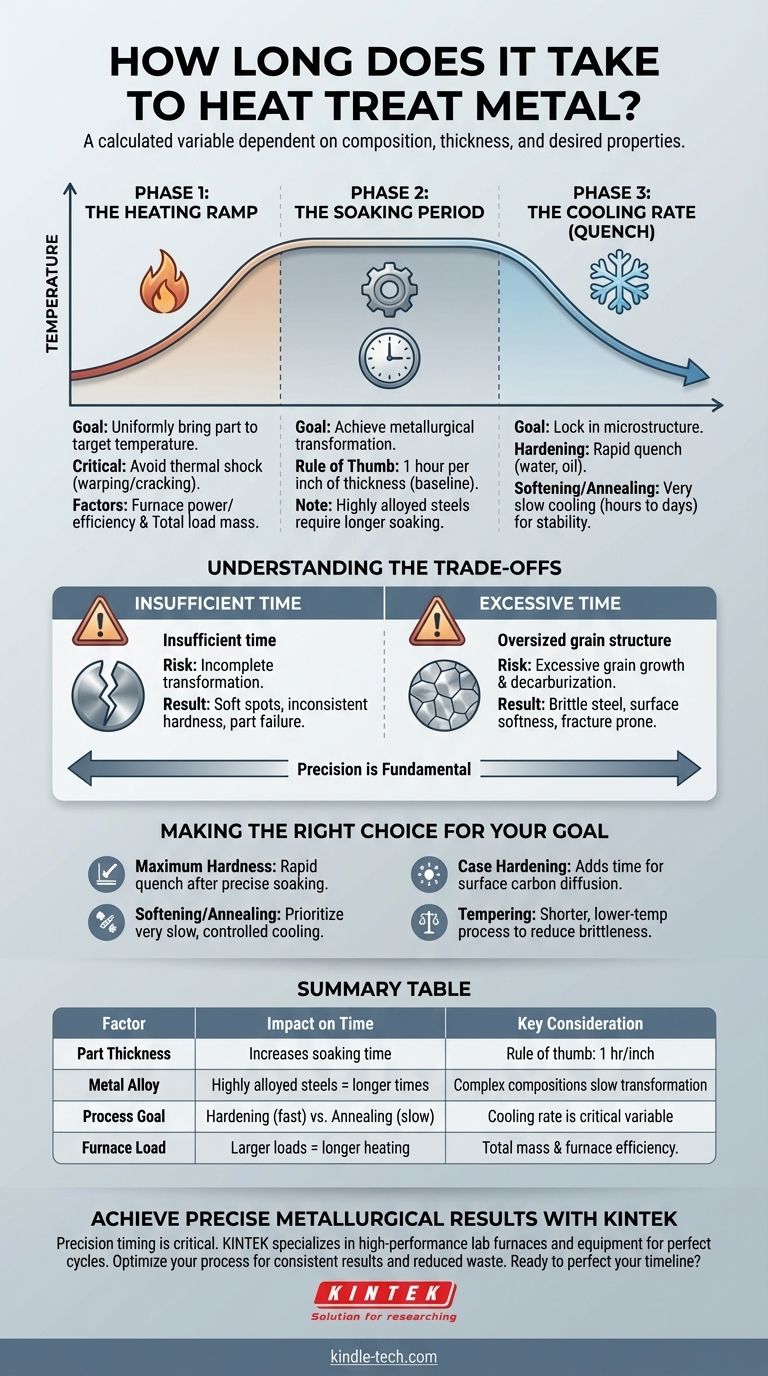
The Three Stages That Determine Total Time
Every heat treatment process, whether for hardening, softening, or stress-relieving, follows a thermal profile. The duration of each stage is governed by different physical principles.
Phase 1: The Heating Ramp
The goal of this stage is to bring the entire part, including its core, to the target temperature uniformly.
Rushing this phase can cause thermal shock, leading to warping or cracking, especially in complex geometries.
The primary factors controlling heating time are the furnace's power and efficiency and the total mass of the load being heated. A large furnace packed with heavy parts will naturally take longer to reach temperature than a small furnace with a single part.
Phase 2: The Soaking Period
This is the most critical stage for achieving the desired metallurgical transformation. The part is held at a specific temperature to allow its internal crystal structure to change uniformly.
The most common rule of thumb for soaking time is one hour for every inch of thickness at the part's thickest cross-section.
However, this is just a baseline. Highly alloyed steels, such as tool steels, contain elements that slow down the internal transformation, requiring significantly longer soaking times than simple carbon steels.
Phase 3: The Cooling Rate (Quench)
The final stage determines the metal's end-state properties. The speed of cooling locks in a specific microstructure.
Hardening requires a very rapid cool-down (quenching) in a medium like water, brine, or oil. While the quench itself is fast, the choice of quenchant and agitation method is critical.
Softening (annealing) or stress-relieving requires a very slow cooling rate, often accomplished by letting the parts cool down inside the furnace over many hours or even days. This allows the microstructure to re-form in its softest, most stable state.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Deviating from the correct time at any stage introduces significant risk. Precision is not optional; it is fundamental to a successful outcome.
The Dangers of Insufficient Time
Rushing the process, especially the soaking period, is a common cause of failure.
If the part is not soaked long enough, the metallurgical transformation will be incomplete. This results in soft spots, inconsistent hardness, and a part that fails to meet its performance specifications.
The Problems with Excessive Time
More is not better. Holding a part at temperature for too long can be just as damaging as not holding it long enough.
The primary risk is excessive grain growth. This makes the steel brittle and prone to fracture, even if it meets hardness requirements.
Another risk is decarburization, where carbon leaches from the surface of the steel, leaving a soft outer layer that is useless for wear resistance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your specific objective dictates the required process and its timing. Use the metallurgical specifications for the alloy as your primary guide, but consider these general principles.
- If your primary focus is maximum hardness and strength: Prioritize a rapid, controlled quench after a precise soaking period calculated for the alloy and thickness.
- If your primary focus is softening or stress relief (annealing): The critical variable is a very slow, controlled cooling rate, which will be the most time-consuming part of the process.
- If your primary focus is case hardening (surface hardness): Processes like carburizing add time, as the part must soak for many hours to allow carbon to diffuse into the surface before the final hardening quench.
- If your primary focus is balancing toughness and hardness (tempering): This is a secondary, lower-temperature process performed after hardening. It is typically shorter, often lasting just a few hours, but is critical for reducing brittleness.
Ultimately, the time required is the time it takes to achieve the exact metallurgical structure your application demands.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Time | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Part Thickness | Increases soaking time | Rule of thumb: 1 hour per inch of thickness |
| Metal Alloy | Highly alloyed steels require longer times | Complex compositions slow internal transformation |
| Process Goal | Hardening (fast quench) vs. Annealing (slow cool) | Cooling rate is the critical time variable |
| Furnace Load | Larger, heavier loads take longer to heat | Total mass and furnace efficiency are key |
Achieve Precise Metallurgical Results with KINTEK
Understanding the precise timing for each stage of heat treatment is critical to achieving the desired hardness, strength, and durability in your metal components. Inconsistent results can lead to part failure, wasted materials, and production delays.
KINTEK specializes in supplying the high-performance lab furnaces and equipment you need to execute perfect heat treatment cycles every time. Our solutions provide the precise temperature control and uniform heating essential for accurate soaking times and controlled cooling rates.
Let us help you optimize your process:
- Select the right furnace for your specific alloy and part size.
- Ensure consistent results with equipment designed for reliability.
- Save time and reduce waste by achieving correct metallurgical transformations.
Ready to perfect your heat treatment timeline? Contact our experts today to discuss your laboratory's specific needs and discover how KINTEK's equipment can bring precision and efficiency to your workflow.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of vacuum hardening? Achieve Superior Precision and Cleanliness for Critical Components
- What is the process of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Purity and Precision in High-Temp Processing
- What is a vacuum furnace used for? Unlock High-Purity Heat Treatment for Superior Materials
- What is a vacuum furnace used for? Unlock Purity in High-Temperature Processing
- What is the structure of a vacuum furnace? A Guide to Its Core Components & Functions



















