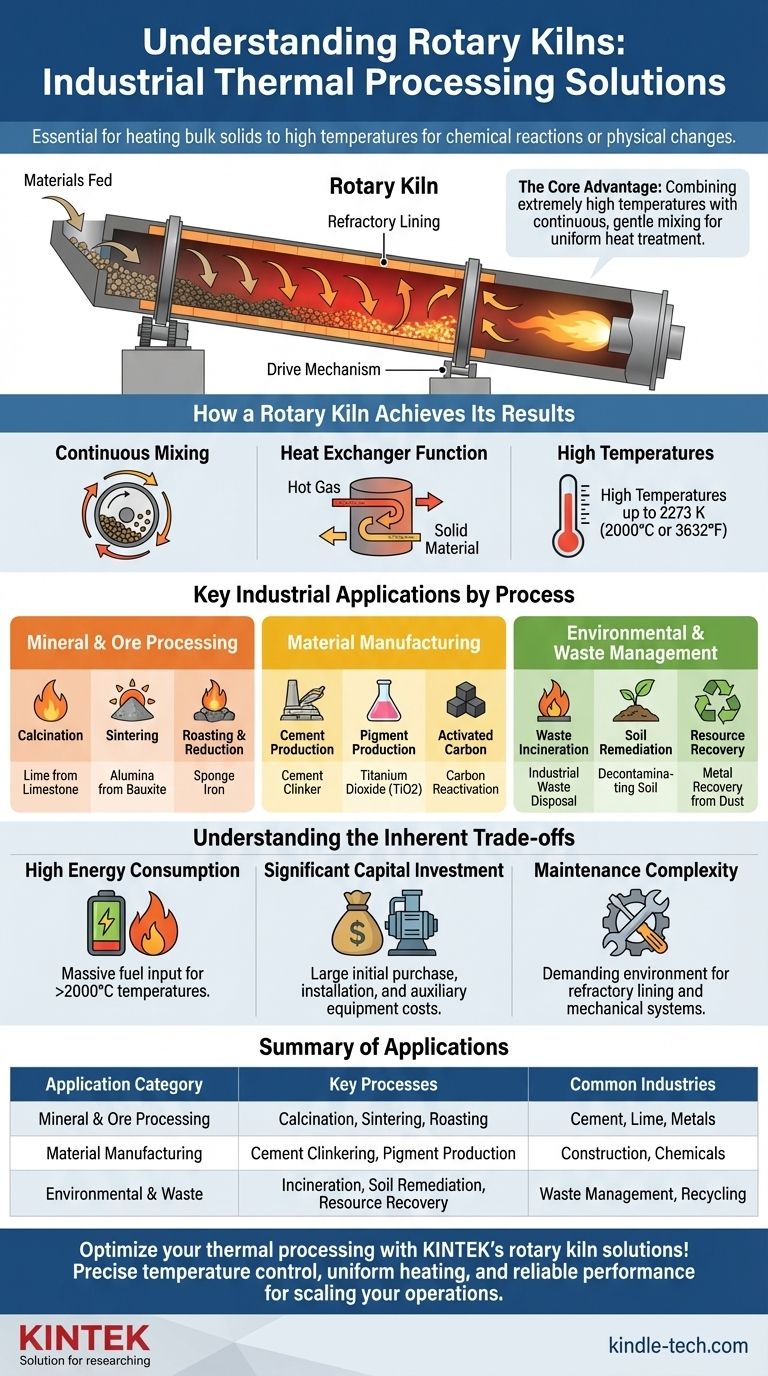
At their core, rotary kilns are industrial furnaces for thermally processing solid materials. They are essential in any process that requires heating bulk solids to very high temperatures to cause a chemical reaction or a physical change. Their applications span from producing fundamental commodities like cement and lime to advanced material manufacturing and environmental remediation, such as incinerating waste or decontaminating soil.
The true value of a rotary kiln lies in its ability to combine extremely high temperatures with continuous, gentle mixing. This unique pairing ensures uniform heat treatment, making it the ideal environment for causing physical and chemical changes in solid materials on an industrial scale.

How a Rotary Kiln Achieves Its Results
A rotary kiln's effectiveness comes from its simple but powerful design: a long, rotating cylinder lined with refractory materials, angled slightly to allow gravity to move materials through it.
The Principle of Continuous Mixing
As the kiln slowly rotates, the solid material inside is constantly lifted and tumbled. This continuous agitation, or cascading motion, ensures that every particle is exposed to the hot gases flowing through the cylinder.
This process guarantees a well-mixed bed of particles, which is critical for achieving uniform temperature distribution and consistent product quality.
The Function as a Heat Exchanger
Fundamentally, a rotary kiln acts as a highly efficient counter-current heat exchanger. Hot gas, produced by a burner at the lower end, flows up the kiln against the flow of the solid material moving downward.
This design maximizes the transfer of thermal energy from the hot gas phase to the solid material, allowing it to undergo the necessary transformations as it travels the length of the kiln.
The Power of High Temperatures
Rotary kilns are engineered to achieve incredibly high temperatures, often reaching up to 2273 K (2000°C or 3632°F). This capability is essential for energy-intensive processes like chemical reductions and mineral phase changes that are impossible at lower temperatures.
Key Industrial Applications by Process
The versatility of the rotary kiln means it is used across dozens of industries. These applications can be grouped into a few primary categories.
Mineral and Ore Processing
This is the most common use-case, where raw materials are transformed into more valuable products.
- Calcination: Decomposing materials by heat, such as producing lime from limestone or alumina from bauxite.
- Sintering: Causing solid particles to fuse together without melting, used for materials like dolomite and magnesite.
- Roasting & Reduction: Chemically changing ores, such as reducing iron ore to produce sponge iron or roasting ilmenite.
Material Manufacturing
Rotary kilns are central to the production of many essential industrial and chemical products.
- Cement Production: The clinkering process in cement manufacturing is almost exclusively done in rotary kilns.
- Pigment Production: Used in the manufacturing of titanium dioxide (TiO2), a common white pigment.
- Activated Carbon: Employed for both the initial production and the subsequent reactivation of spent activated carbon.
Environmental and Waste Management
The kiln's ability to achieve complete combustion and thermal decomposition makes it ideal for treating hazardous materials.
- Waste Incineration: Safely disposing of industrial waste, sewage sludge, and even scrap tires at high temperatures.
- Soil Remediation: Heating contaminated soil to desorb or destroy pollutants like hydrocarbons.
- Resource Recovery: Volatilizing valuable metals like zinc and lead from furnace dust or recovering waste lime for reuse.
Understanding the Inherent Trade-offs
While incredibly effective, the design and operation of rotary kilns present clear trade-offs that are critical to understand.
High Energy Consumption
Achieving and maintaining temperatures over 2000°C requires a massive input of fuel. This makes rotary kilns one of the most energy-intensive pieces of equipment in any industrial plant, representing a significant operational cost.
Significant Capital Investment
Rotary kilns are large, heavy, and complex machines. The initial purchase price, combined with the cost of installation, foundation work, and auxiliary equipment (like burners and seals), constitutes a major capital expenditure.
Maintenance Complexity
The combination of high temperatures, abrasive materials, and constant rotation creates a demanding maintenance environment. The refractory lining must be periodically replaced, and the mechanical systems, particularly the large seals and drive mechanisms, require regular and specialized attention to prevent failure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use a rotary kiln is driven by the specific requirements of the thermal process.
- If your primary focus is producing bulk commodities like cement or lime: The rotary kiln is the undisputed industry standard due to its unmatched efficiency, throughput, and reliability at scale.
- If your primary focus is processing diverse or sensitive materials: The kiln's adjustable rotation speed and precise temperature control make it a highly versatile tool for catalyst activation, ore upgrading, or ceramics processing.
- If your primary focus is environmental remediation or waste disposal: The kiln's ability to achieve complete combustion and uniform thermal desorption makes it a robust and reliable solution for destroying contaminants and minimizing waste volume.
Ultimately, the rotary kiln's mastery of combining intense heat with constant motion has made it an irreplaceable cornerstone of modern material transformation.
Summary Table:
| Application Category | Key Processes | Common Industries |
|---|---|---|
| Mineral & Ore Processing | Calcination, Sintering, Roasting | Cement, Lime, Metals |
| Material Manufacturing | Cement Clinkering, Pigment Production | Construction, Chemicals |
| Environmental & Waste | Incineration, Soil Remediation, Resource Recovery | Waste Management, Recycling |
Optimize your thermal processing with KINTEK’s rotary kiln solutions! Whether you're producing cement, processing minerals, or managing hazardous waste, our lab equipment and consumables are designed to deliver precise temperature control, uniform heating, and reliable performance. Let us help you scale your operations efficiently — contact our experts today to discuss your specific needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature for activated carbon regeneration? Key Ranges from 220°C to 900°C
- What is a fluidized bed reactor used for? Unlock Superior Solid-to-Gas and Liquid Conversion
- What is the thermal regeneration process of activated carbon? Restore Performance and Cut Costs
- What is the mechanism of pyrolysis? Unlock the Power of Thermal Decomposition Without Oxygen
- What is the process of carbon reactivation? A Sustainable Solution for Spent Activated Carbon
- What is the temperature range of a rotary kiln? A Guide to Custom Thermal Profiles
- What are the products of catalytic pyrolysis? Unlock High-Value Biofuels & Chemicals
- How does a rotary kiln work? Unlock Continuous, High-Volume Thermal Processing



















