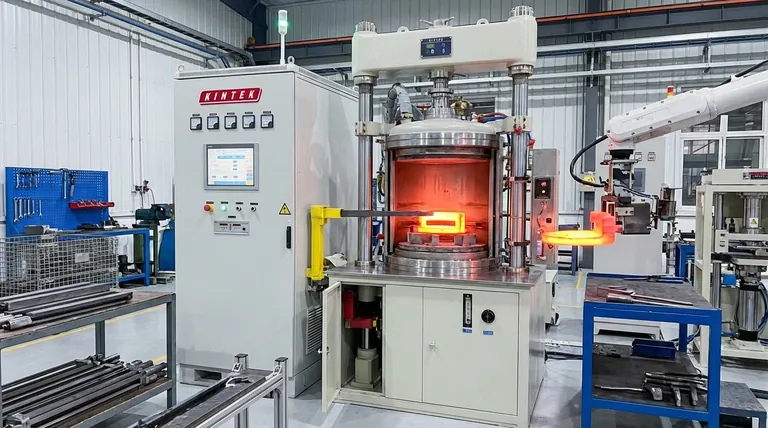
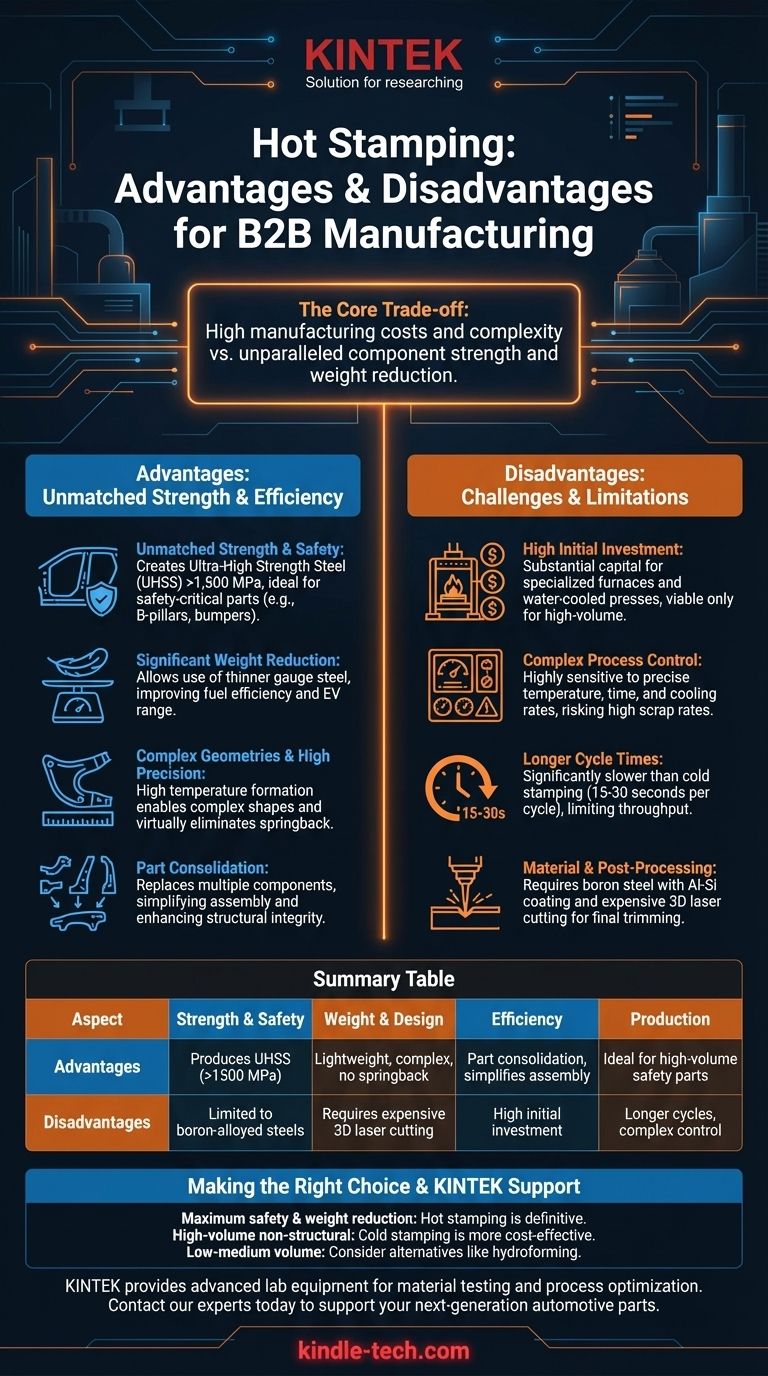
At its core, hot stamping is a manufacturing process that intentionally combines forming and heat treatment to create steel components with exceptional strength. Its primary advantage is the ability to produce ultra-high-strength, lightweight parts with complex shapes, a feat often impossible with traditional cold stamping. However, these benefits come at the cost of higher initial investment, increased process complexity, and longer cycle times.
The decision to use hot stamping hinges on a critical trade-off: accepting higher manufacturing costs and complexity in exchange for unparalleled component strength and weight reduction. It is the definitive choice for safety-critical parts, but an inefficient one for less demanding applications.

Why Choose Hot Stamping? The Core Advantages
Hot stamping, also known as press hardening, is not just a different way to shape metal; it's a way to fundamentally change its properties during formation. This unique capability delivers several key benefits, particularly in the automotive industry.
Unmatched Strength and Safety
The process involves heating a boron steel blank to over 900°C, forming it, and then rapidly quenching it within the die. This rapid cooling transforms the steel's microstructure into martensite, an extremely hard and strong phase.
The resulting components possess Ultra-High Strength Steel (UHSS) properties, often exceeding 1,500 MPa in tensile strength. This makes them ideal for automotive safety cage components like B-pillars, roof rails, and bumpers that must withstand severe crash impacts.
Significant Weight Reduction
Because the final part is so strong, engineers can design it using a thinner gauge of steel compared to what would be required with conventional high-strength steels.
This direct reduction in material thickness leads to a significant decrease in component weight. For automakers, this translates directly to improved fuel efficiency or, in electric vehicles, extended battery range.
Complex Geometries with High Precision
Forming steel at such high temperatures makes it extremely malleable. This allows for the creation of deep-drawn, complex part geometries that would fracture or tear if attempted with cold stamping.
Furthermore, the in-die quenching process virtually eliminates springback—the tendency of cold-formed metal to partially return to its original shape. The result is exceptional dimensional accuracy and consistency from part to part.
Part Consolidation
A single, intricately shaped hot-stamped part can often replace an assembly of multiple, weaker, cold-stamped components that were previously welded or fastened together.
This consolidation reduces the total number of parts, simplifies the vehicle assembly process, and eliminates potential points of failure, further enhancing structural integrity.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
While its benefits are transformative, hot stamping is a demanding and expensive process. These disadvantages make it unsuitable for many applications where its unique properties are not a strict requirement.
High Initial Investment
The capital expenditure for a hot stamping line is substantial. It requires specialized equipment, including high-temperature furnaces for heating blanks and presses with water-cooled dies to achieve the necessary quenching rates.
This high barrier to entry means the process is typically only viable for high-volume production where the cost can be amortized over millions of parts.
Complex Process Control
The entire process is highly sensitive to process variables. The temperature of the blank, the transfer time from furnace to press, and the cooling rate within the die must be precisely controlled.
Any deviation can result in a part that does not meet the required mechanical properties, leading to high scrap rates if the process is not perfectly optimized and monitored.
Longer Cycle Times
Compared to traditional cold stamping, which can run at dozens of strokes per minute, hot stamping is significantly slower. The need to heat each blank and then hold it in the die for quenching adds considerable time to each cycle.
A typical hot stamping cycle time can range from 15 to 30 seconds, limiting overall production throughput.
Material and Post-Processing Limitations
Hot stamping is almost exclusively used with boron-alloyed steels. These blanks require a special aluminum-silicon (Al-Si) coating to prevent severe scaling and oxidation at high temperatures.
Once the part is hardened, it is too hard to be trimmed or pierced with conventional mechanical dies. This necessitates the use of expensive 3D laser cutting for final trimming and hole creation, adding another layer of cost and complexity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct manufacturing process requires a clear understanding of your project's primary objective. Hot stamping is a specialized tool, and its application should be deliberate.
- If your primary focus is maximum vehicle safety and weight reduction: Hot stamping is the definitive and often non-negotiable choice for critical structural components like A/B pillars, tunnels, and bumper beams.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production of non-structural parts: Traditional cold stamping is vastly more cost-effective and faster for components like door panels, fenders, or brackets where ultra-high strength is not required.
- If your primary focus is low-to-medium volume production or prototyping: The prohibitive tooling and equipment costs of hot stamping make it impractical. Alternative methods like hydroforming or fabricating from advanced high-strength steels should be considered.
Understanding this balance between ultimate performance and process investment is the key to leveraging hot stamping effectively.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Strength & Safety | Produces UHSS parts (>1500 MPa) for crash safety | Limited to boron-alloyed steels with Al-Si coating |
| Weight & Design | Enables lightweight, complex geometries with no springback | Requires expensive 3D laser cutting for post-processing |
| Efficiency | Allows part consolidation, simplifying assembly | High initial investment for furnaces and water-cooled presses |
| Production | Ideal for high-volume safety-critical components | Longer cycle times (15-30 sec) and complex process control |
Need to achieve the perfect balance of strength and weight for your components? KINTEK specializes in providing the advanced lab equipment and consumables necessary for developing and optimizing manufacturing processes like hot stamping. Whether you're in R&D or quality control, our solutions help you test materials, simulate conditions, and ensure precision. Contact our experts today to discover how we can support your laboratory's role in creating the next generation of high-performance automotive parts.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Heated Vacuum Press Machine Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Electric Heated Hydraulic Vacuum Heat Press for Lab
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot press sintering furnace? Achieve 99.1% Density in CuW30 Composites
- What advantages does hot pressing sintering equipment provide for NASICON? Achieve 100% Dense Solid Electrolyte Plates
- Why is a vacuum essential for sintering metal-ceramic composites? Achieve Pure, High-Density Results
- How does the uniaxial pressing function of a vacuum hot press furnace influence the microstructure of ZrC-SiC ceramics?
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot press for CuCr50? Achieve Superior Density & Purity in Alloy Production



















