In essence, the primary advantages of high-frequency heating are its incredible speed, precision, and efficiency. This technology generates heat directly inside a material, rather than applying it from an external source. This fundamental difference allows for rapid, uniform, and highly controlled heating that conventional methods like ovens or flames simply cannot replicate.
High-frequency heating is not just a faster way to apply warmth; it's a fundamentally different mechanism. By generating heat within the material itself, it bypasses the slow process of thermal conduction, enabling rapid, uniform, and highly targeted results that solve many common manufacturing challenges.

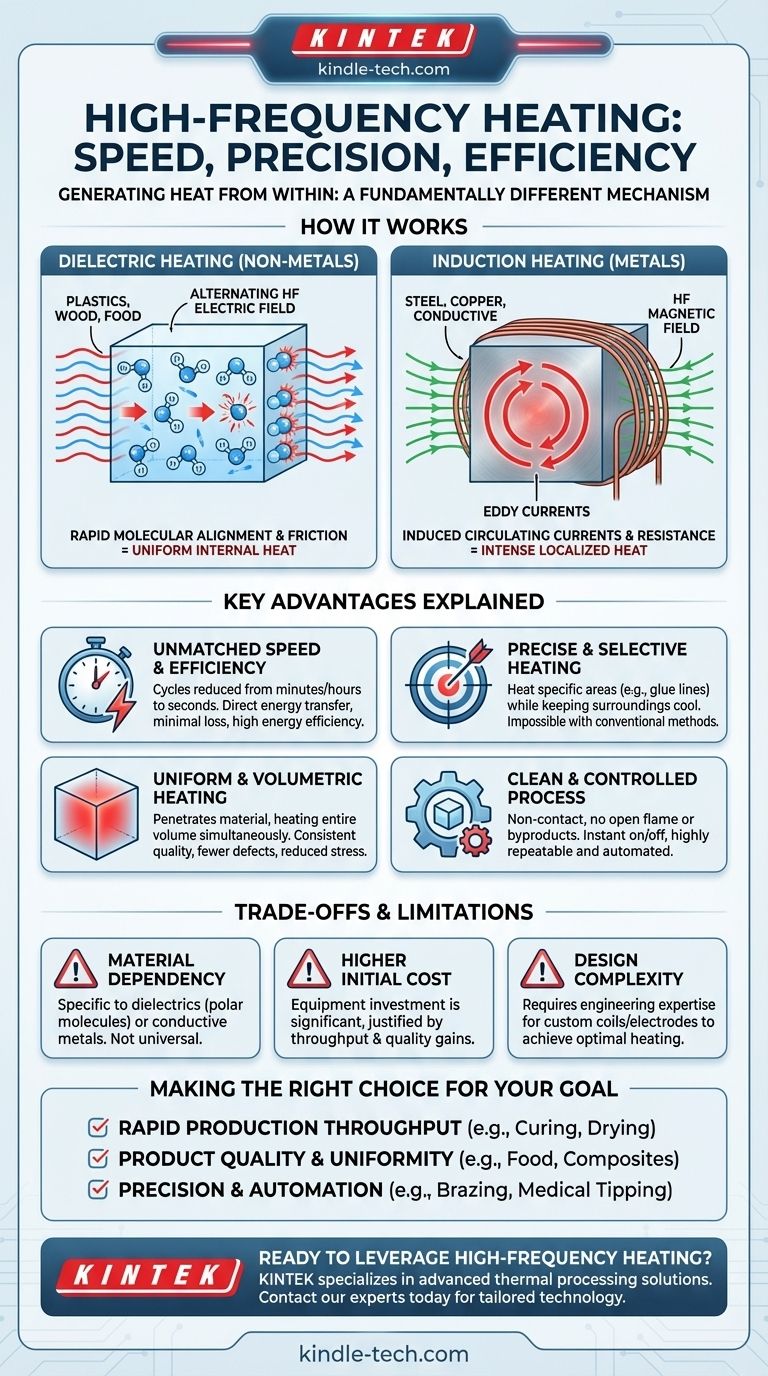
How High-Frequency Heating Works
To understand its advantages, you must first understand its core principle: generating heat from within. High-frequency (HF) energy, typically radio frequency (RF) or microwave energy, interacts with materials in one of two ways.
Dielectric Heating for Non-Metals
In materials like plastics, wood, or food, an alternating high-frequency electric field is applied.
Polar molecules within the material, such as water, act like tiny magnets. They rapidly try to align with the oscillating field, causing intense intermolecular friction that generates uniform heat throughout the material's volume.
Induction Heating for Metals
For conductive materials like steel or copper, a high-frequency magnetic field is used.
This field induces powerful circulating currents, known as eddy currents, within the metal. The material's natural electrical resistance opposes these currents, generating intense, localized heat very quickly.
The Key Advantages Explained
This internal heating mechanism is the source of every major benefit of HF technology.
Unmatched Speed and Efficiency
Because HF energy bypasses slow thermal conduction, heating cycles can be reduced from minutes or hours to mere seconds.
Energy is transferred directly to the workpiece with minimal loss to the surrounding environment, resulting in significantly higher energy efficiency compared to a conventional furnace that must heat the air and its own walls.
Precise and Selective Heating
The electromagnetic field can be precisely shaped and aimed using applicators or induction coils.
This allows you to heat a specific area—like the glue line on a wood joint or the tip of a surgical tool—while leaving the rest of the assembly completely cool. This level of control is impossible with most other methods.
Uniform and Volumetric Heating
HF energy penetrates the material, generating heat through its entire volume simultaneously.
This eliminates the common "hot outside, cold inside" problem found with conventional ovens. The result is a more consistent product quality, reduced internal stresses, and fewer defects from uneven heating or cooling.
A Clean and Controlled Process
HF heating is a non-contact process with no open flame or combustion byproducts, making it ideal for cleanroom and medical applications.
The power can be turned on and off instantly and is precisely regulated by modern electronics, enabling highly repeatable and easily automated manufacturing processes.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, HF heating is not a universal solution. Its effectiveness is highly dependent on the target material and the specific application.
Material Dependency is Critical
The biggest limitation is that the technology is material-specific. Dielectric heating requires materials with polar molecules (dielectrics), while induction heating only works on electrically conductive materials. It is ineffective on materials that lack these properties.
Higher Initial Equipment Cost
The initial capital investment for HF generators, applicators, and coils can be significantly higher than for a simple convection oven or gas furnace. However, this cost is often justified by increased throughput, higher efficiency, and improved product quality.
Complexity of Application Design
Designing the right induction coil or electrode plates for a specific part is a science. Achieving optimal heating patterns and efficiency often requires engineering expertise and customization, unlike a one-size-fits-all oven.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine if HF heating is the right solution, align its strengths with your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is rapid production throughput: HF heating is ideal for inline processes like curing adhesives, drying coatings, or surface hardening where speed is the dominant factor.
- If your primary focus is product quality and uniformity: Its volumetric heating is perfect for applications like food processing, welding plastics, or preheating composites, as it prevents defects from uneven temperatures.
- If your primary focus is precision and automation: HF heating excels in automated lines for tasks like brazing, soldering, or medical catheter tipping where only a specific zone must be heated repeatably.
By understanding its unique mechanism of internal heat generation, you can leverage high-frequency heating to solve complex manufacturing challenges that are impractical or impossible with conventional methods.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Speed & Efficiency | Bypasses thermal conduction; cycles reduced to seconds with high energy efficiency. |
| Precision & Selectivity | Heats specific areas while leaving surrounding parts cool; ideal for automation. |
| Uniform & Volumetric Heating | Eliminates 'hot outside, cold inside' problem; consistent quality and fewer defects. |
| Clean & Controlled Process | Non-contact with no combustion byproducts; easily regulated and repeatable. |
Ready to leverage high-frequency heating to solve your manufacturing challenges?
At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced thermal processing solutions, including high-frequency heating systems for applications like adhesive curing, brazing, and precision drying. Our expertise ensures you get the right equipment for rapid production, superior product quality, and automated precision.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can enhance your lab or production line's efficiency and performance with tailored high-frequency heating technology.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Infrared Heating Quantitative Flat Plate Press Mold
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
- Cylindrical Lab Electric Heating Press Mold for Laboratory Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the disadvantages of core type induction heating? Poor Adaptability for Complex Parts
- What is plasma arc melting? Achieve Unmatched Purity for High-Performance Metals
- What is induction brazing used for? High-Speed, Precise Joining for Automotive & HVAC
- Can copper be melting in induction furnace? Unlock Superior Melting Precision & Quality
- What metals cannot be induction heated? A guide to material suitability and heating efficiency.
- What are the characteristics of induction furnace? High-Efficiency, Clean Melting for Superior Metal Quality
- What is the process of vacuum casting? Create High-Quality Prototypes & Small Batches
- Is induction heat instant? Discover the Secret to Lightning-Fast Cooking



















