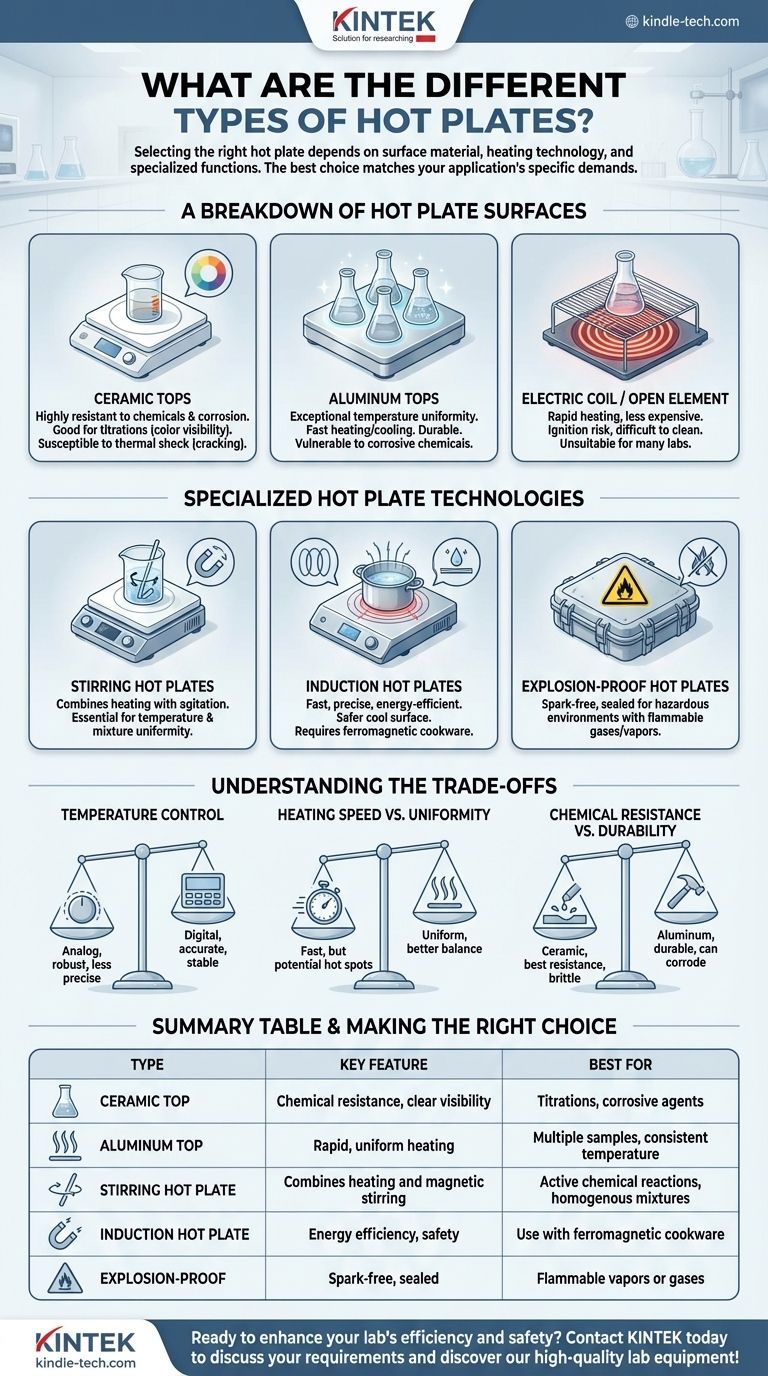
When selecting a hot plate, it's crucial to understand they are not all the same. Hot plates are primarily categorized by their surface material and heating technology, including ceramic, aluminum, electric coil, and induction. They are further distinguished by specialized functions like integrated magnetic stirring or safety features for hazardous locations.
The most effective hot plate is not the most powerful or expensive one, but the one whose material, heating method, and control system directly match the demands of your specific application—be it chemical resistance, temperature uniformity, or operational safety.
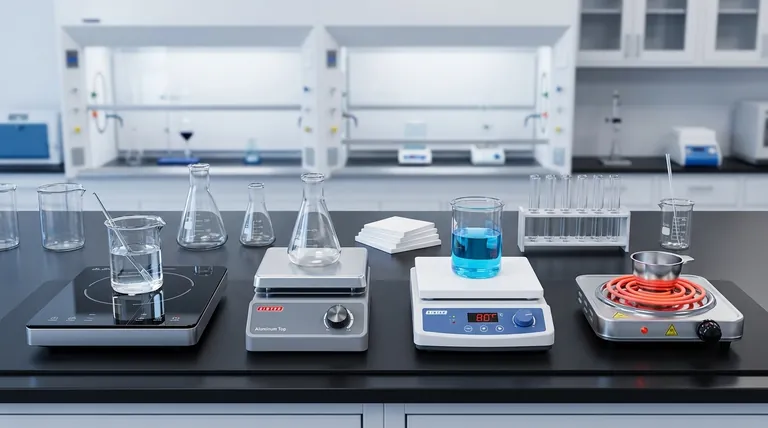

A Breakdown of Hot Plate Surfaces
The surface of a hot plate is the primary point of contact and dictates many of its core characteristics, from chemical compatibility to how it distributes heat.
Ceramic Tops
Ceramic surfaces are highly resistant to corrosion and most chemicals, making them a standard in laboratory settings.
Their white surface also makes it easy to observe color changes in a solution, which is critical for processes like titrations.
While they can handle very high temperatures, they are susceptible to thermal shock and can crack if a cold item is placed on a very hot surface.
Aluminum Tops
Aluminum tops provide exceptional temperature uniformity across the entire heating surface. This is vital when multiple containers need to be heated equally at the same time.
They heat up and cool down much faster than ceramic. Aluminum is also more durable and resistant to physical impact.
However, aluminum is vulnerable to corrosive chemicals, which can damage the surface over time.
Electric Coil / Open Element
This is the classic, often most basic design, where an exposed electric coil provides direct radiant heat to the vessel.
These models offer very rapid heating and are typically less expensive.
Their primary drawbacks are safety and cleaning. The exposed element is an ignition risk, and spills are difficult to clean, making them unsuitable for many professional lab environments.
Specialized Hot Plate Technologies
Beyond the surface material, distinct technologies offer enhanced functionality for specific tasks.
Stirring Hot Plates
Also known as hot plate stirrers, these devices combine heating with agitation. They contain a rotating magnet under the surface.
When a small, coated magnet called a stir bar is placed in a liquid, it couples with the rotating magnet, stirring the solution continuously.
This dual action is essential for ensuring both temperature and mixture uniformity, which is critical for many chemical reactions and biological preparations.
Induction Hot Plates
Induction technology does not heat the surface of the plate directly. Instead, it generates a magnetic field that induces an electric current within the vessel itself, causing the vessel to heat up.
This method is incredibly fast, precise, and energy-efficient. The cooktop surface remains much cooler than on other hot plates, significantly increasing safety.
The critical limitation is that induction only works with ferromagnetic cookware, such as iron or steel. Standard laboratory glassware (like borosilicate) will not heat up on its own.
Explosion-Proof Hot Plates
These are purpose-built for use in hazardous environments containing flammable gases or vapors.
They are engineered with spark-free components and fully sealed electronics to prevent any internal arc from igniting the ambient atmosphere.
Using a standard hot plate in such an environment poses a severe risk of explosion.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right hot plate requires balancing performance characteristics against the needs of your work and environment.
Temperature Control: Digital vs. Analog
Analog controls use a simple rotating knob. They are robust, straightforward, and cost-effective but lack precision and repeatability.
Digital controls use a microprocessor and an LED or LCD display for setting the exact target temperature. They offer superior accuracy, stability, and often include programmable timers or safety shutoffs.
Heating Speed vs. Uniformity
A fast heat-up time does not always mean uniform heat. Open coil elements are very fast but can create "hot spots," while aluminum tops offer an excellent balance of speed and superior uniformity.
Chemical Resistance vs. Durability
Ceramic offers the best chemical resistance but can be brittle. Aluminum is mechanically durable but can be corroded by certain substances. The choice depends entirely on what you will be working with.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision should be guided by your primary task.
- If your primary focus is chemical resistance and clear visibility: A ceramic top hot plate is your best choice, especially for titrations or working with corrosive agents.
- If your primary focus is rapid, uniform heating for multiple samples: An aluminum top hot plate excels where consistent temperature across the entire surface is critical.
- If you need to ensure a homogenous mixture while heating: A magnetic stirring hot plate is the essential tool for active chemical reactions.
- If you are working in a hazardous environment with flammable vapors: You must use a certified explosion-proof hot plate for safety.
- If your priorities are energy efficiency and safety with compatible metal cookware: An induction hot plate offers unparalleled performance and a safer work surface.
Understanding these core differences empowers you to select a tool that is not only effective but also fundamentally safe for your work.
Summary Table:
| Type | Key Feature | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Ceramic Top | Chemical resistance, clear visibility | Titrations, corrosive agents |
| Aluminum Top | Rapid, uniform heating | Multiple samples, consistent temperature |
| Stirring Hot Plate | Combines heating and magnetic stirring | Active chemical reactions, homogenous mixtures |
| Induction Hot Plate | Energy efficiency, safety (heats vessel directly) | Use with ferromagnetic cookware |
| Explosion-Proof Hot Plate | Spark-free, sealed for hazardous environments | Flammable vapors or gases |
Ready to enhance your lab's efficiency and safety? Choosing the right hot plate is critical for your specific application, whether you need chemical resistance, precise temperature control, or magnetic stirring. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables tailored to meet your laboratory's unique needs. Our experts can help you select the perfect hot plate to ensure optimal performance and safety. Contact us today to discuss your requirements and discover how KINTEK can support your laboratory's success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Temperature Wear-Resistant Alumina Al2O3 Plate for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
- Laboratory Small Constant Temperature Heated Magnetic Stirrer Heater and Stirrer
- Custom-Made Alumina Zirconia Special-Shaped Ceramic Plates for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Processing
- Precision Machined Yttria Stabilized Zirconia Ceramic Plate for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
People Also Ask
- What is the process of pressing sintering? A Guide to Powder Metallurgy & Ceramics Fabrication
- What is the role of a laboratory hydraulic press in the preparation of inorganic perovskite energy materials?
- Why is a heated laboratory hydraulic press necessary for composite laminates? Achieve Void-Free Structural Integrity
- How does a programmable hot press contribute to the manufacturing of NiO-YSZ anode supports for fuel cells?
- What technical conditions does a heated hydraulic press provide for PEO batteries? Optimize Solid-State Interfaces
- What is the function of a laboratory high-temperature hydraulic press? Optimize MEA Fabrication for HCl Electrolysis
- What is the temperature of hot forging? Achieve Superior Strength and Formability
- What are the different types of press machines? Choose the Right Heating Tech for Your Application



















